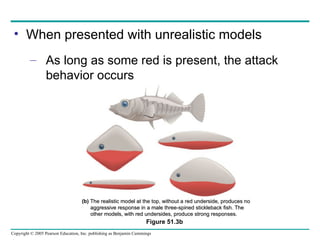
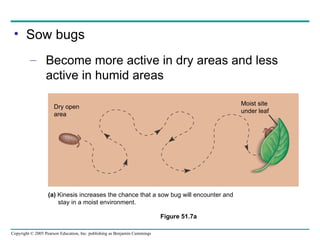
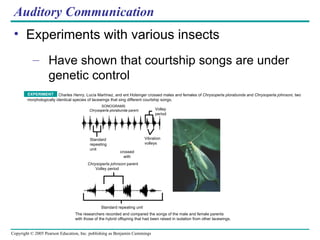
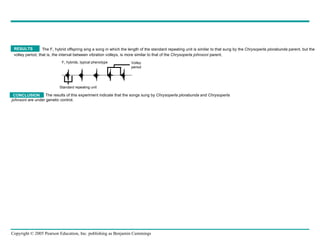
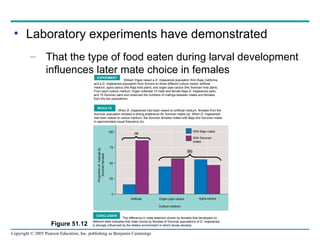
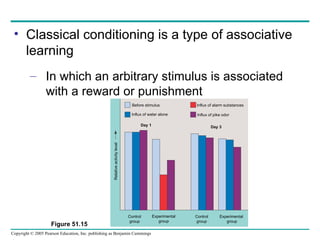
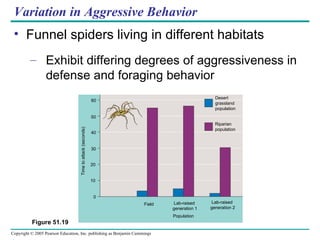
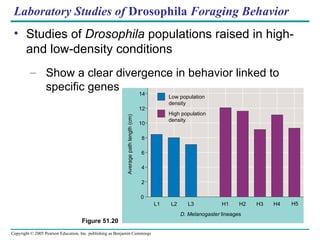
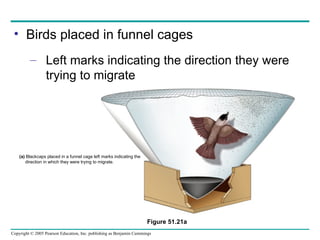
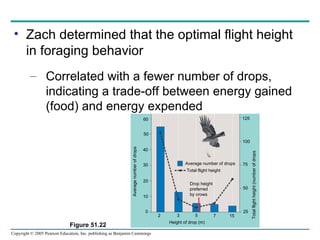
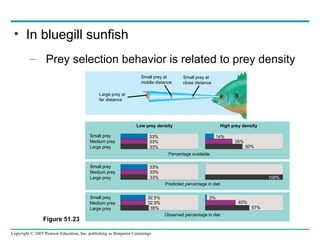
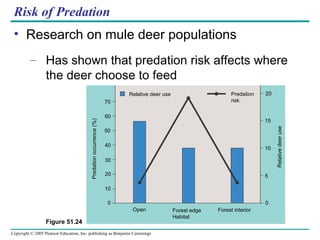
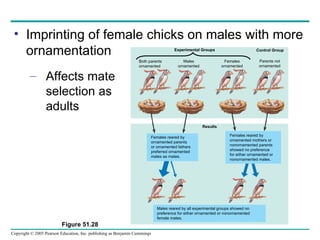
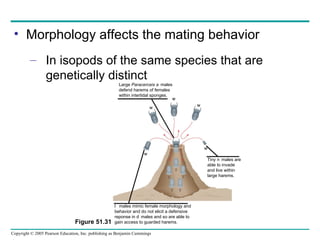
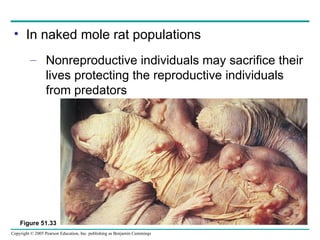
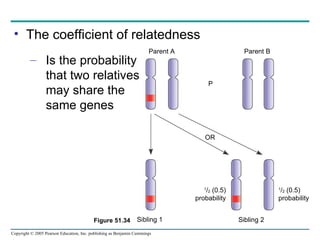
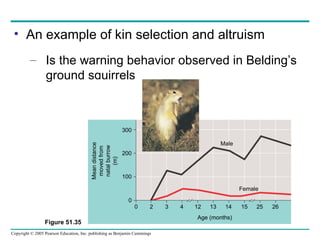
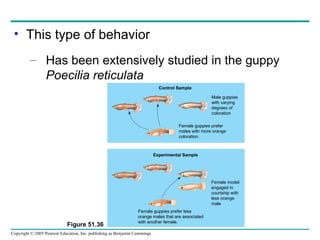
Behavioral ecology studies animal behavior from both proximate and ultimate perspectives. Proximate questions examine the mechanisms and stimuli that trigger behaviors, while ultimate questions address evolutionary significance. Many behaviors have genetic components and are influenced by environment. Behaviors like communication, learning, and mating systems can evolve through natural selection if they influence survival and reproduction.