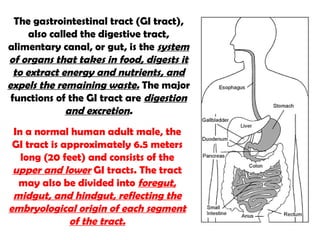
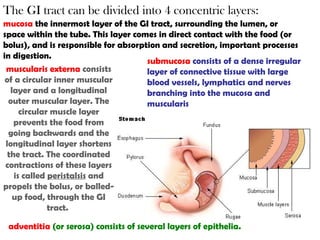
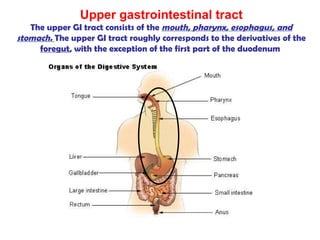
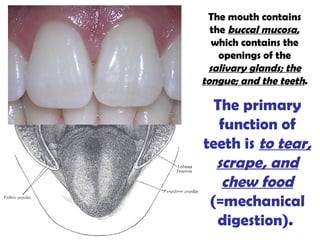
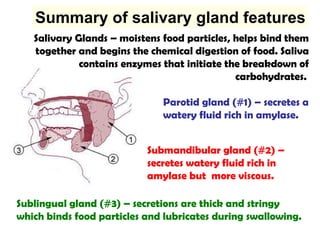
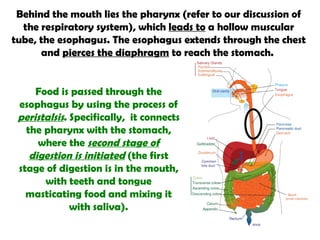
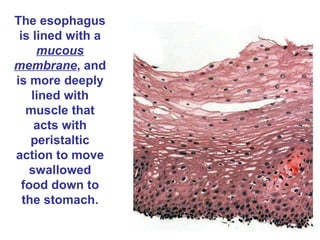
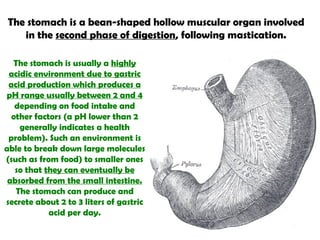
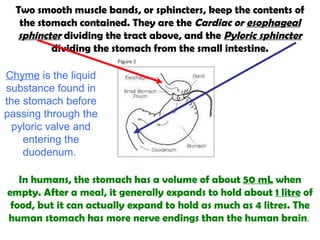
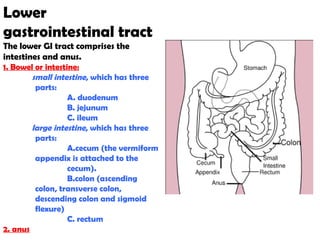
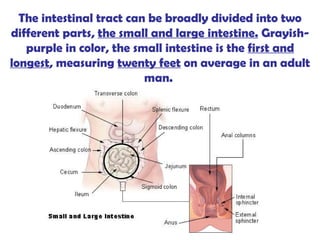
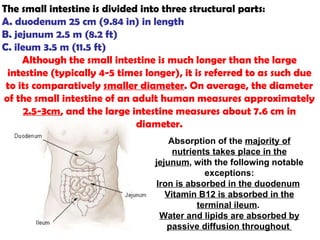
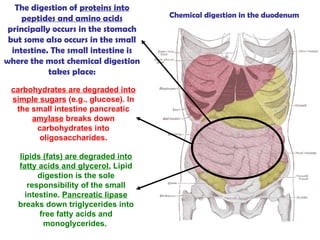
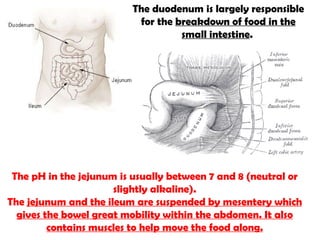
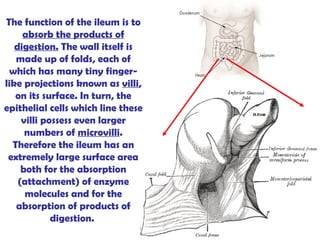
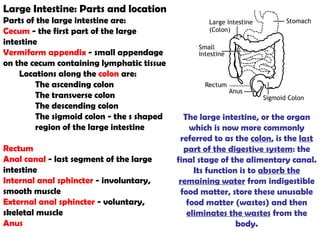
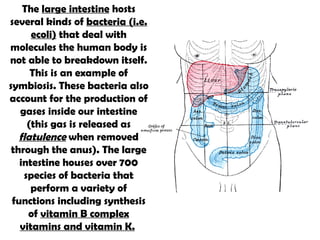
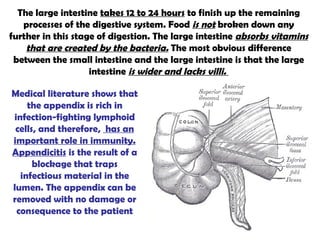
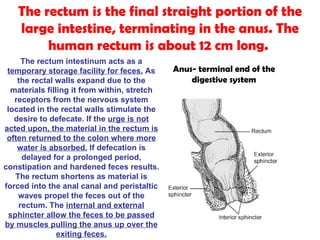
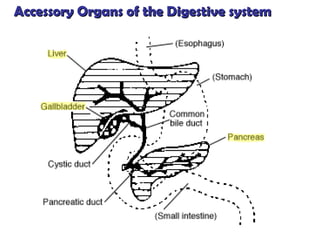
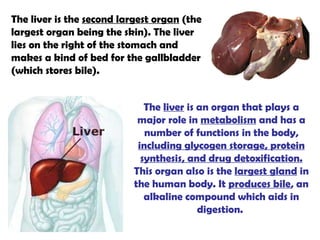
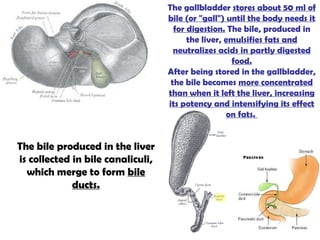
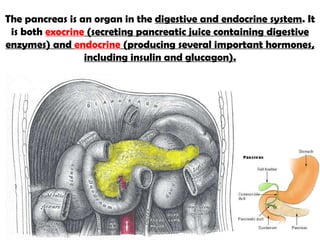
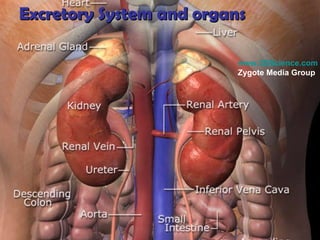
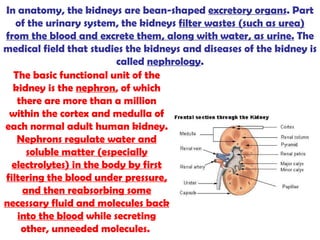
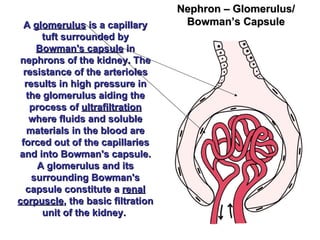
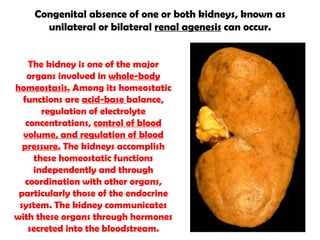
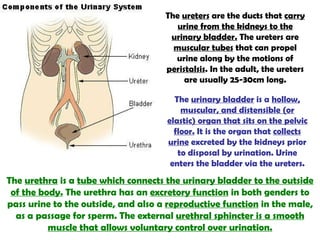
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract) digests food and expels waste. It has 4 layers and is divided into upper and lower tracts. The upper tract includes the mouth, esophagus, and stomach. The stomach acidifies food and the lower tract, including the small and large intestines, further digests and absorbs nutrients before waste is excreted. Accessory organs like the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder produce substances like bile and enzymes to aid digestion. The kidneys filter waste from the blood to produce urine for excretion via the ureters, bladder, and urethra.