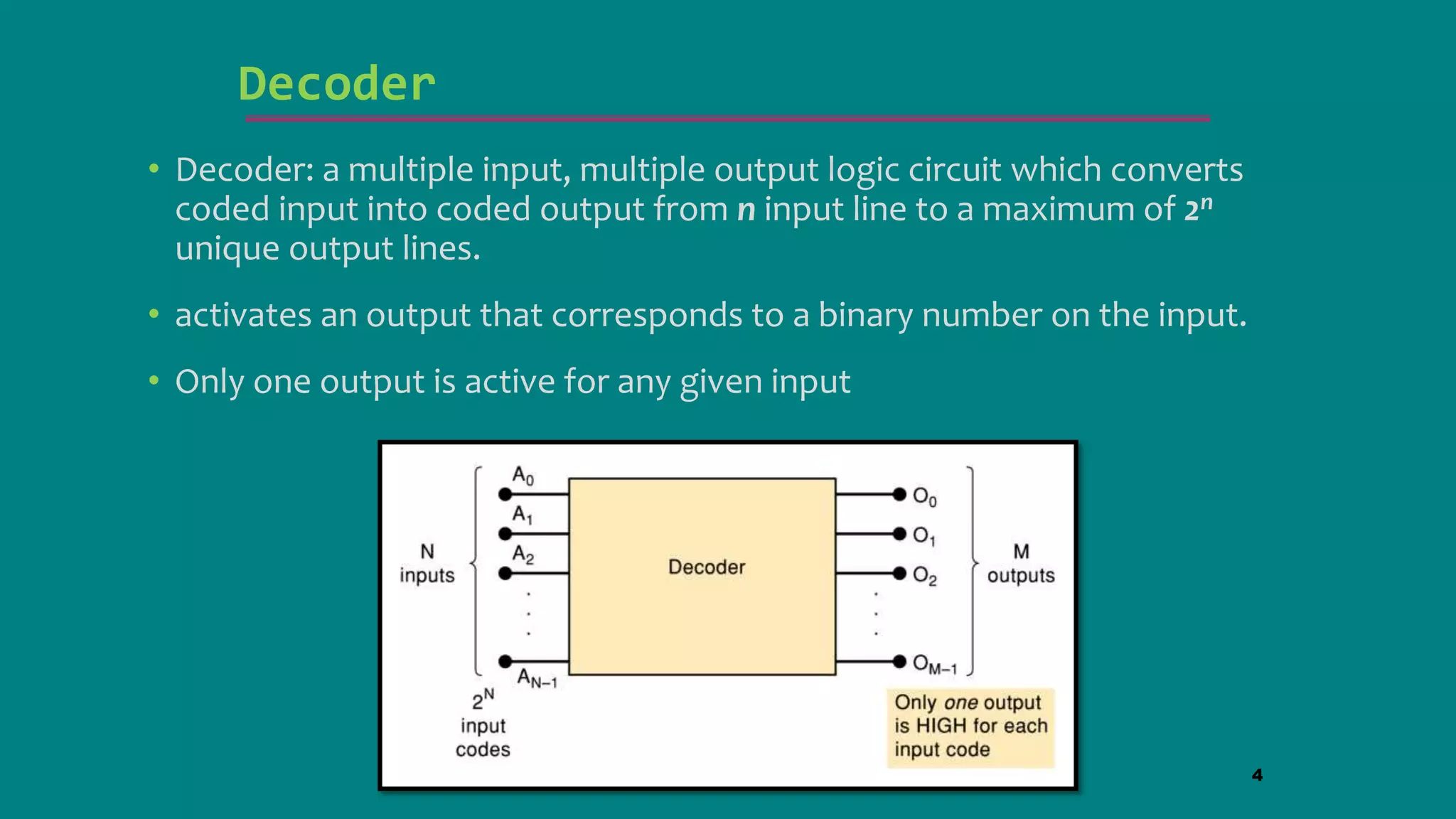
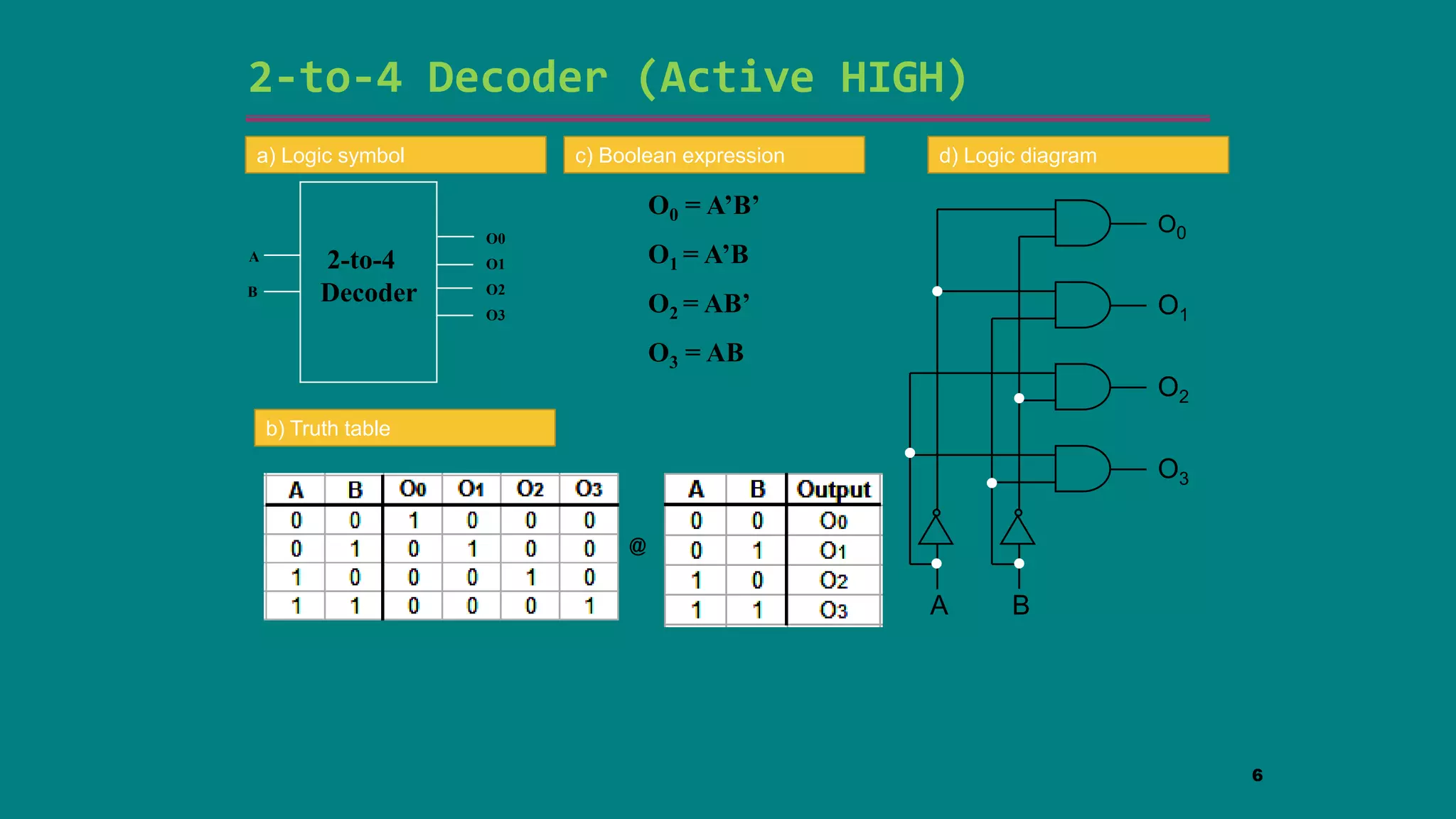
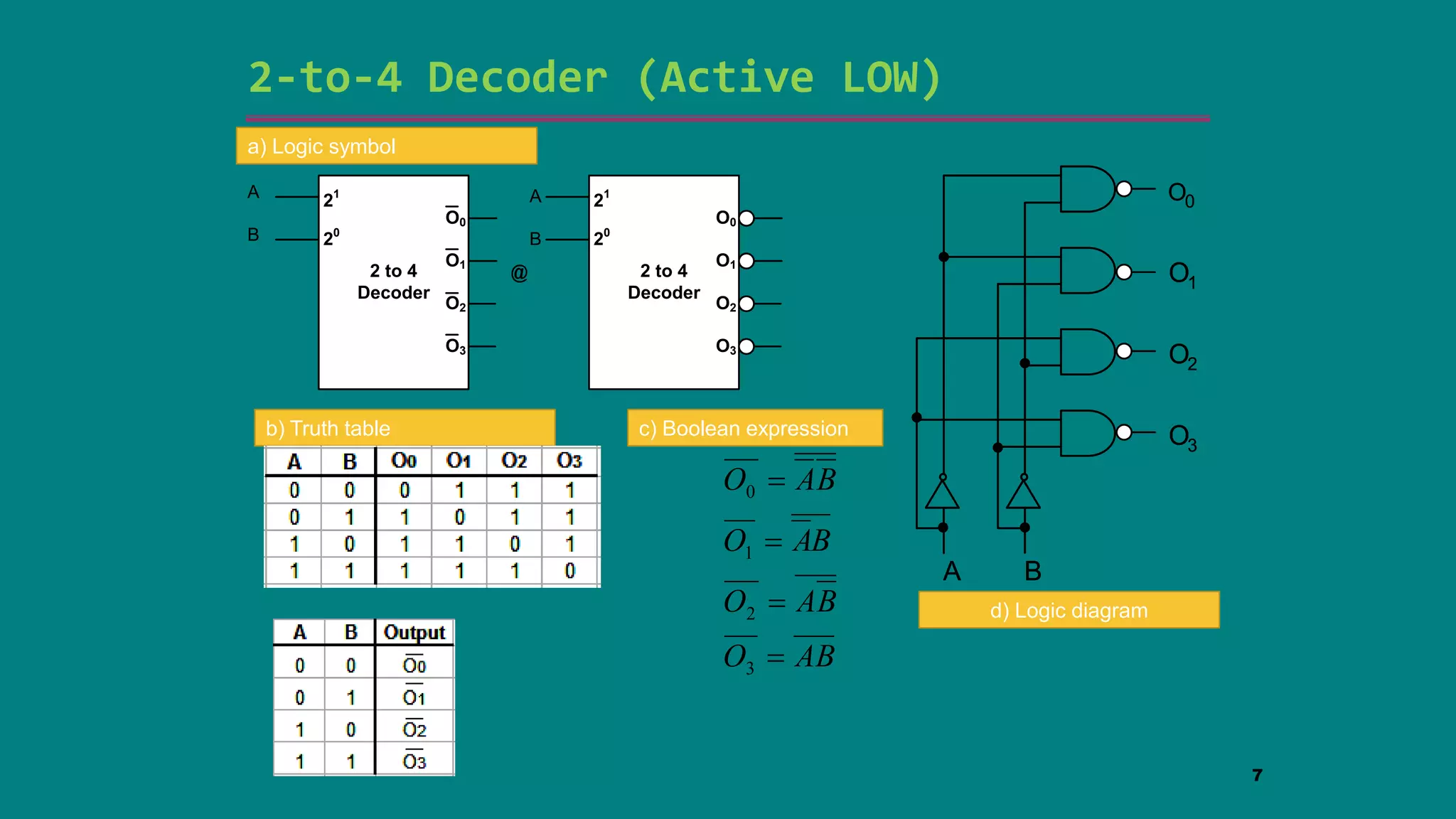
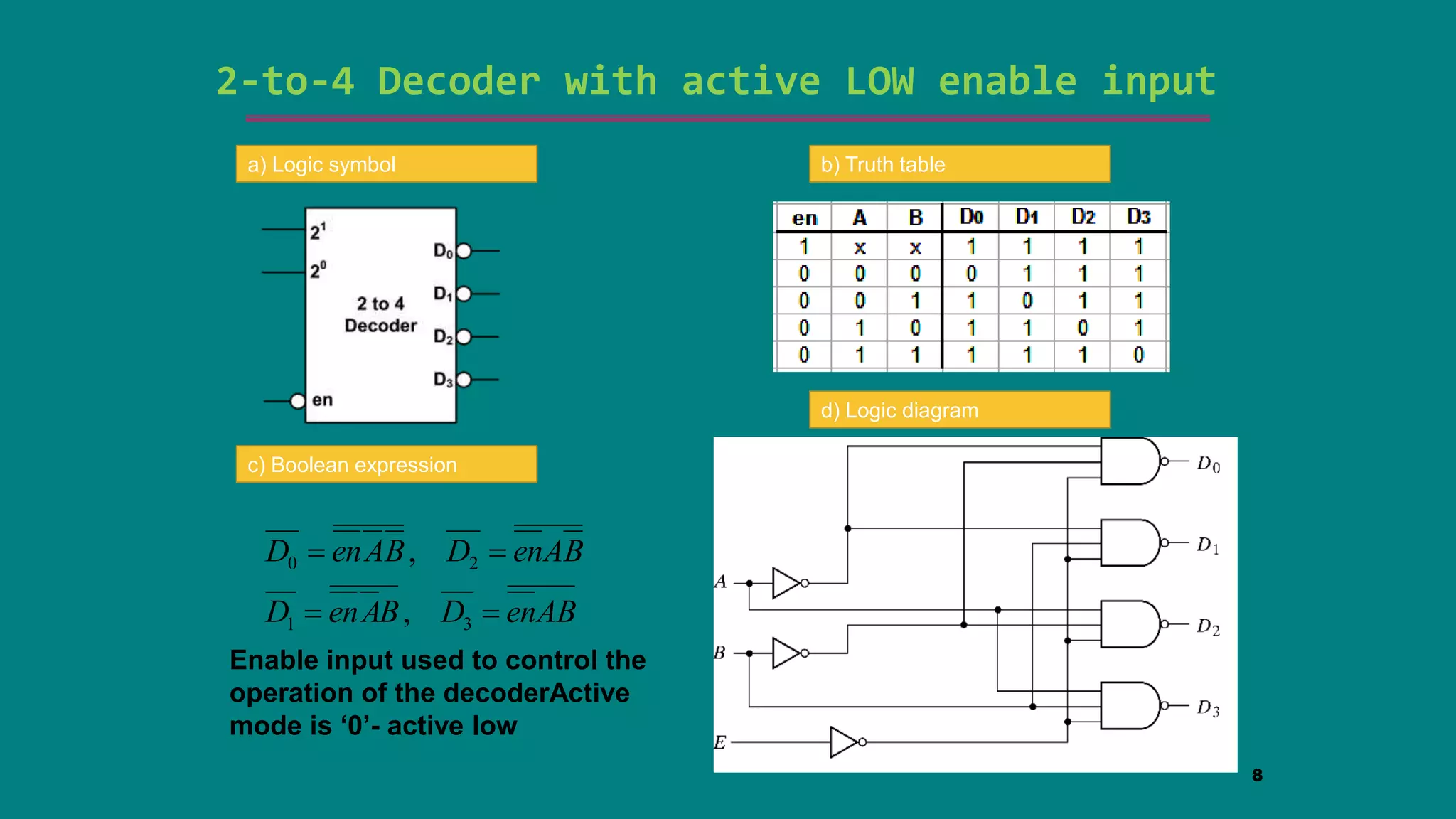
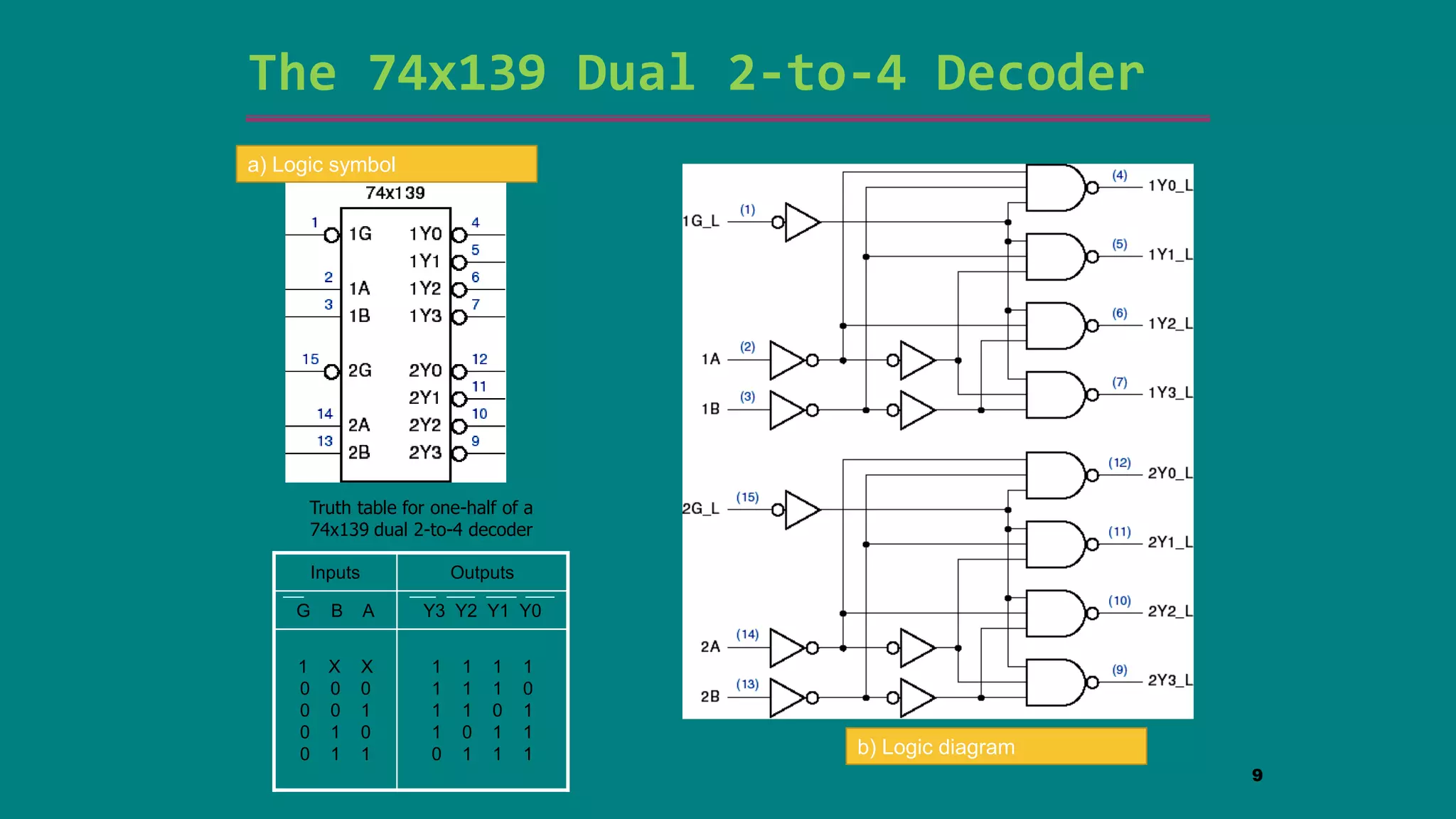
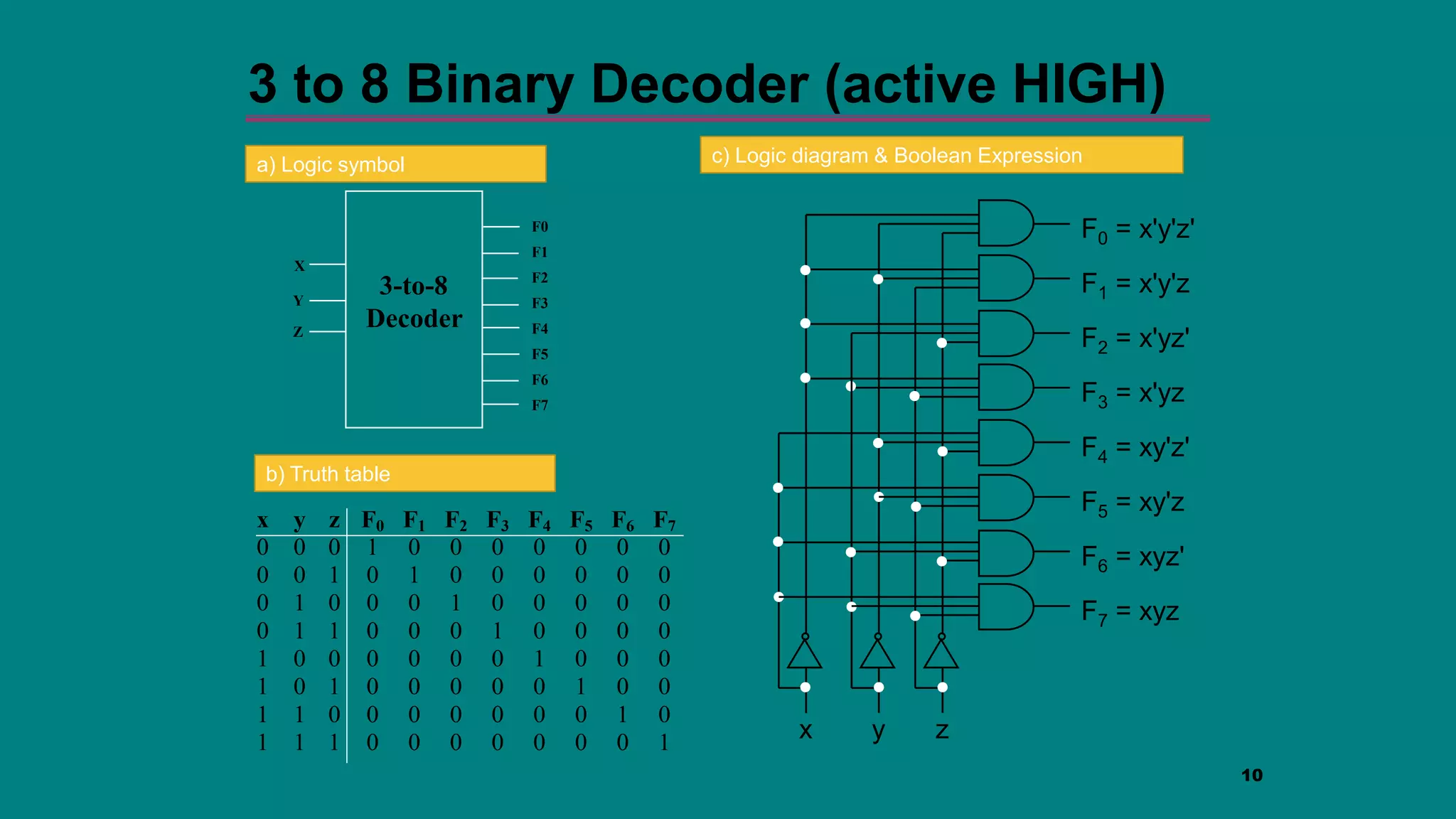
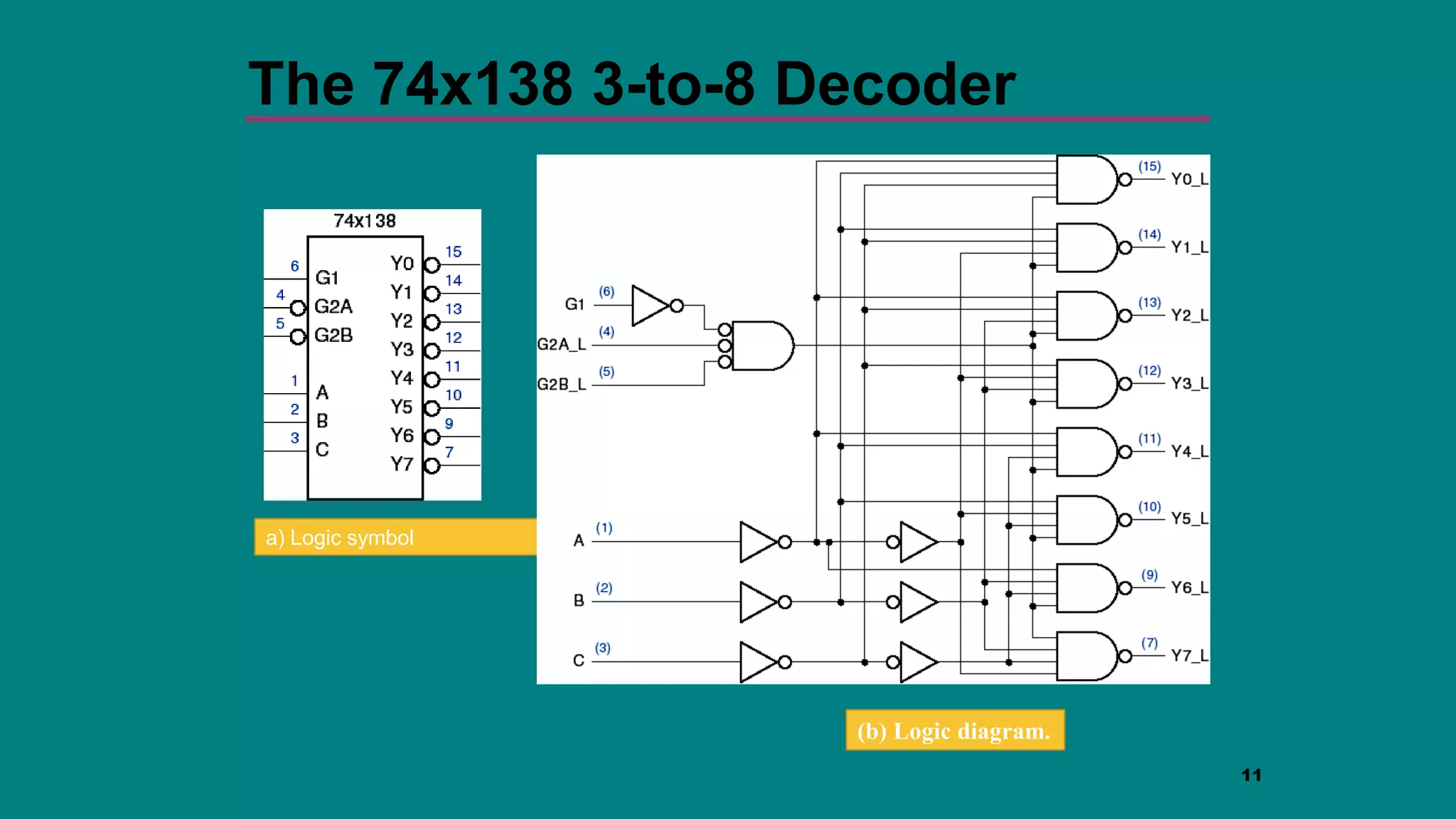
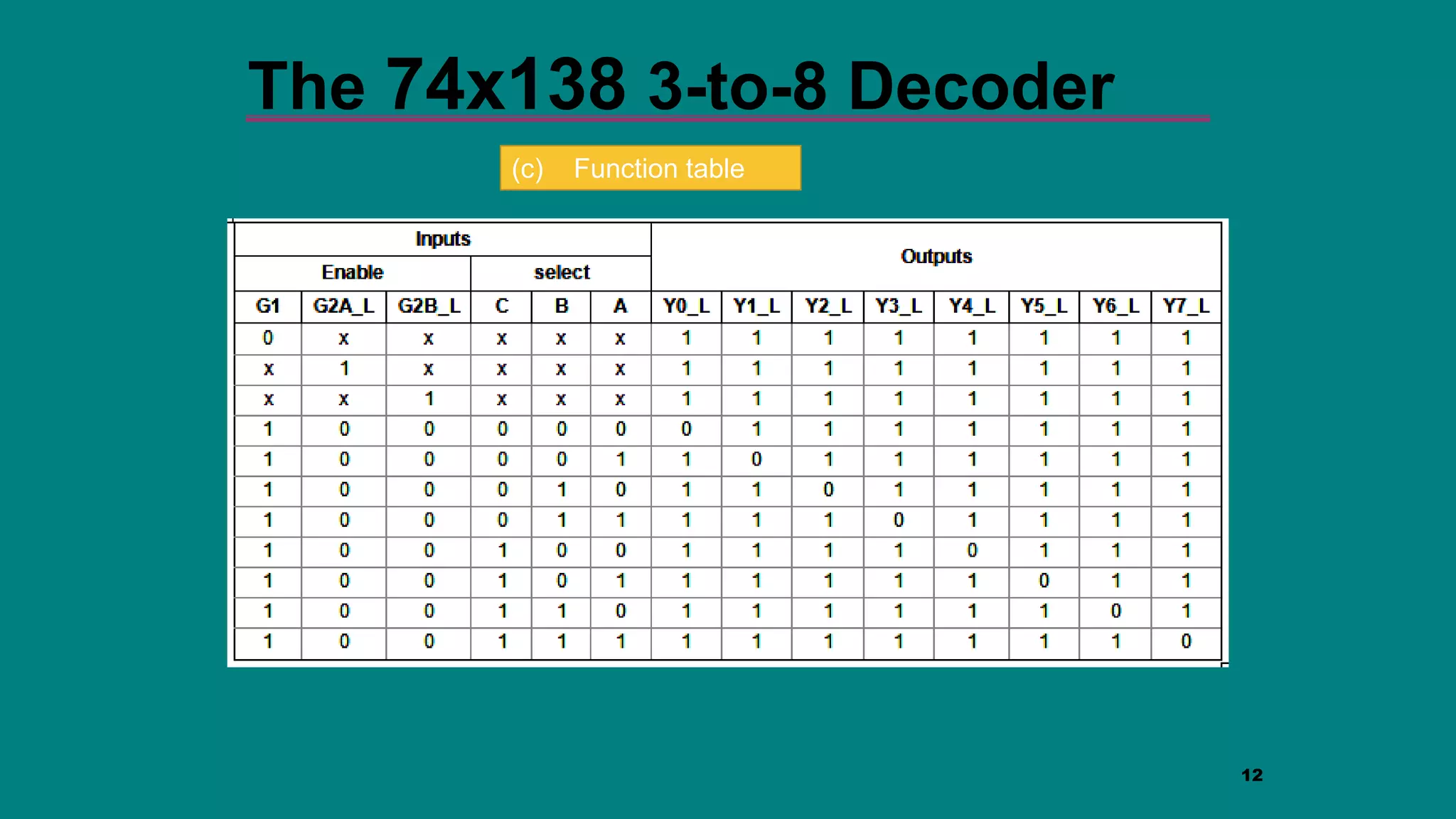
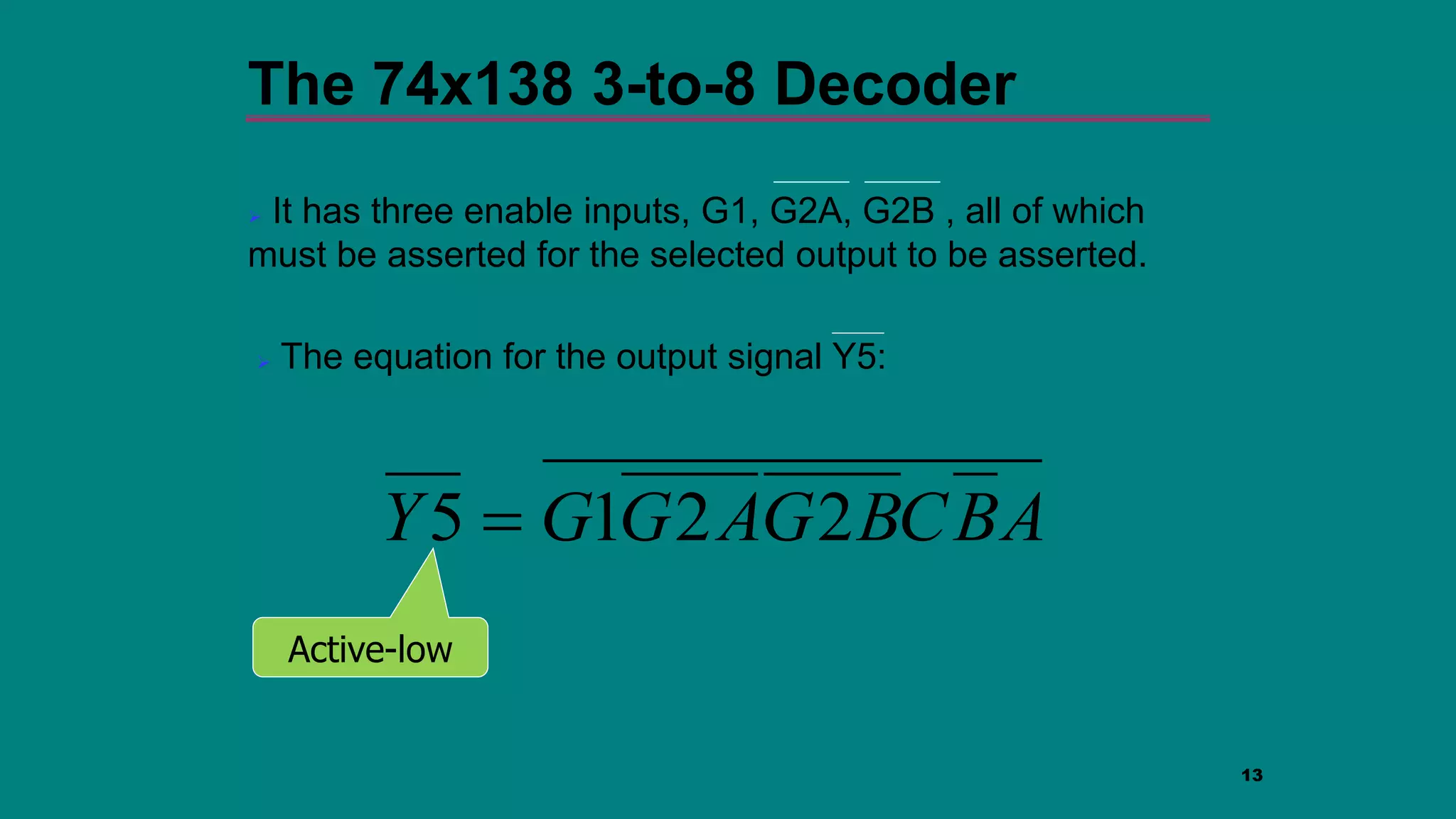
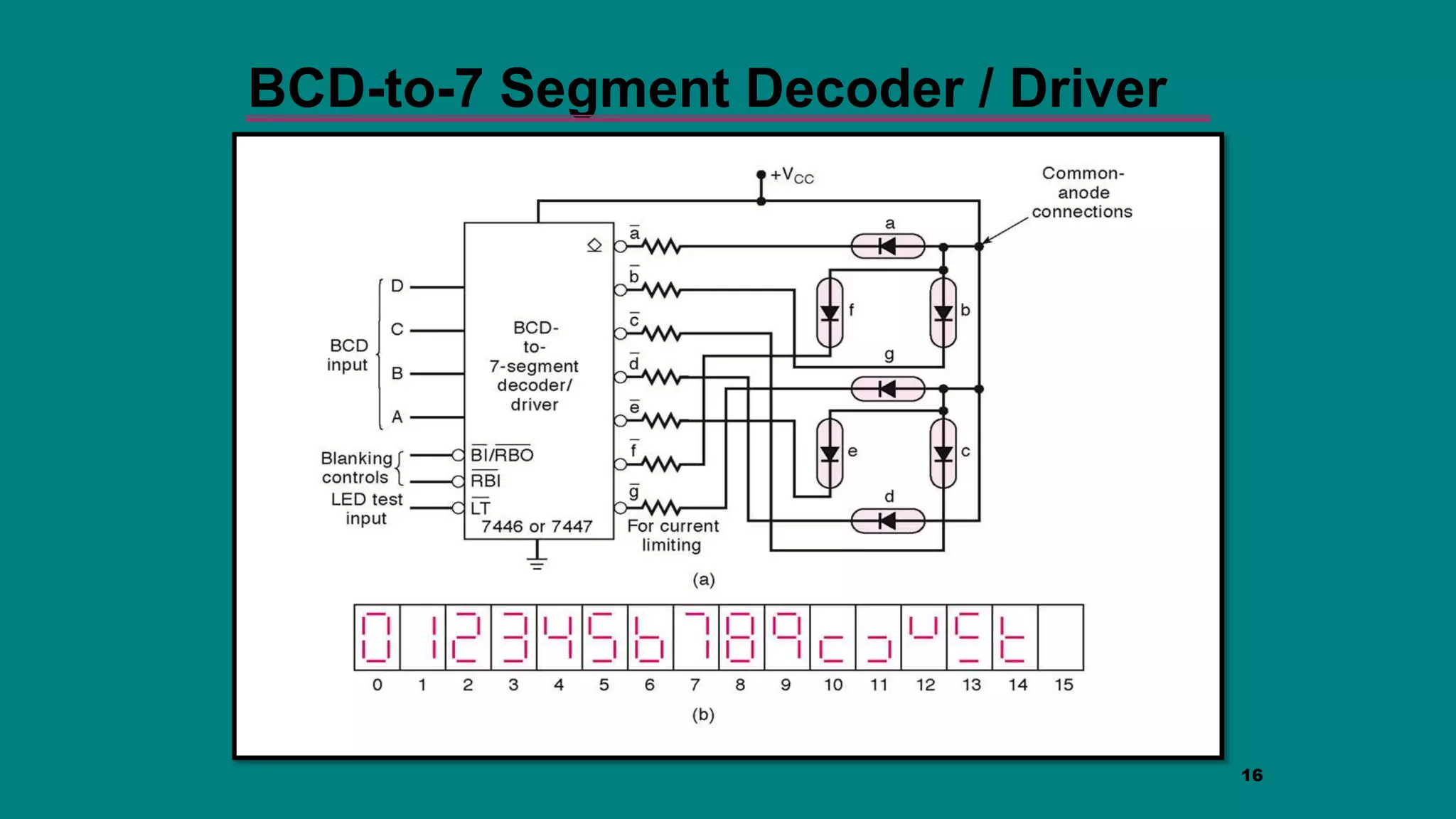
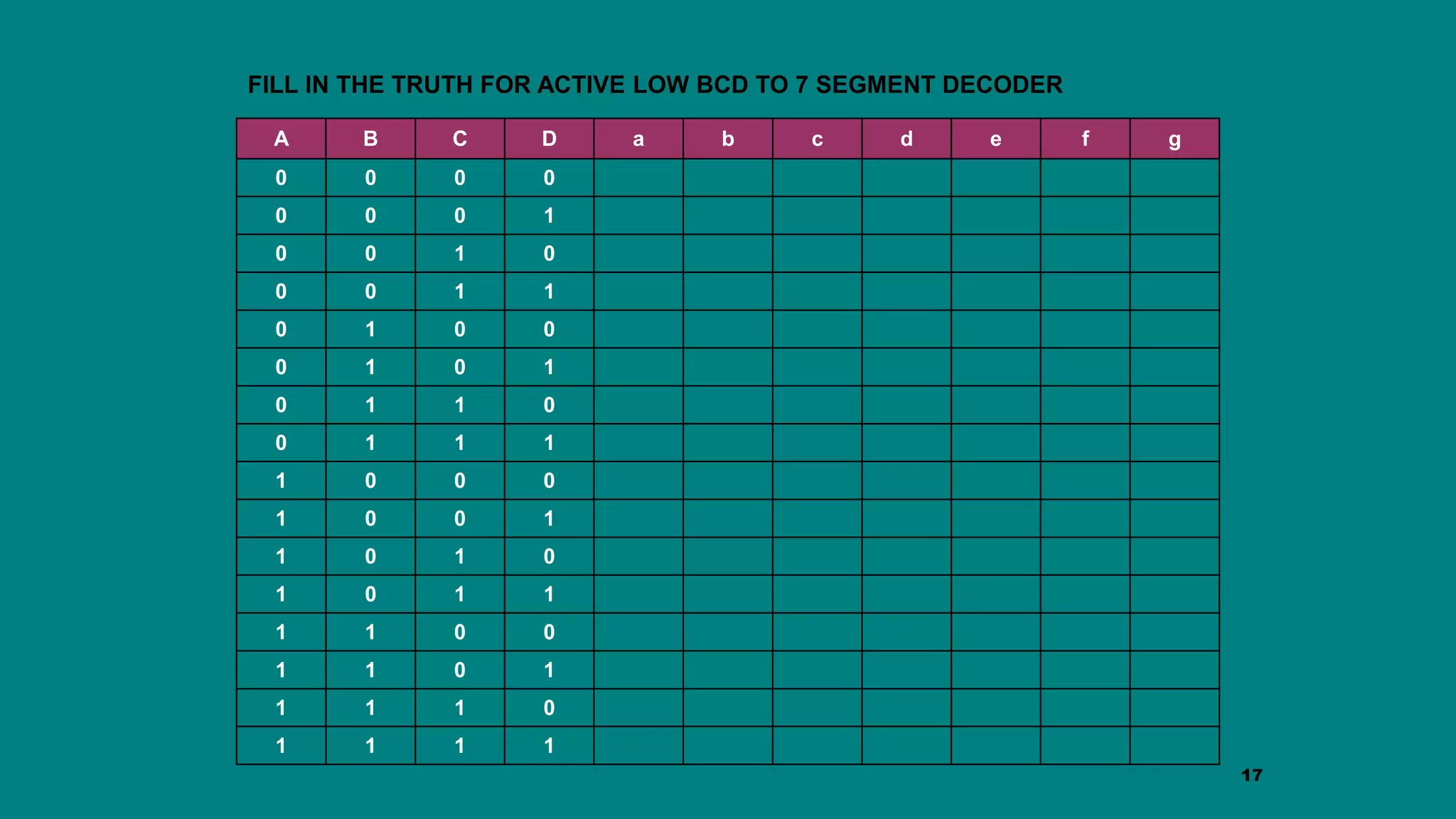
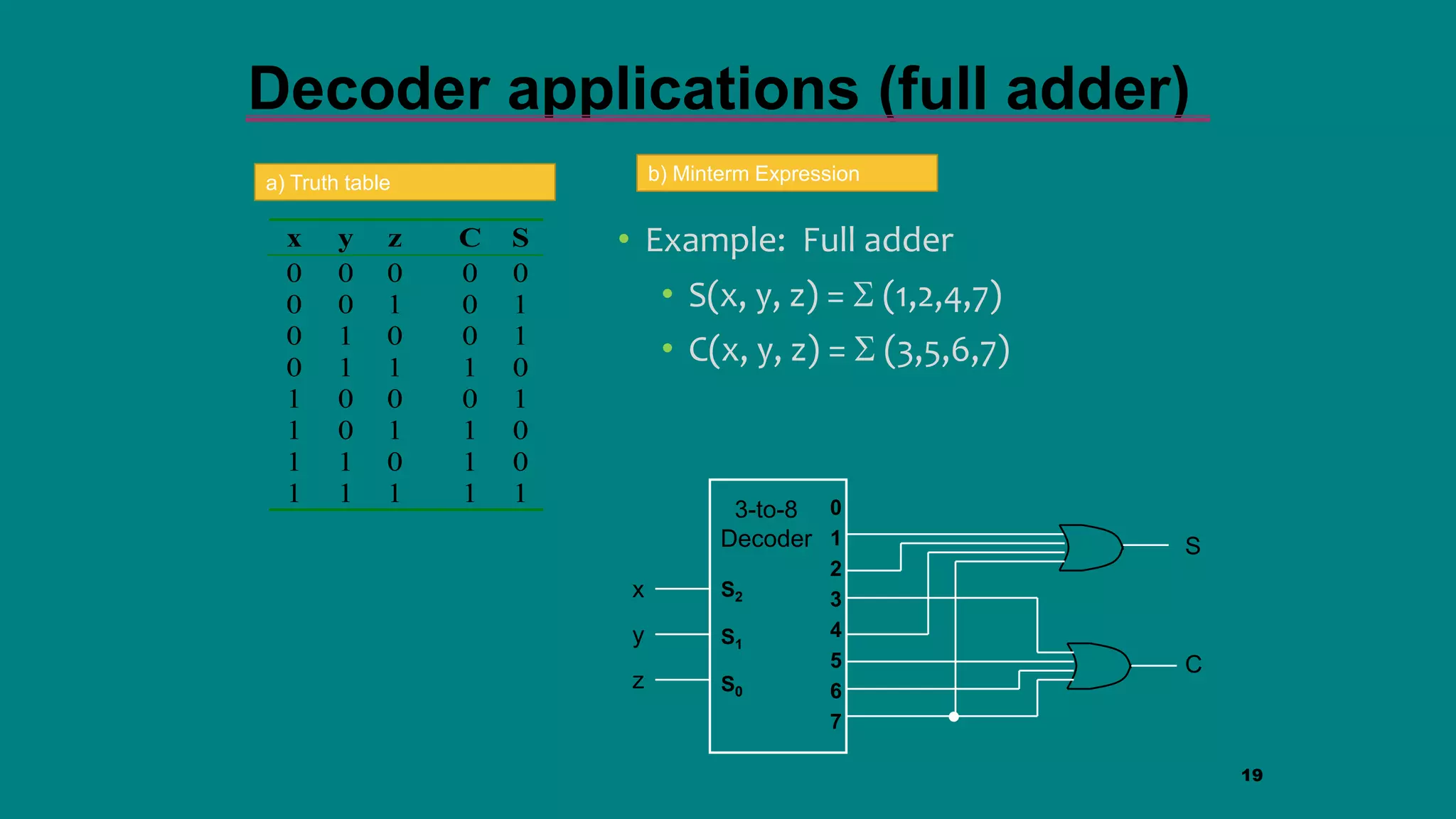
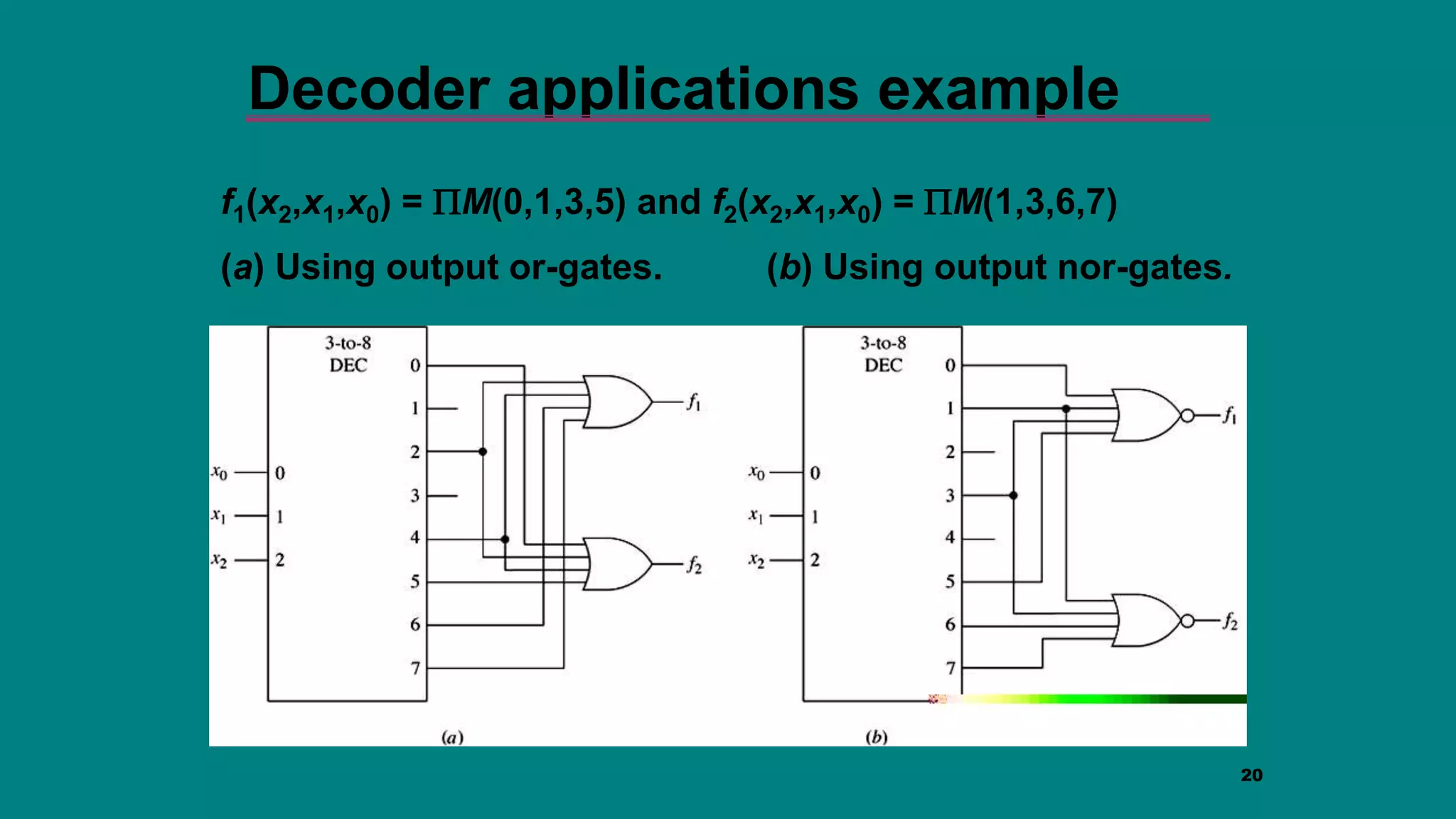
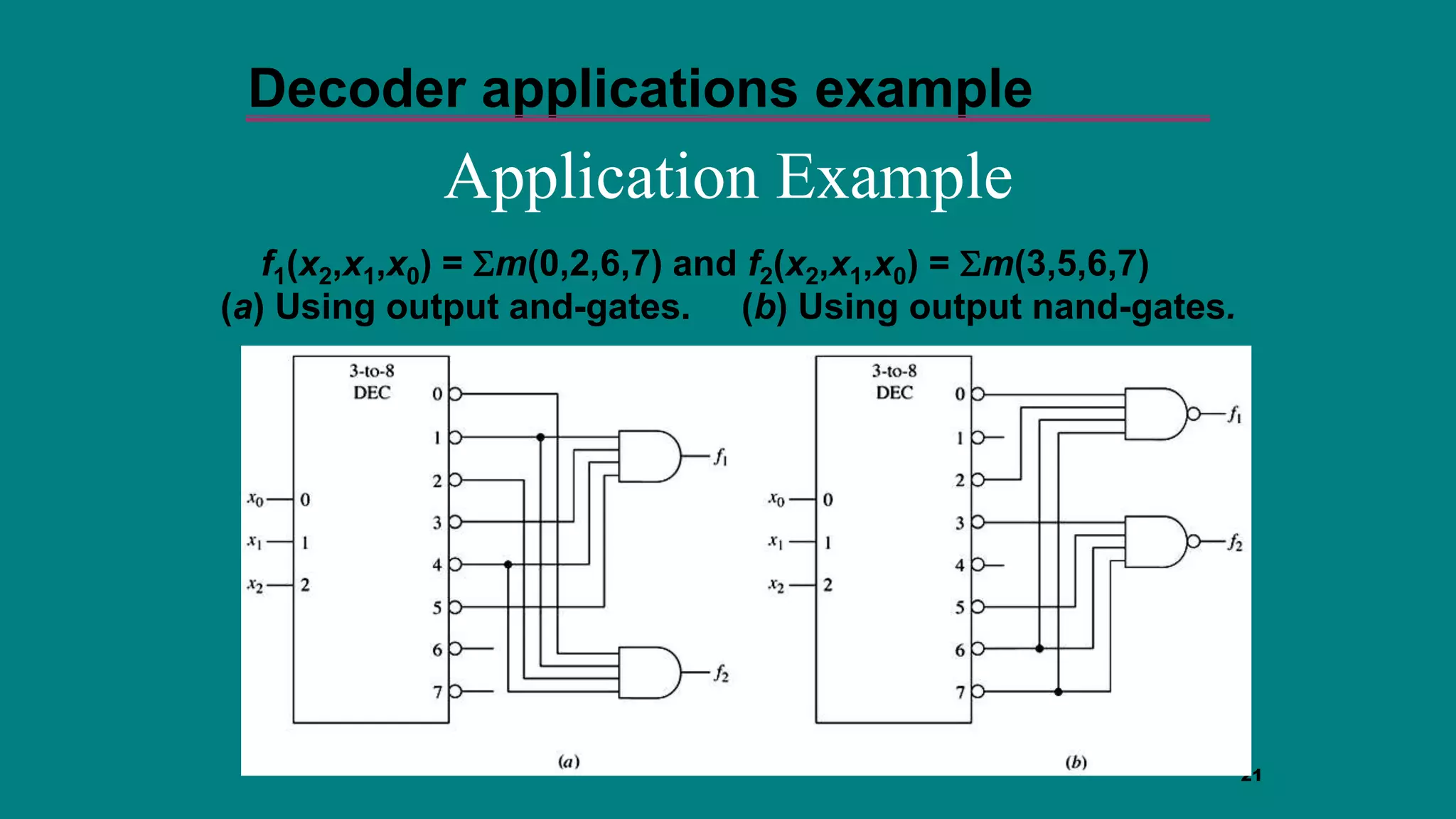
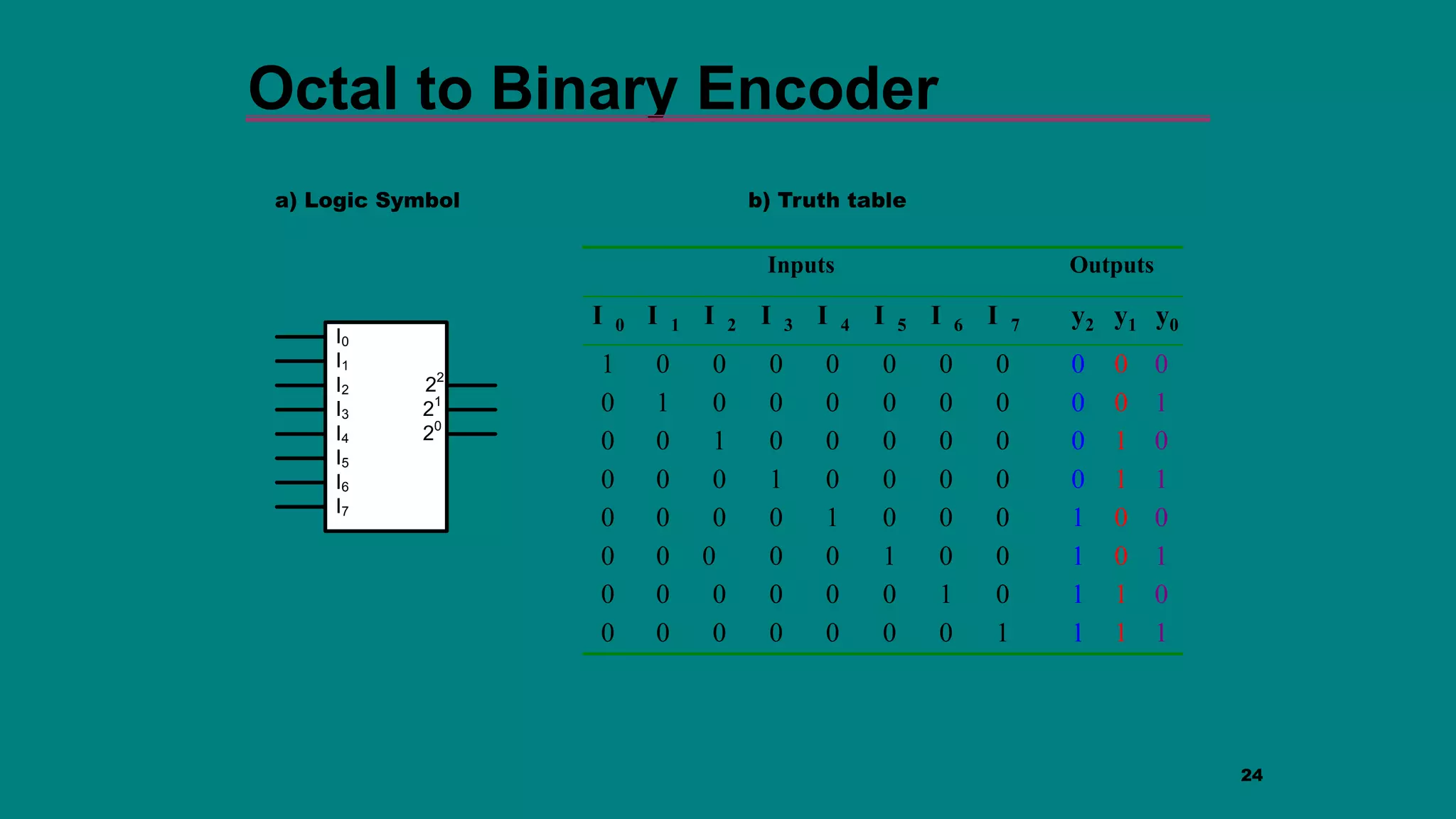
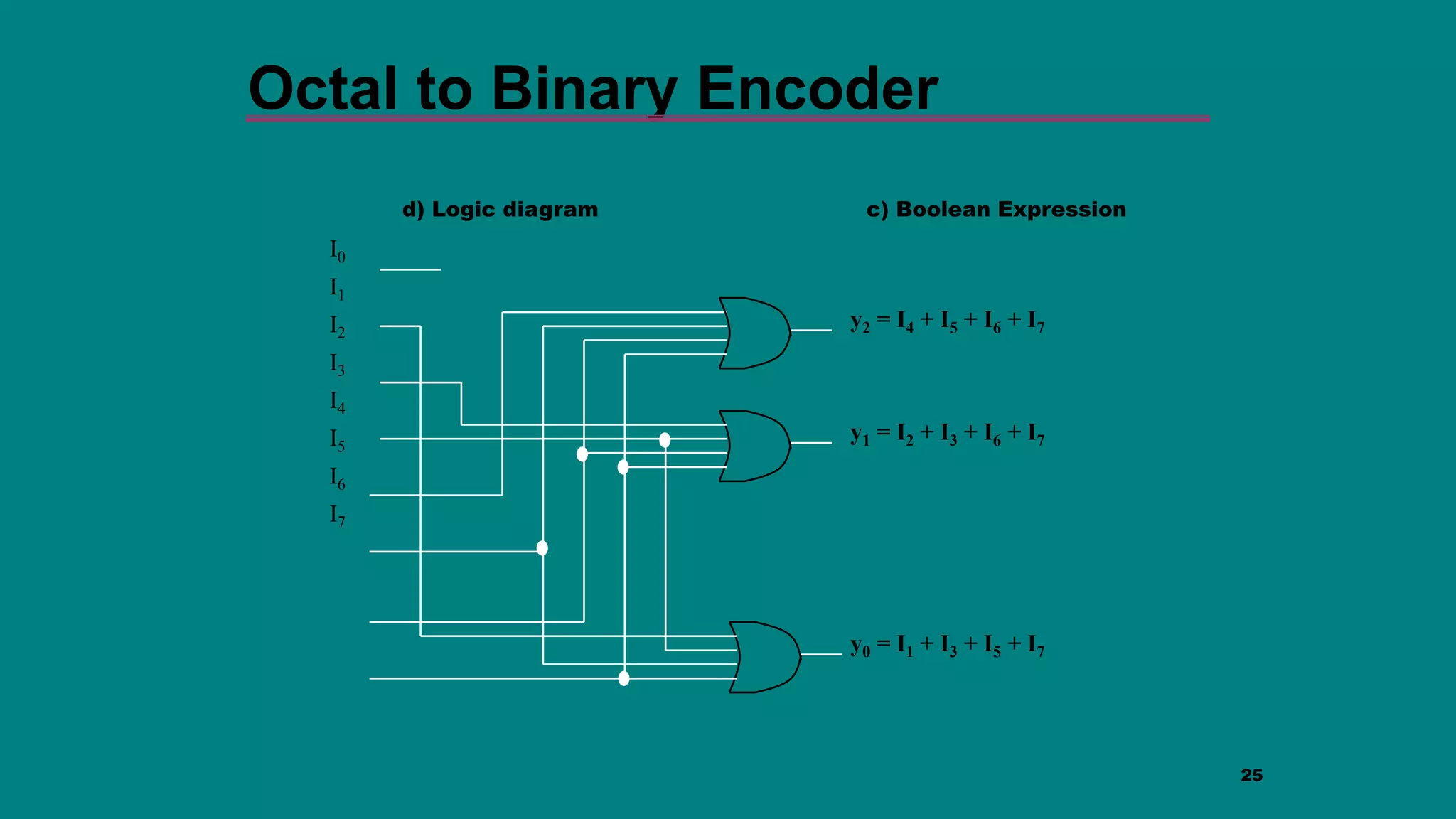
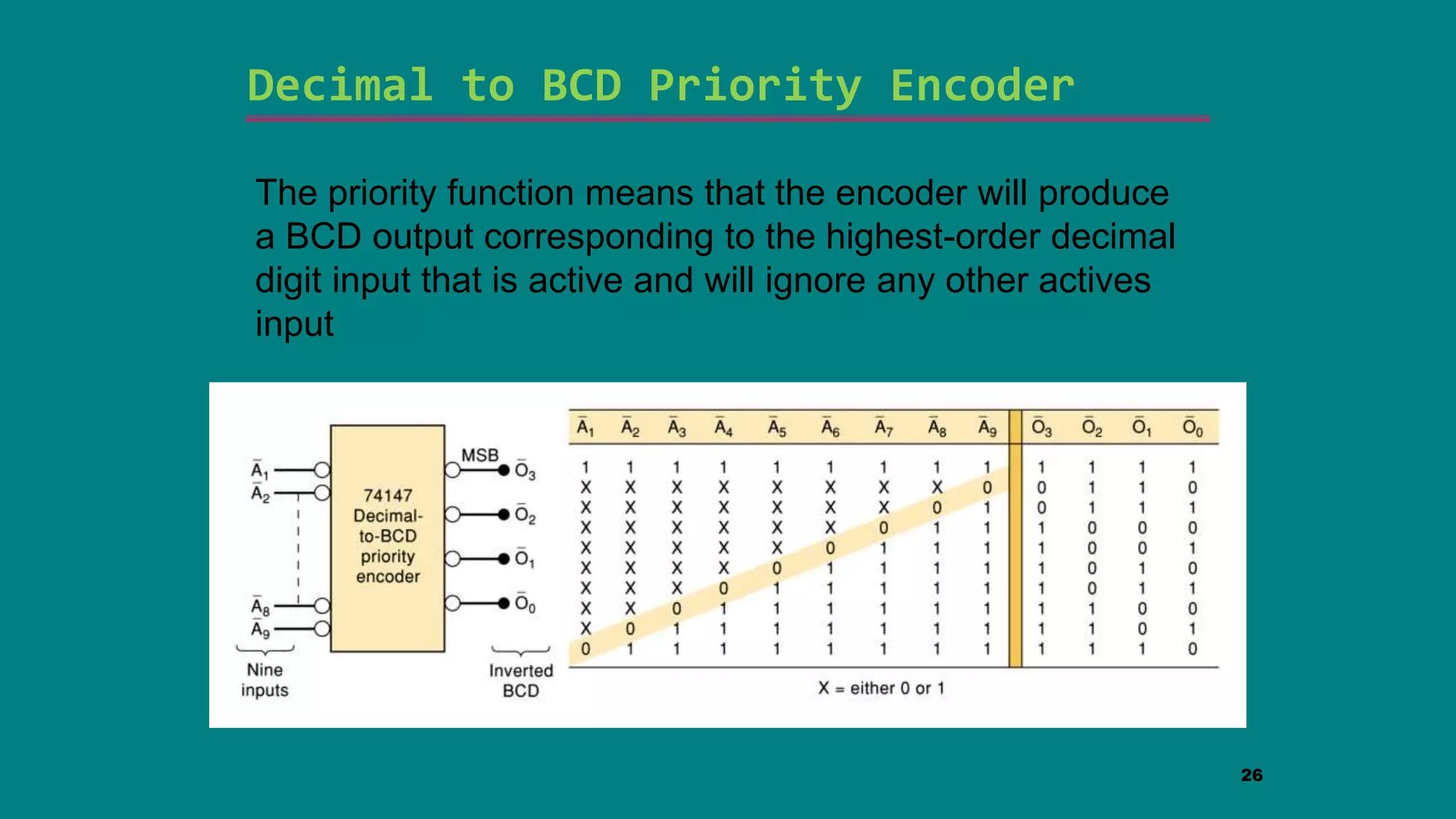
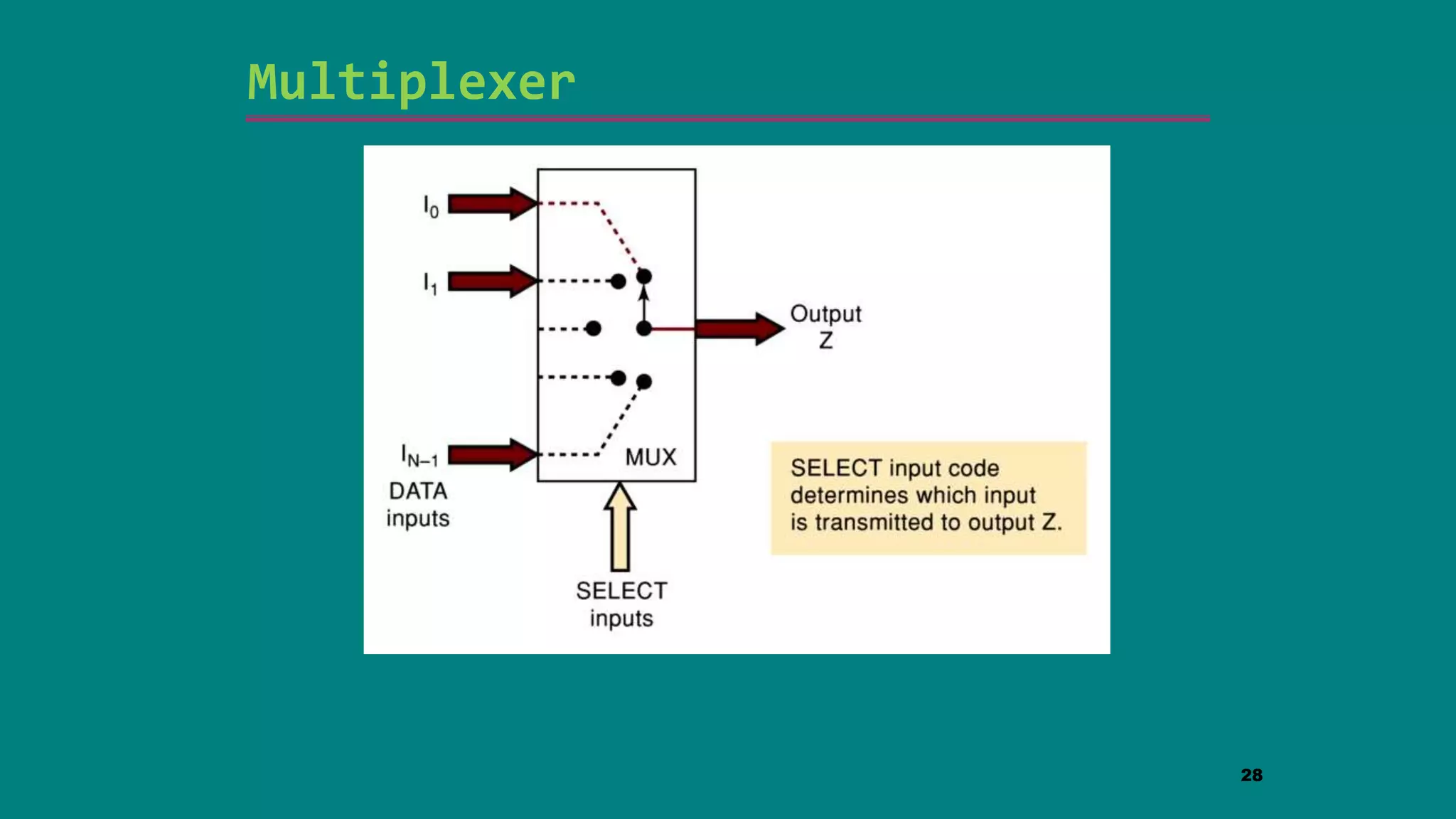
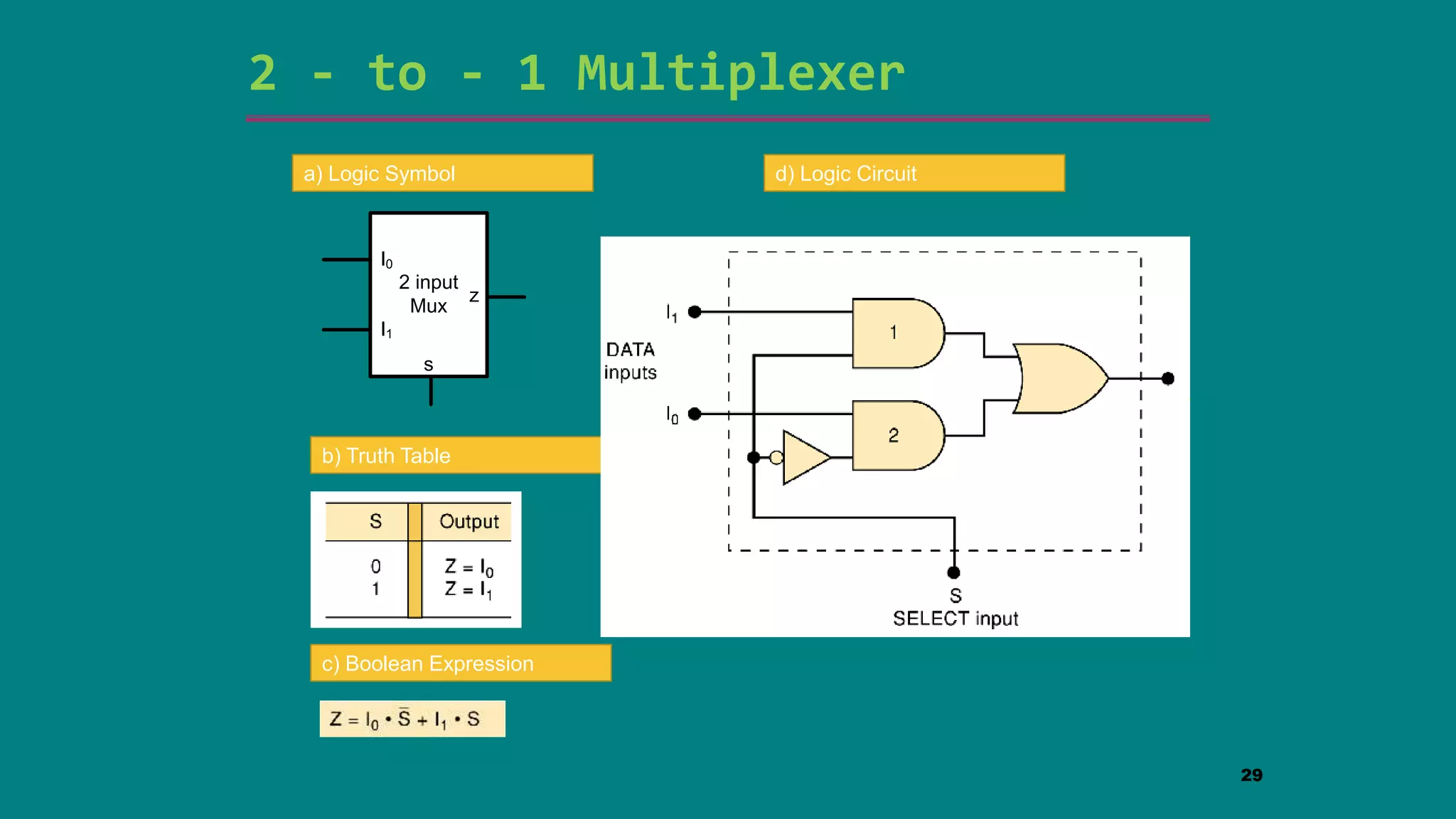
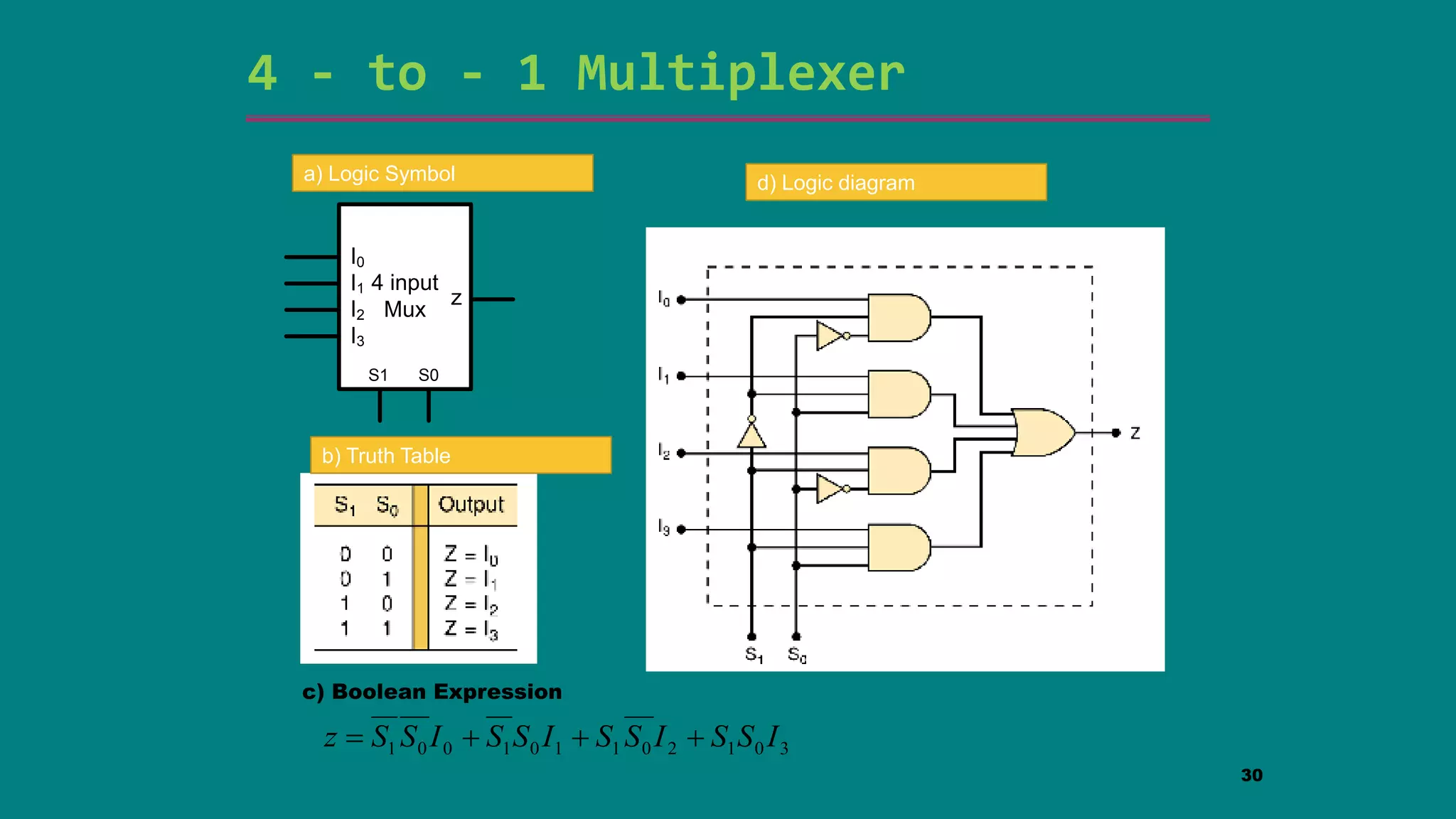
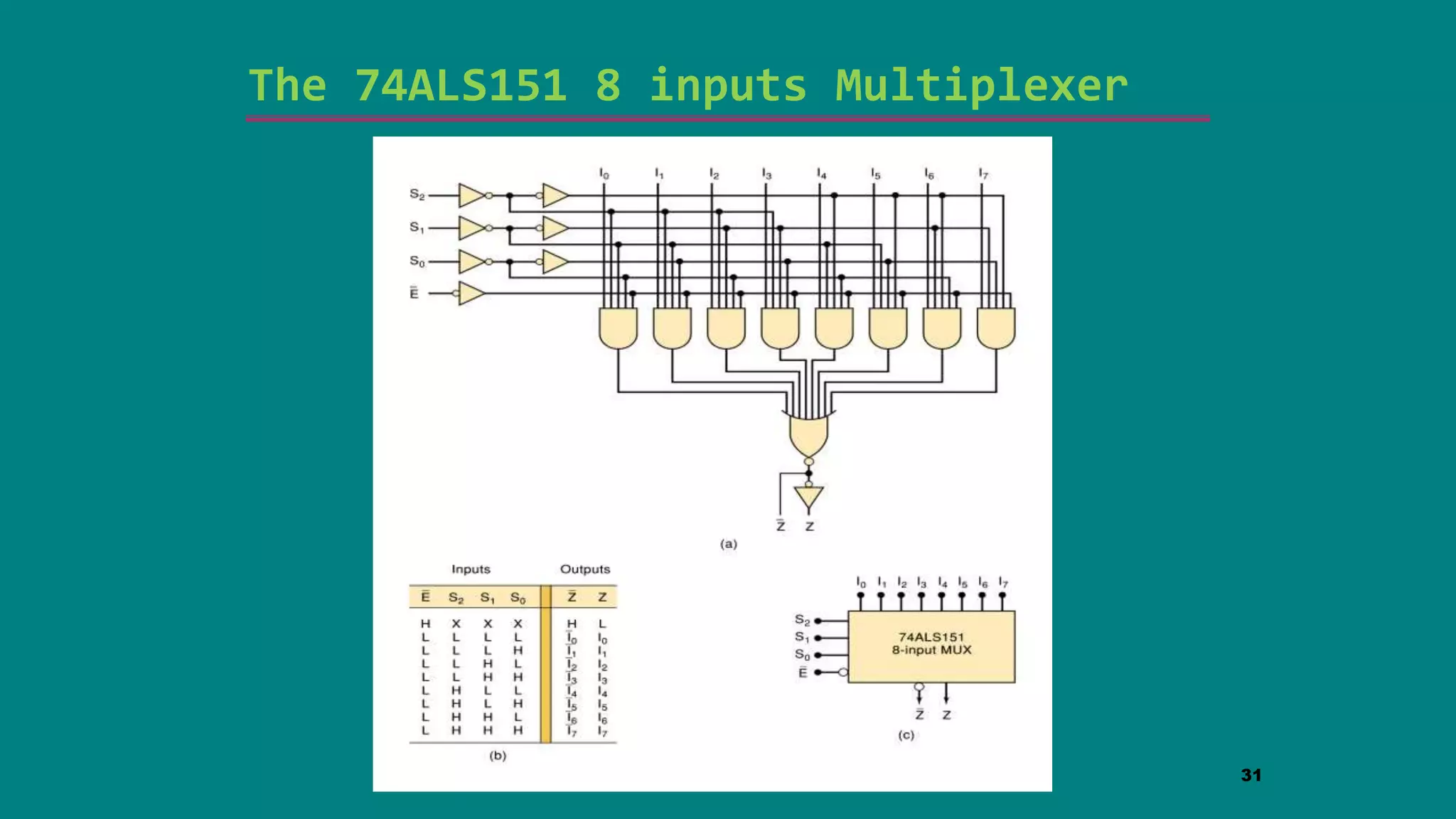
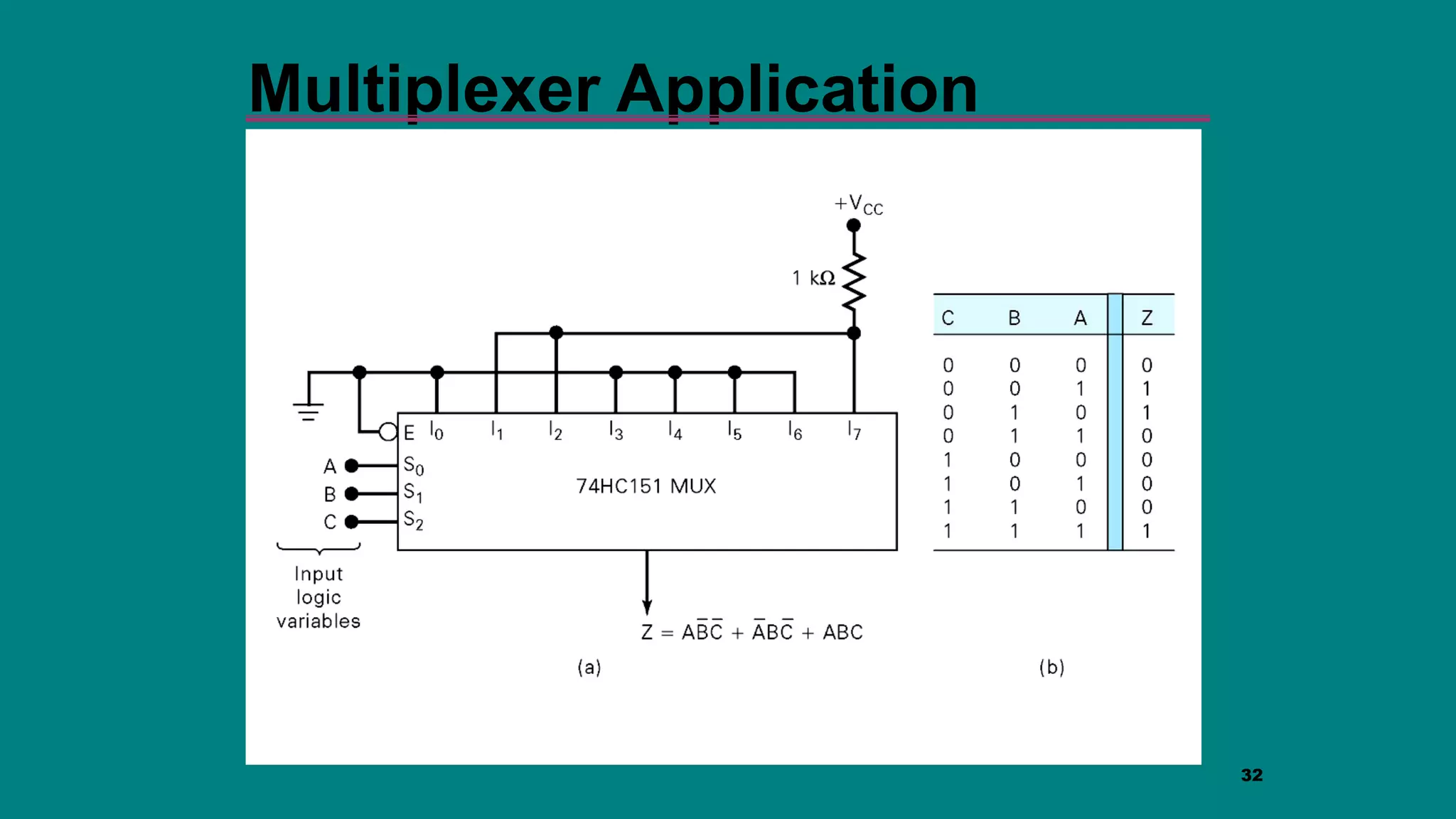
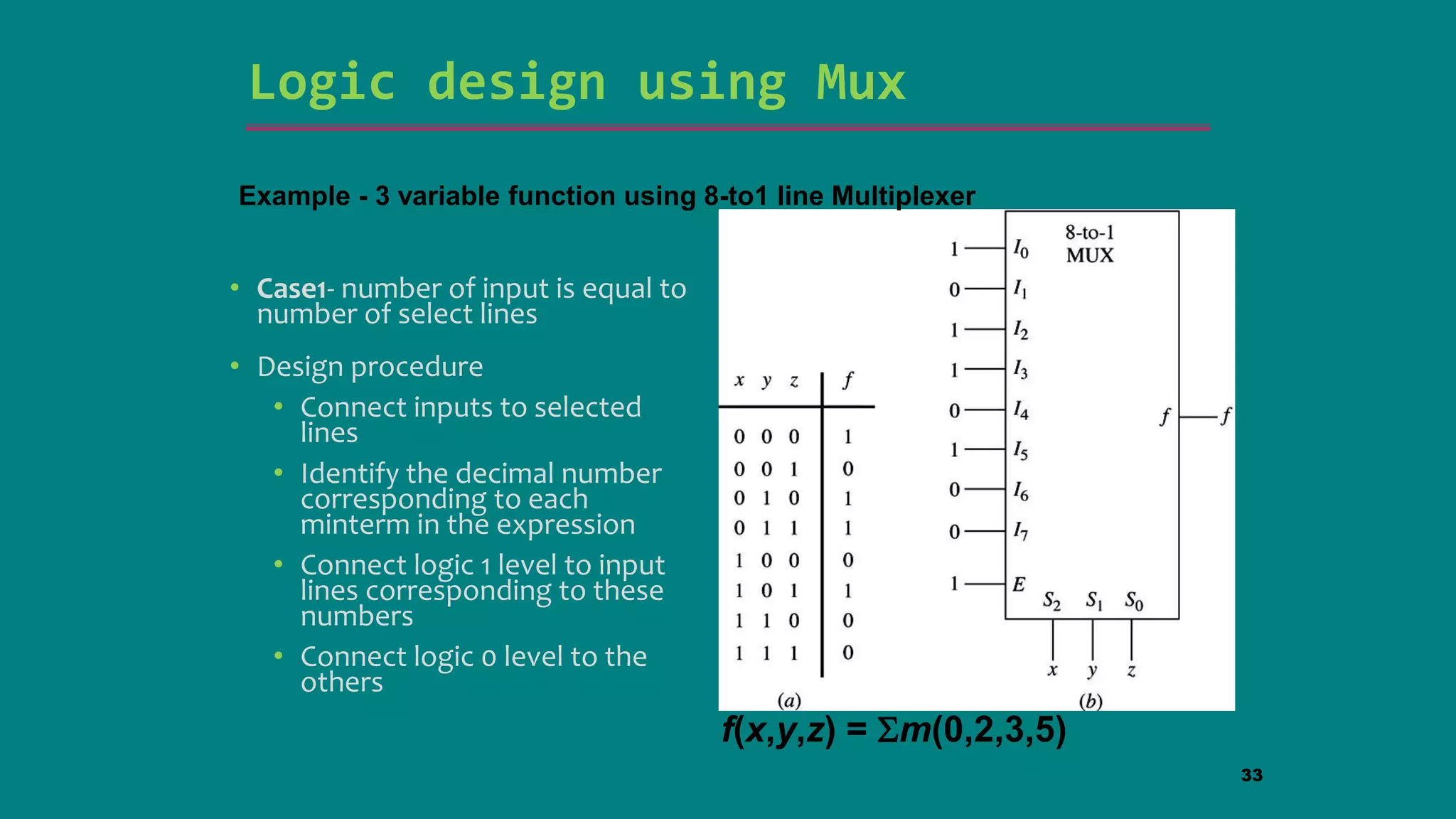
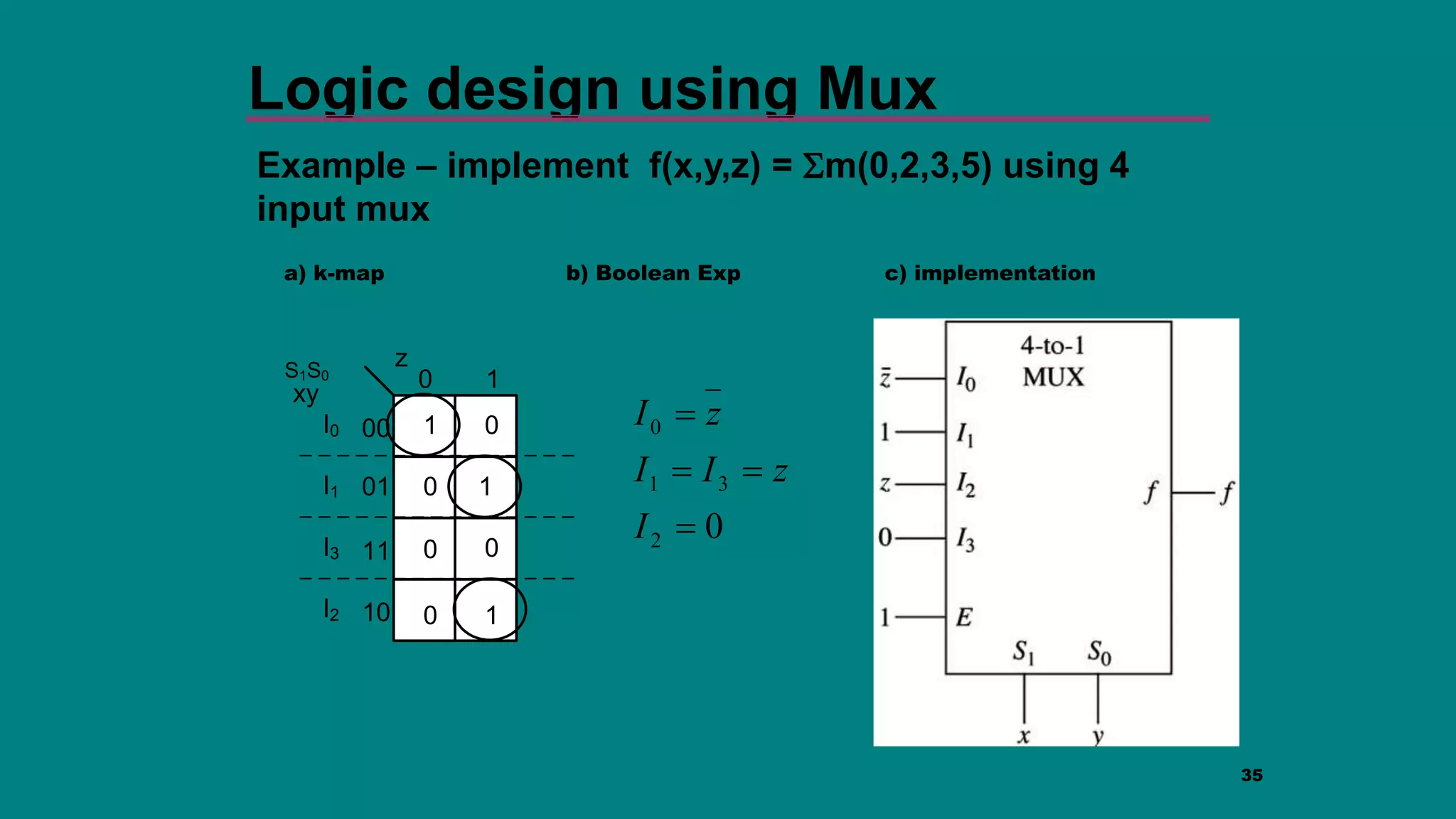
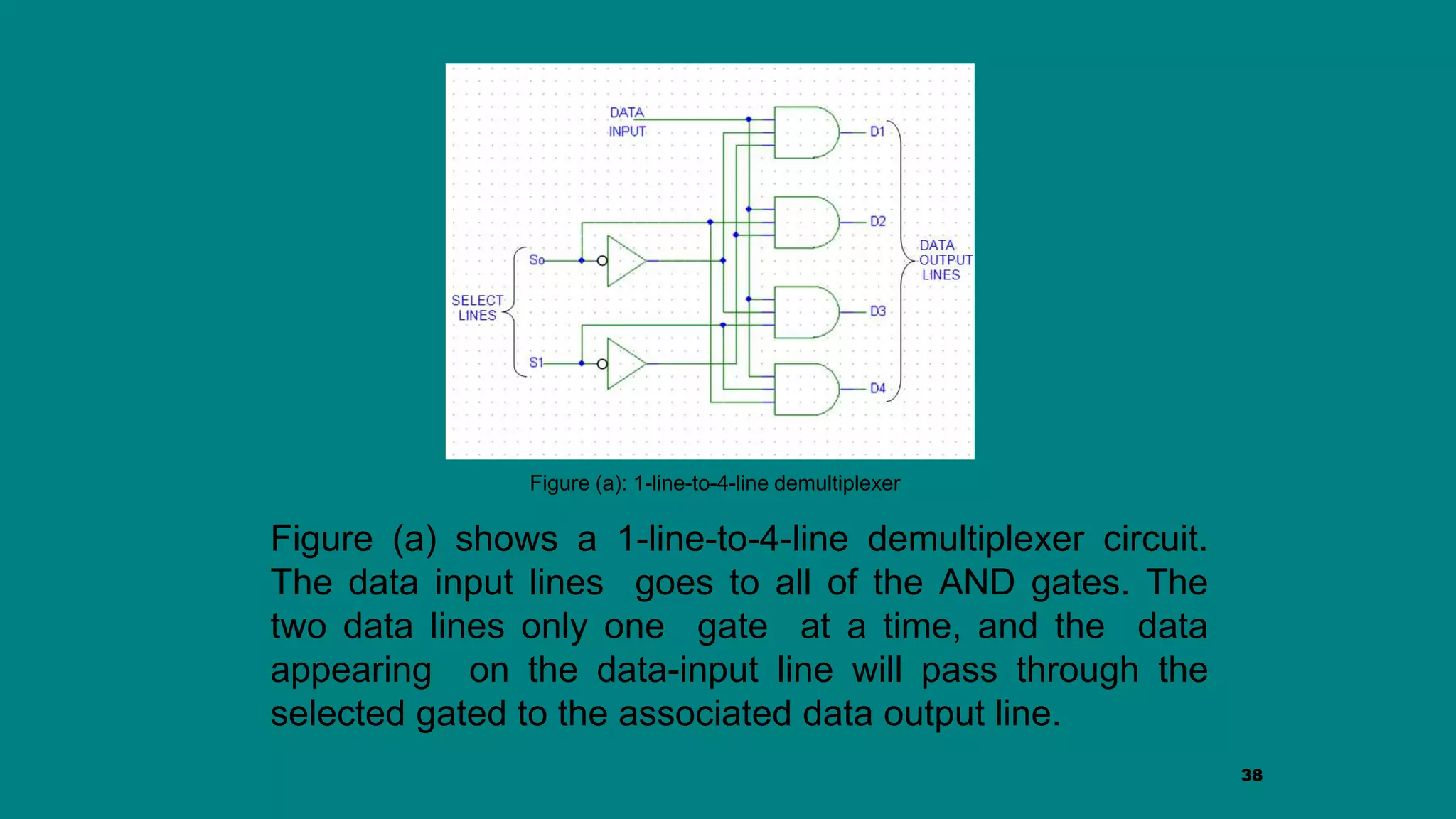
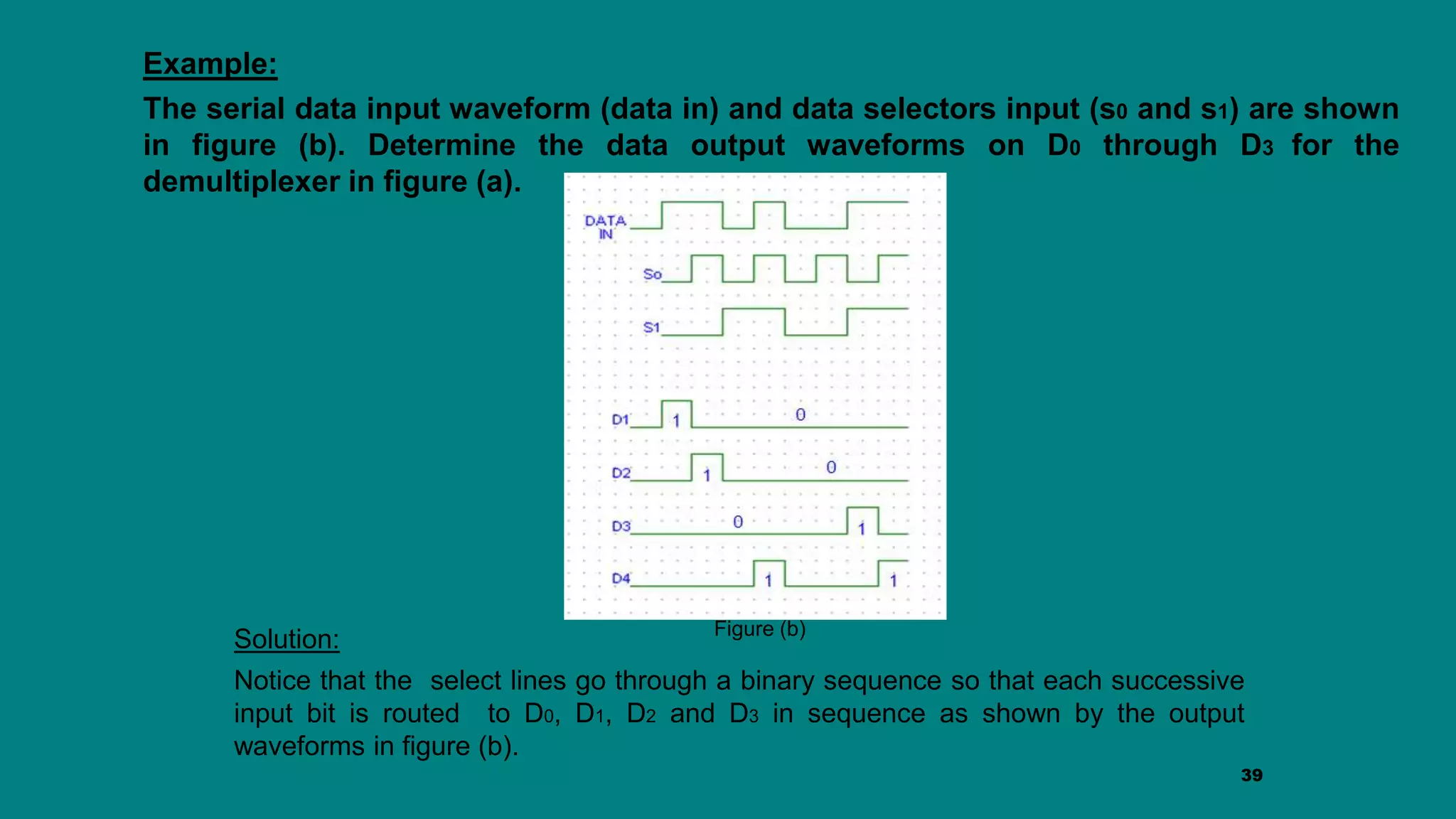
The document discusses combinational logic circuits including decoders, encoders, multiplexers and demultiplexers. It explains that decoders convert coded inputs to coded outputs, with only one output active at a time. Examples of 2-to-4 and 3-to-8 decoders are provided along with their truth tables and logic diagrams. Encoders perform the reverse function of decoders. Multiplexers allow selecting one of several data inputs to output, while demultiplexers distribute a single input to multiple outputs. Applications in designing logic functions using decoders and multiplexers are also covered.