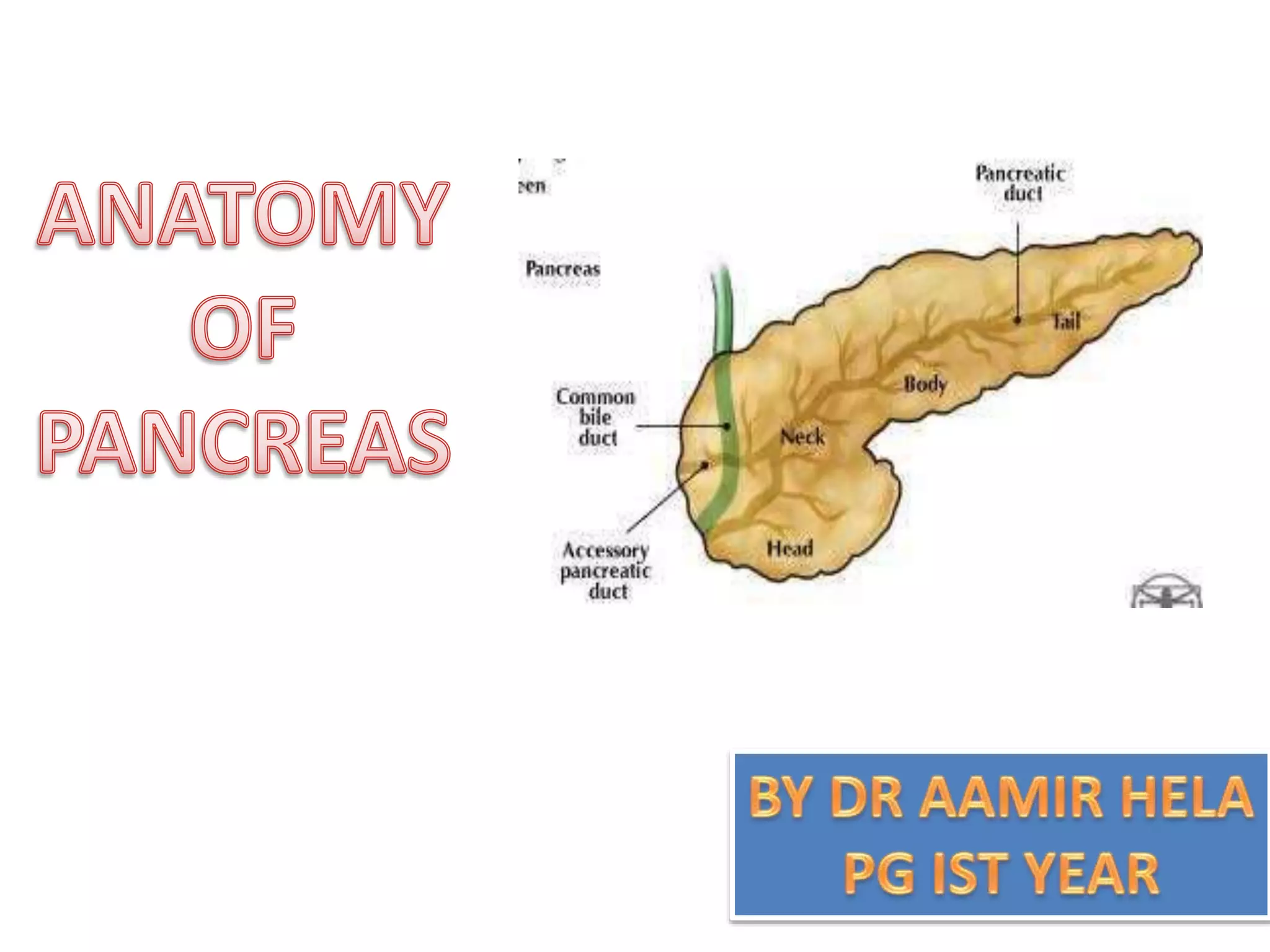
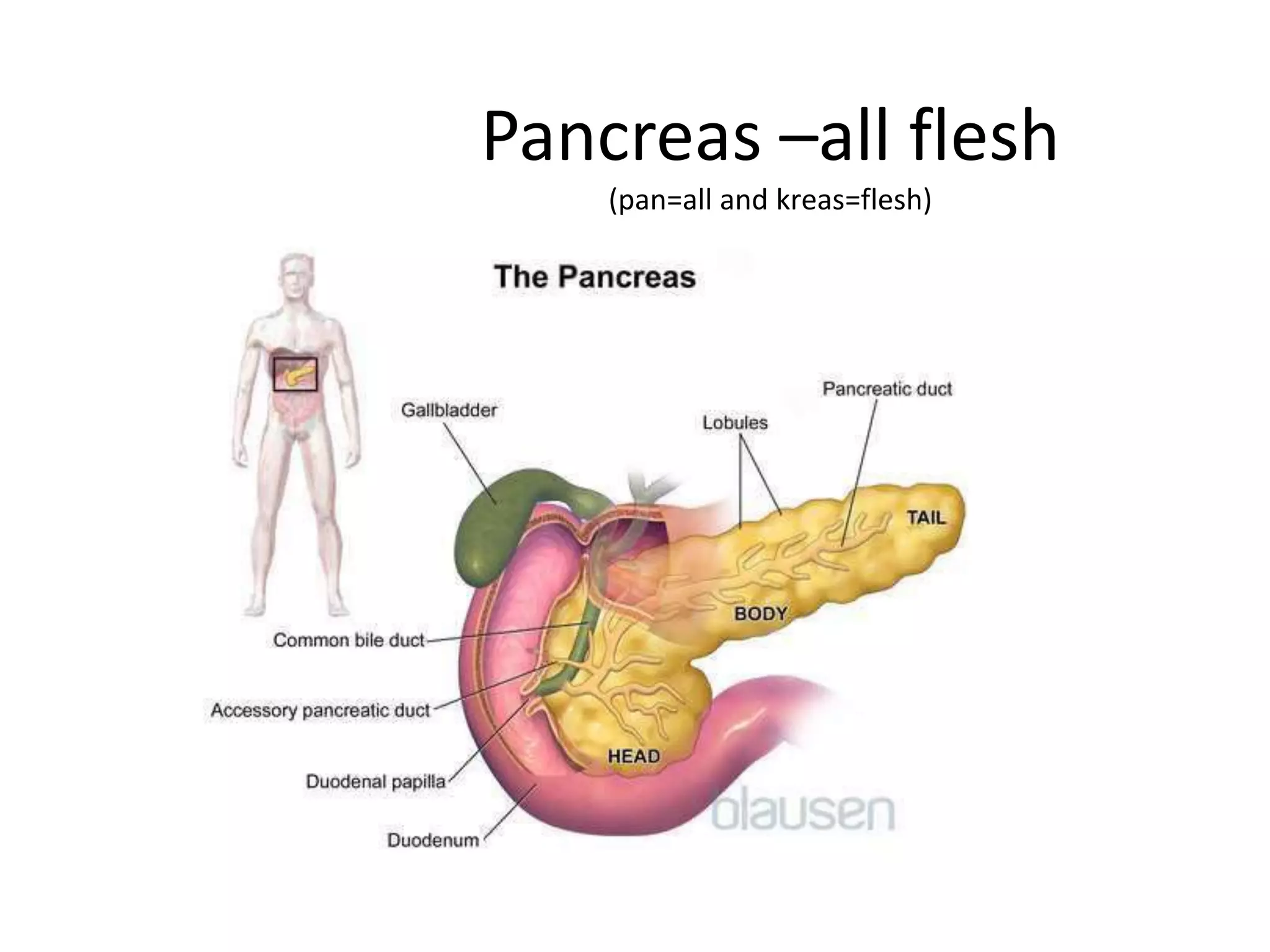
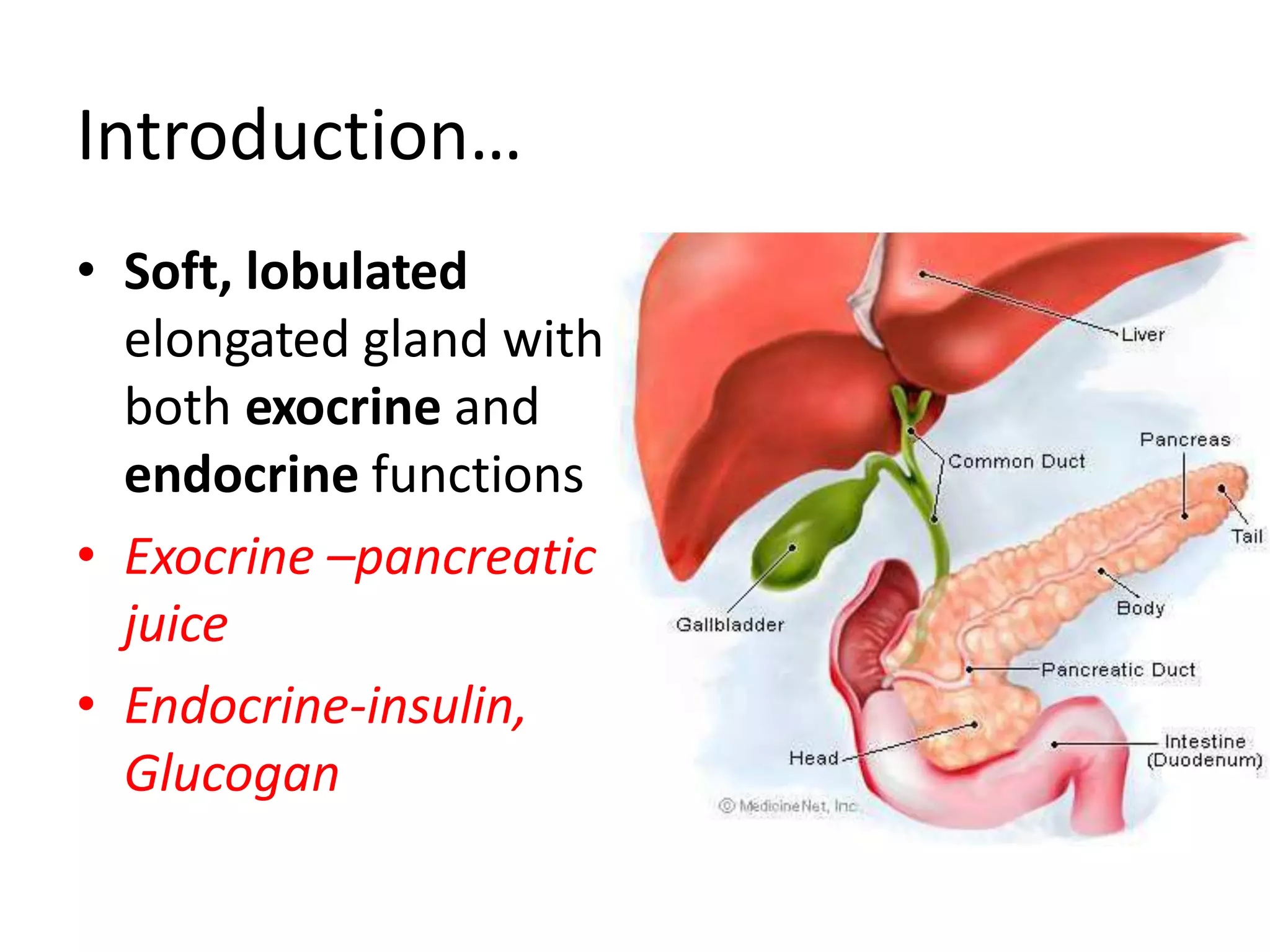
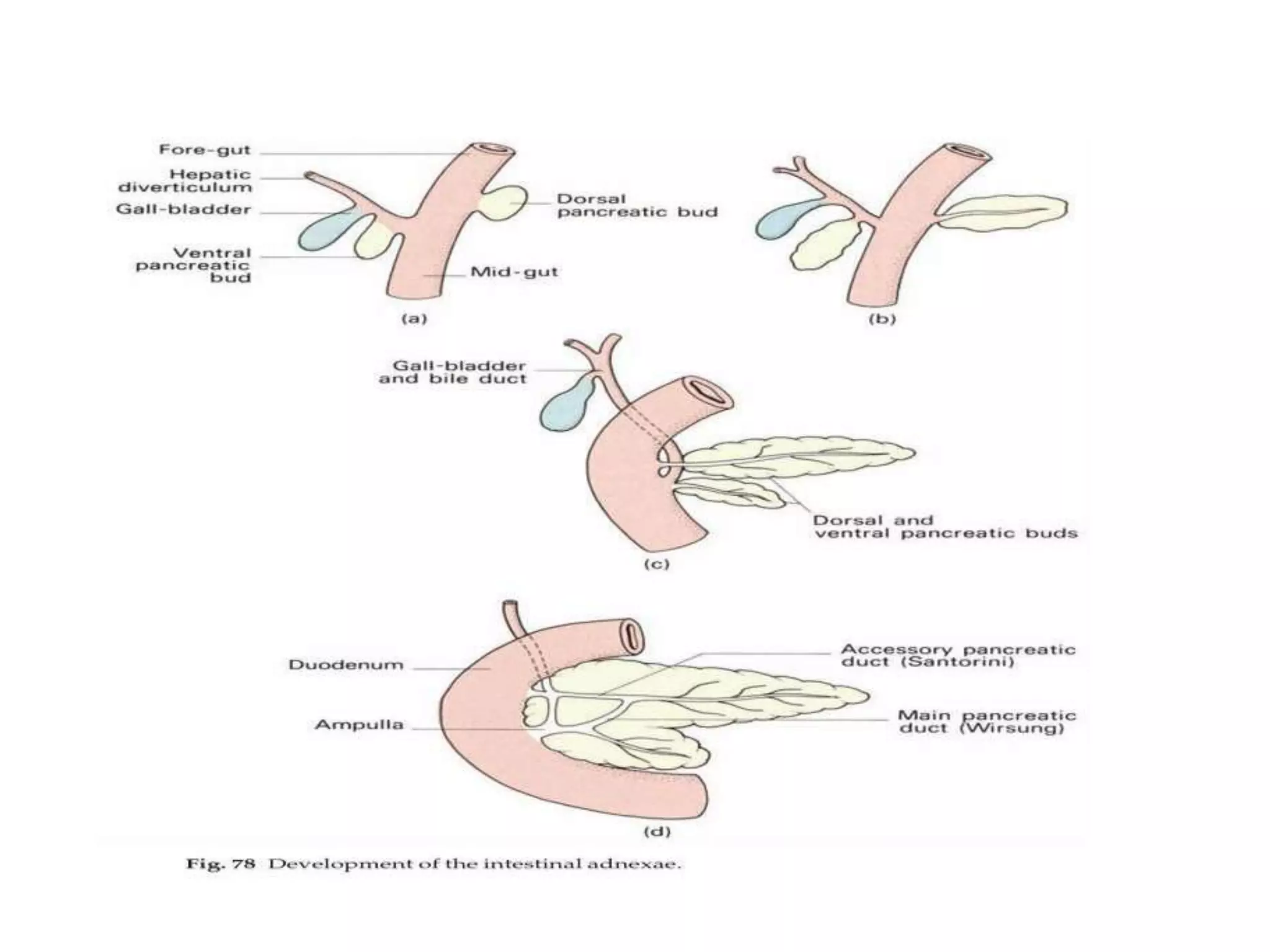
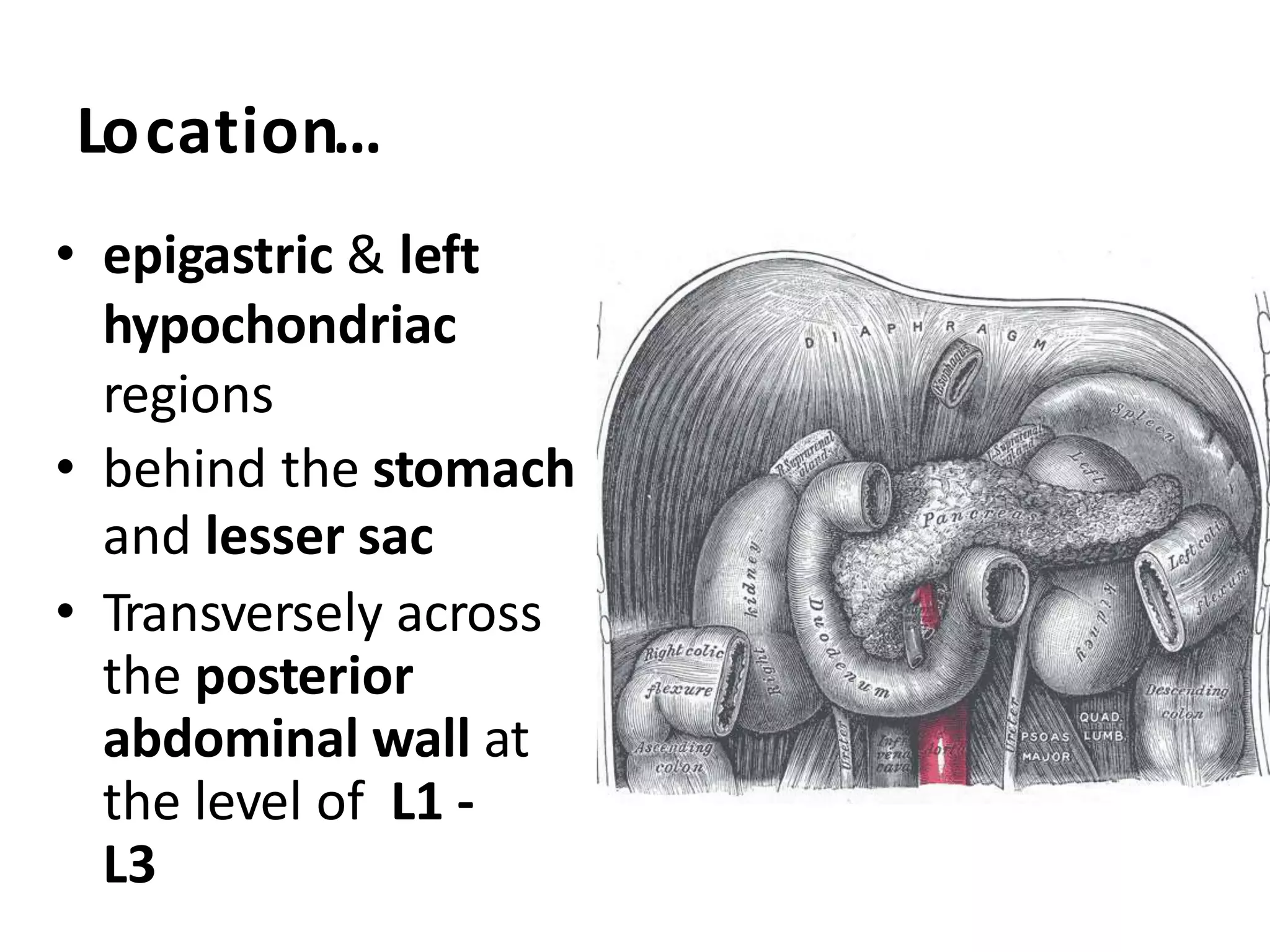
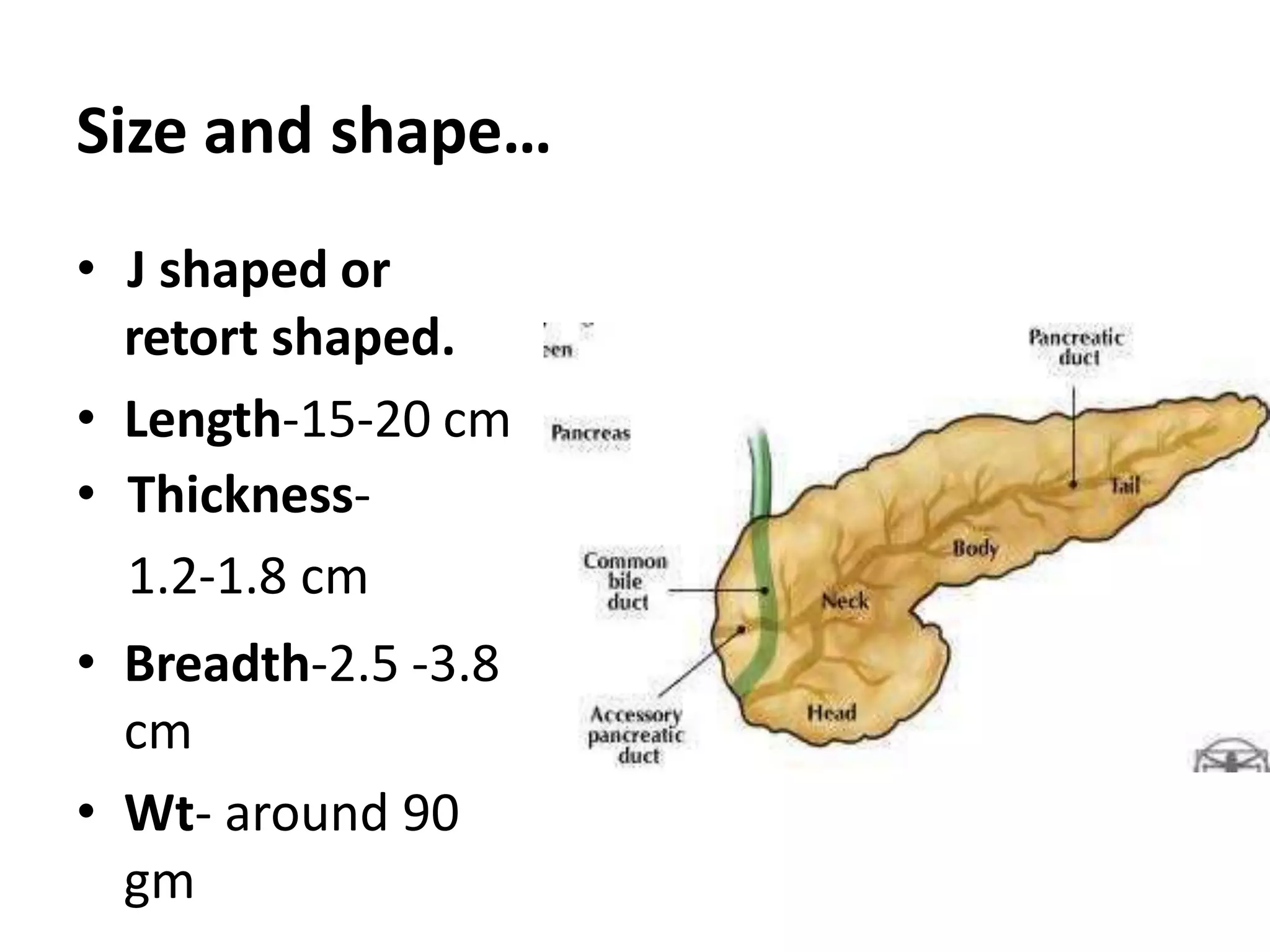
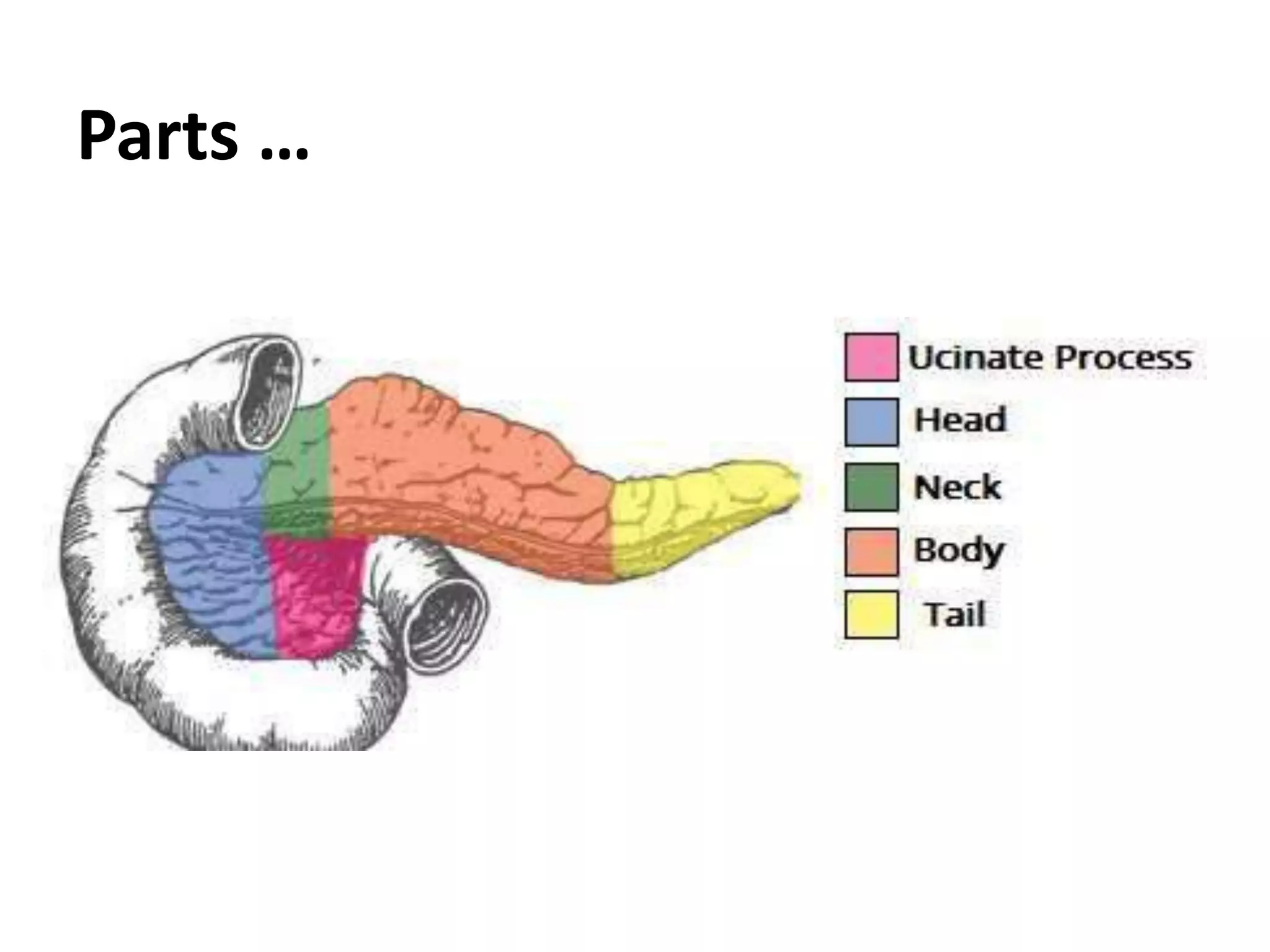
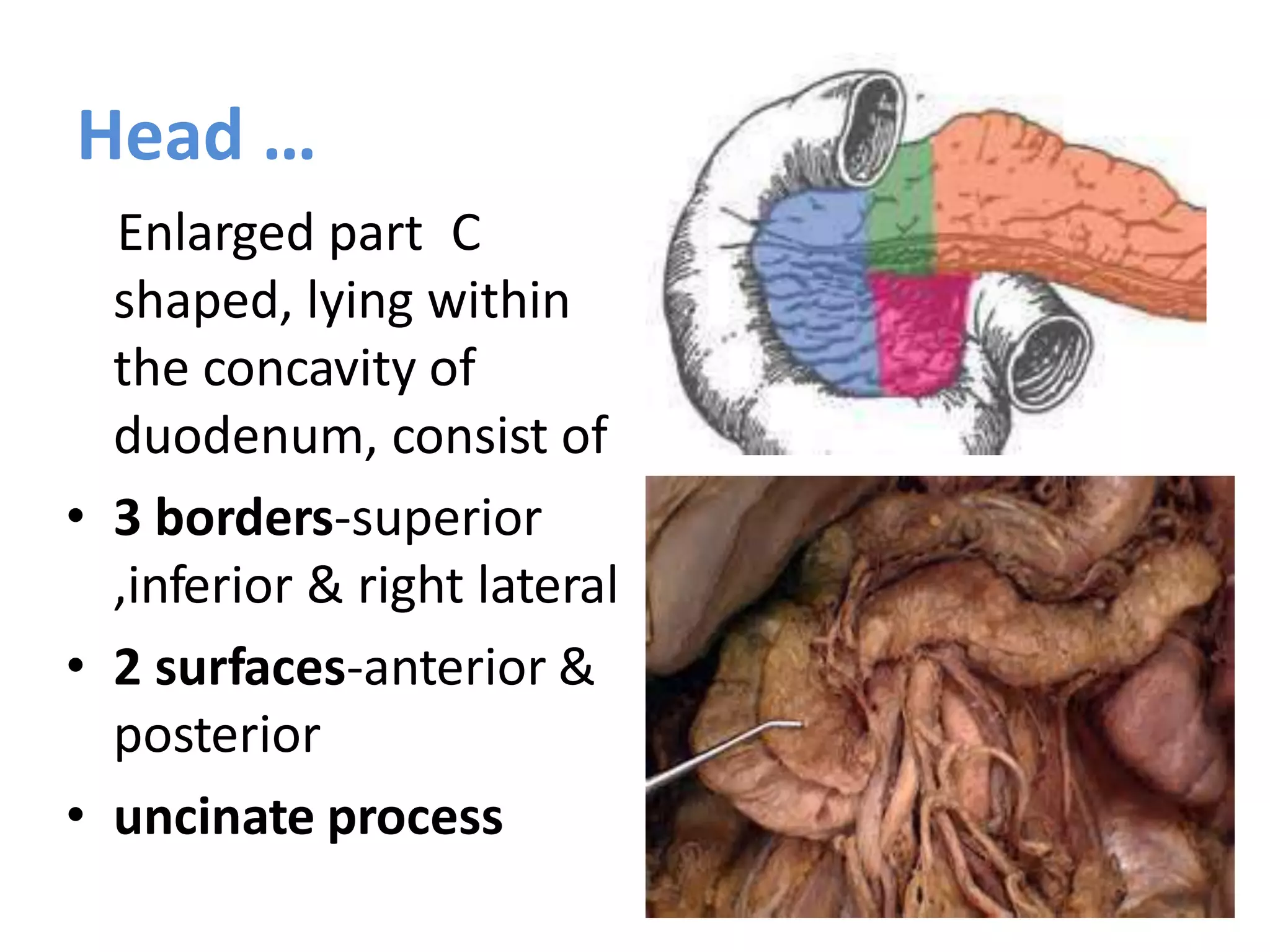
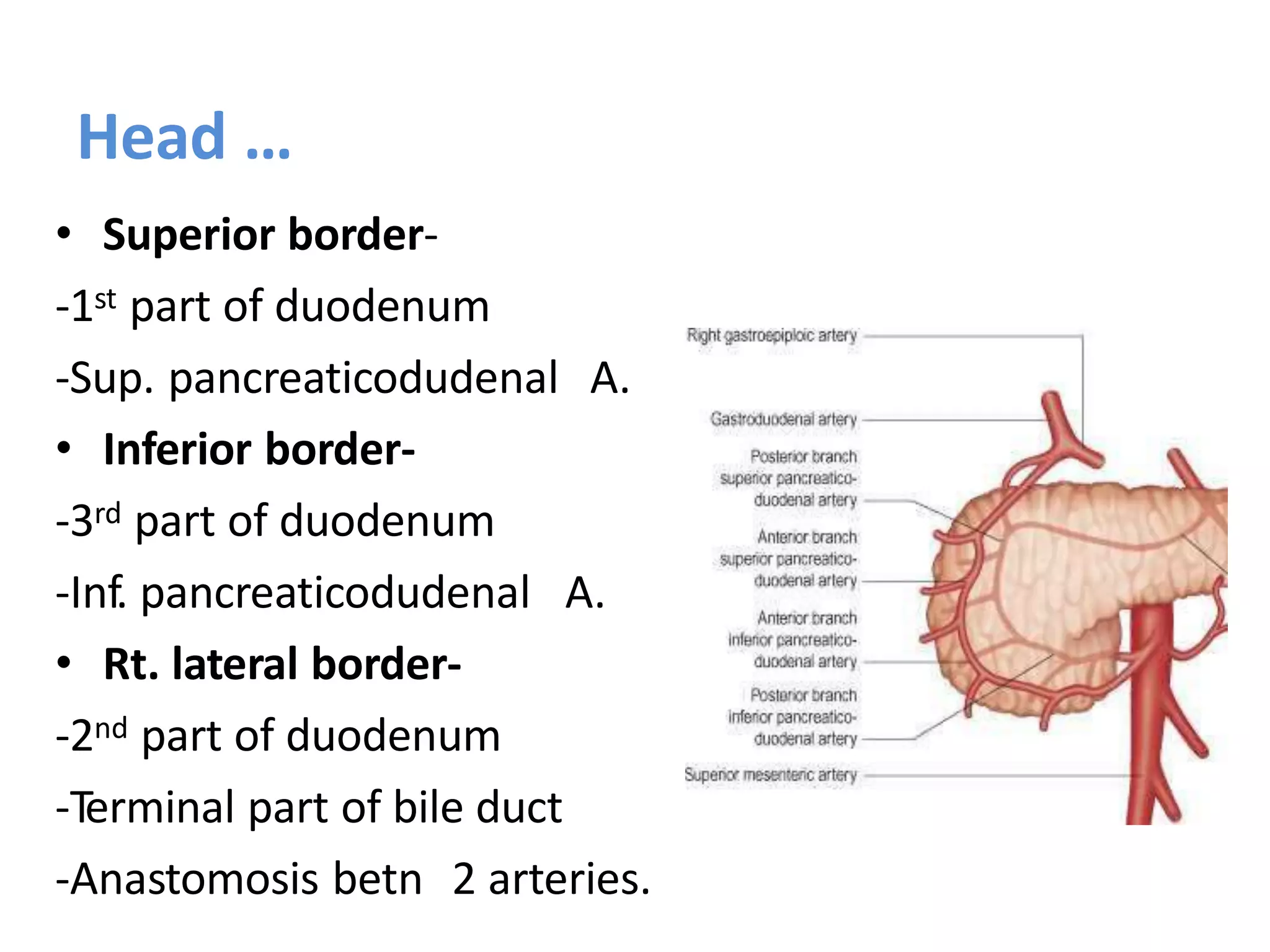
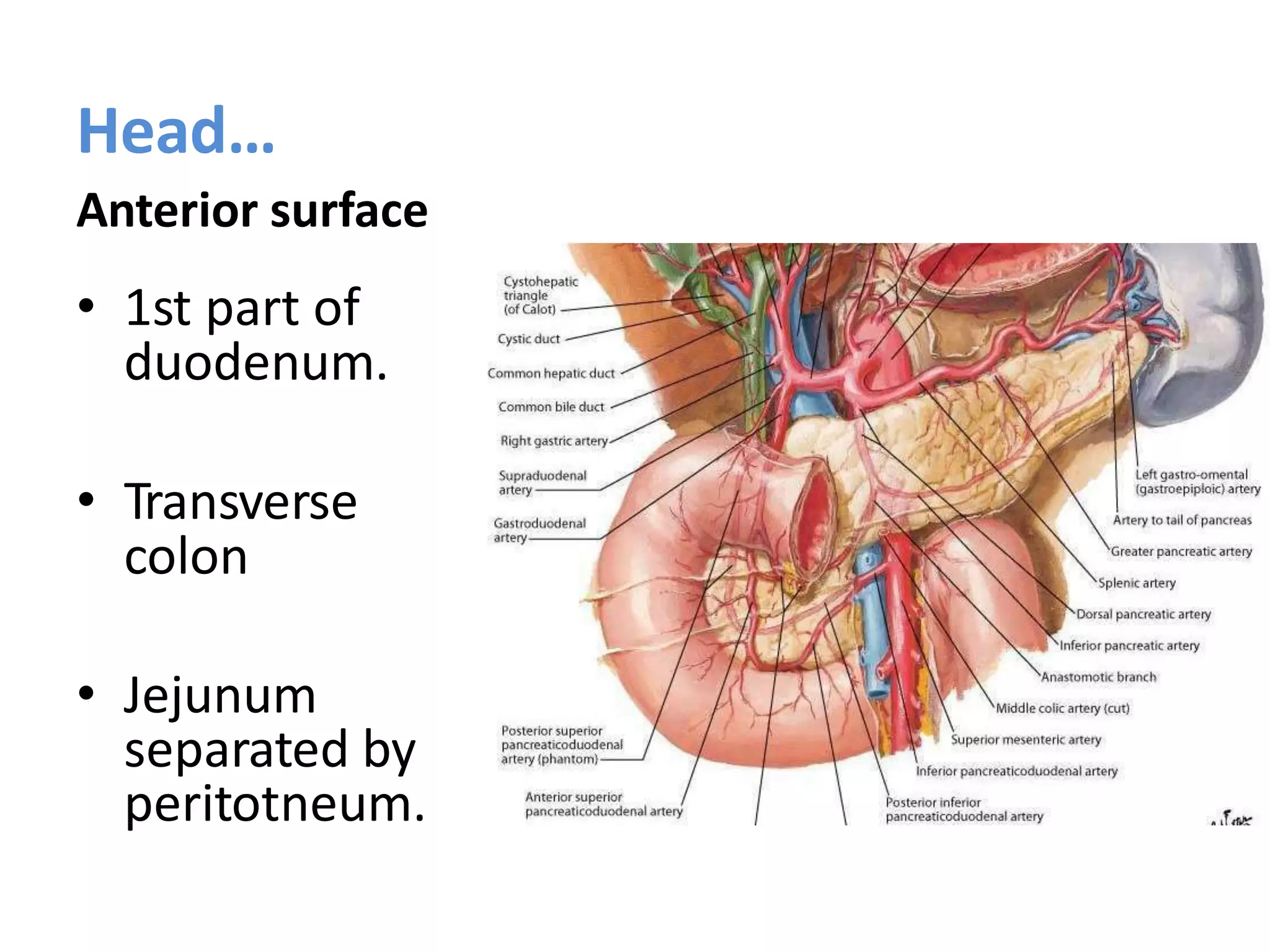
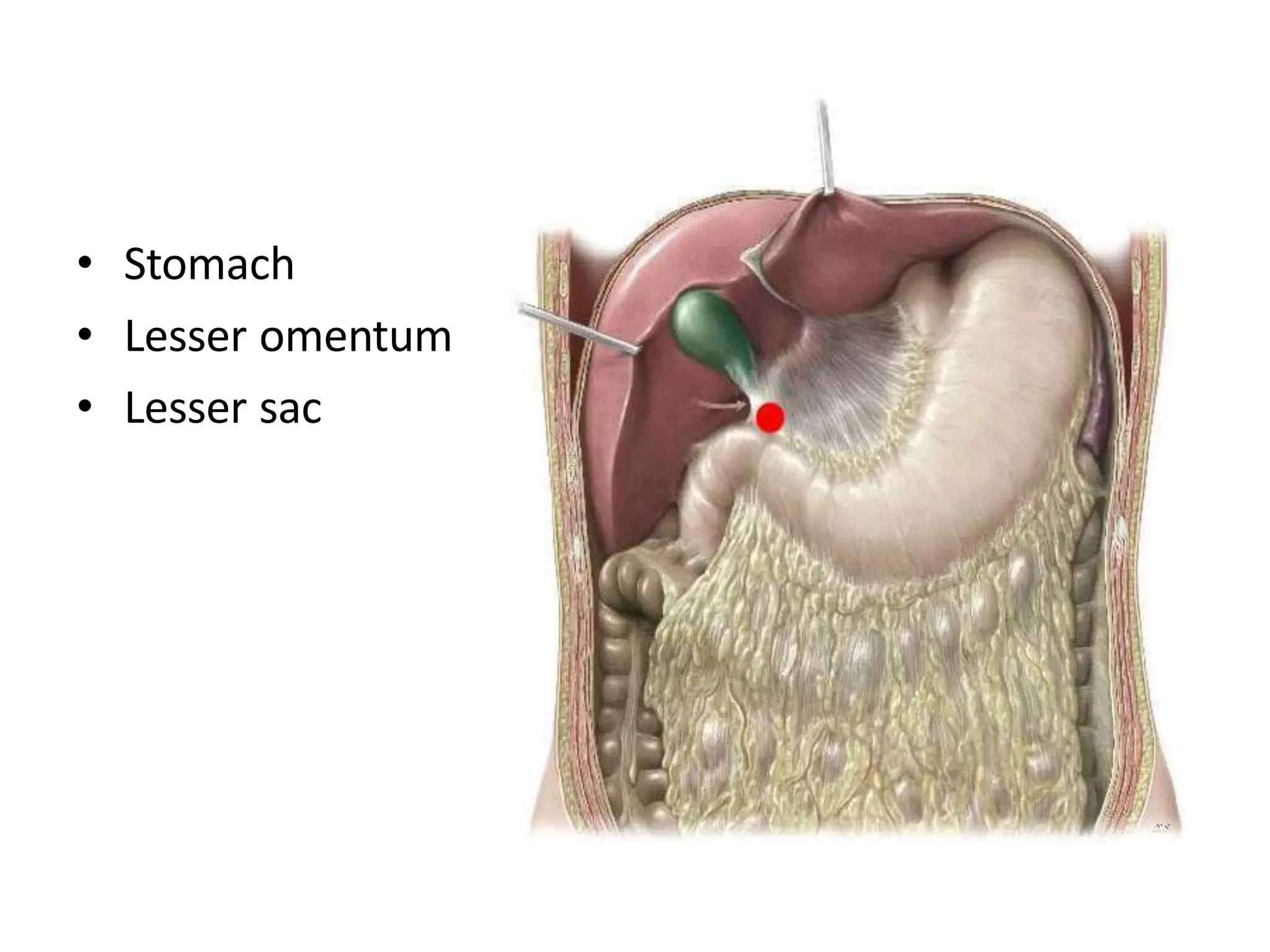
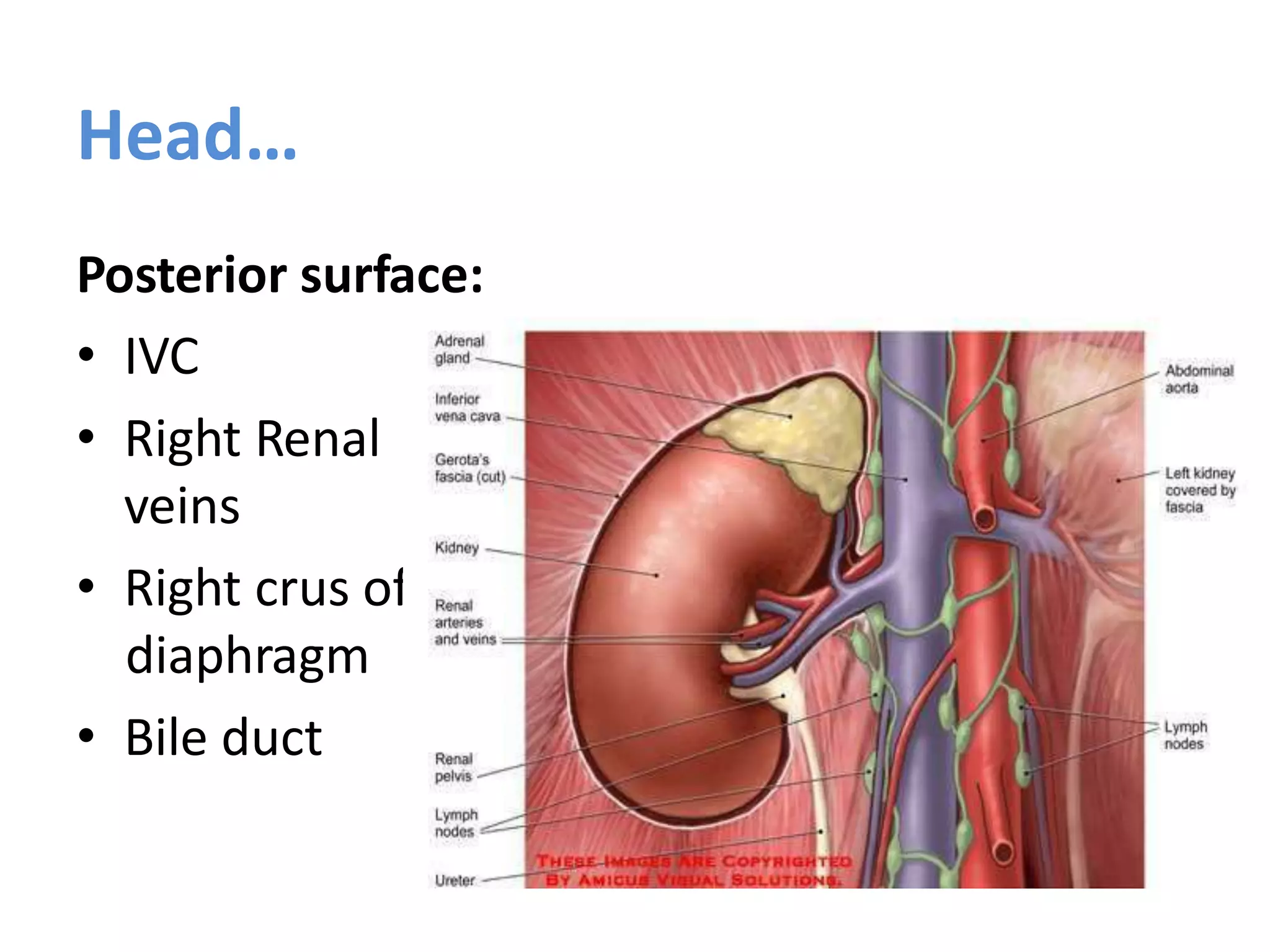
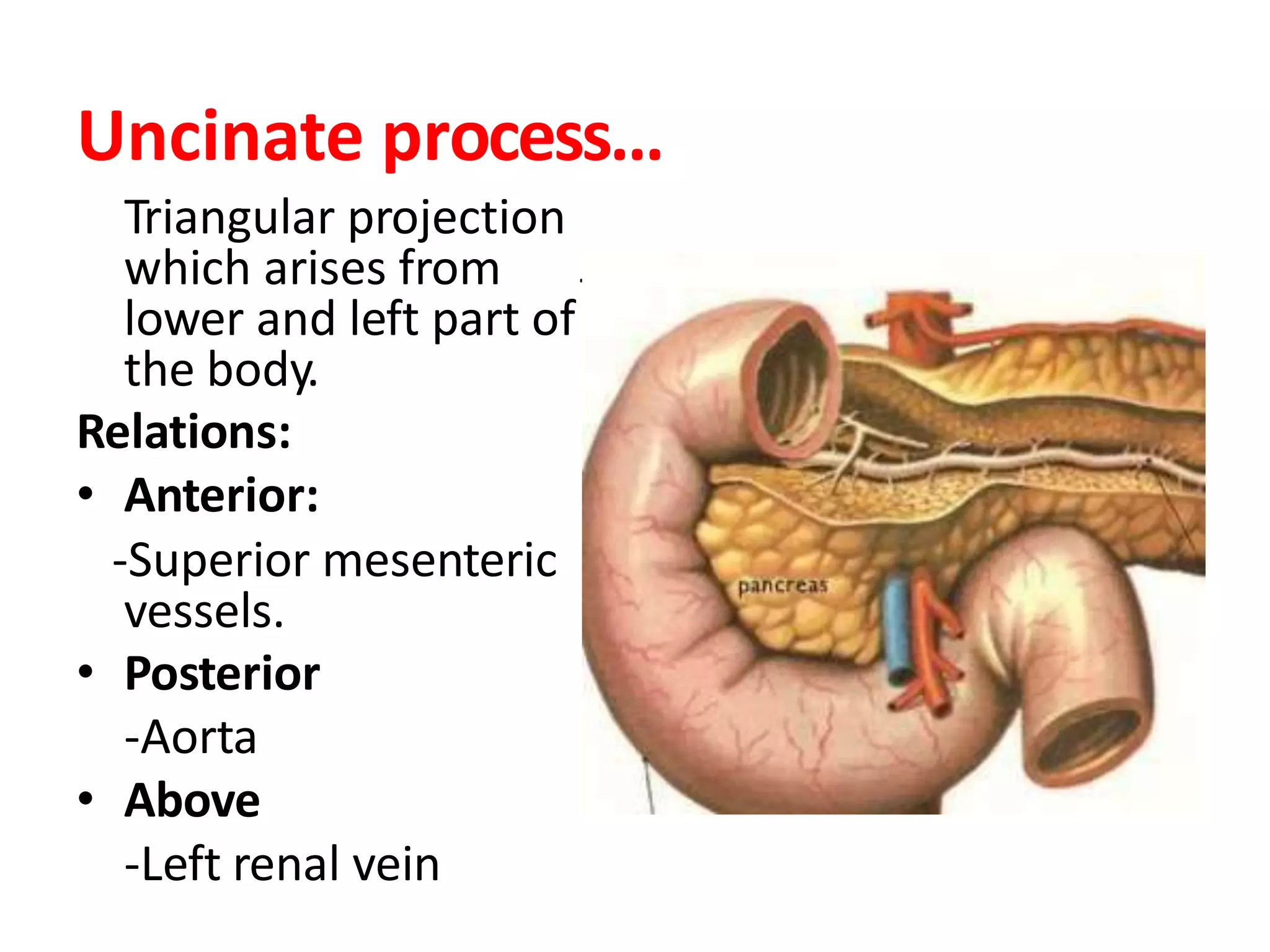
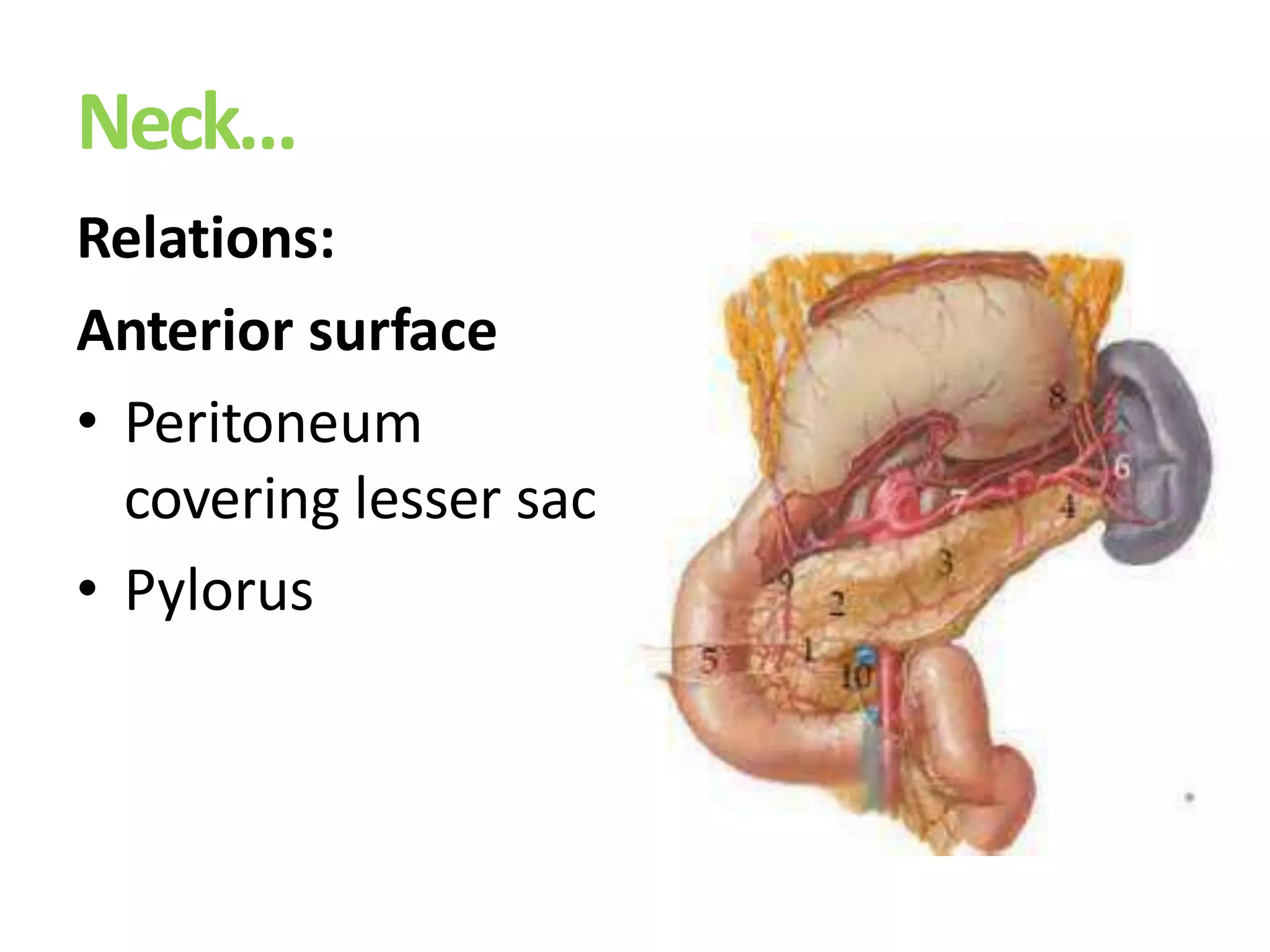
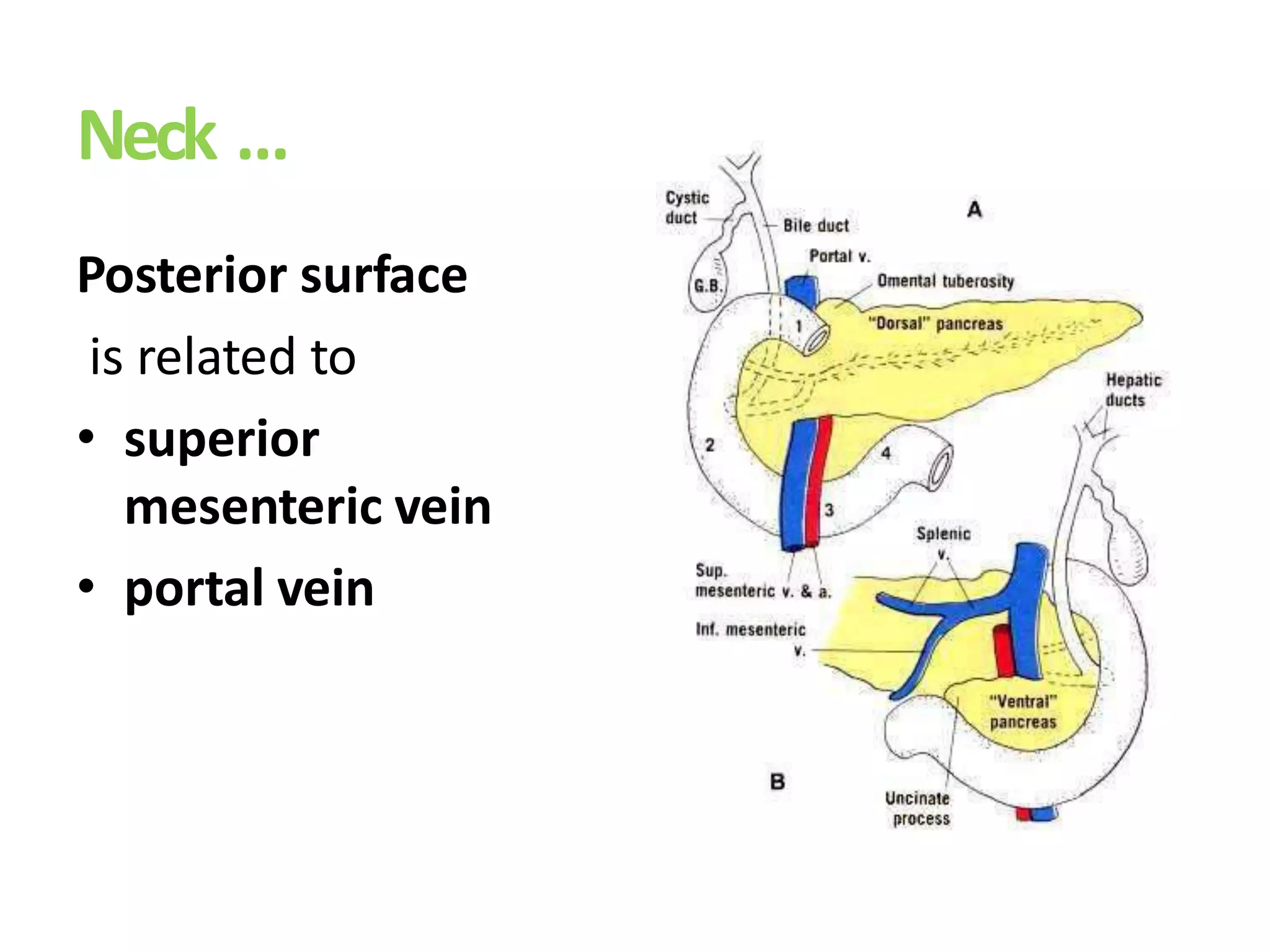
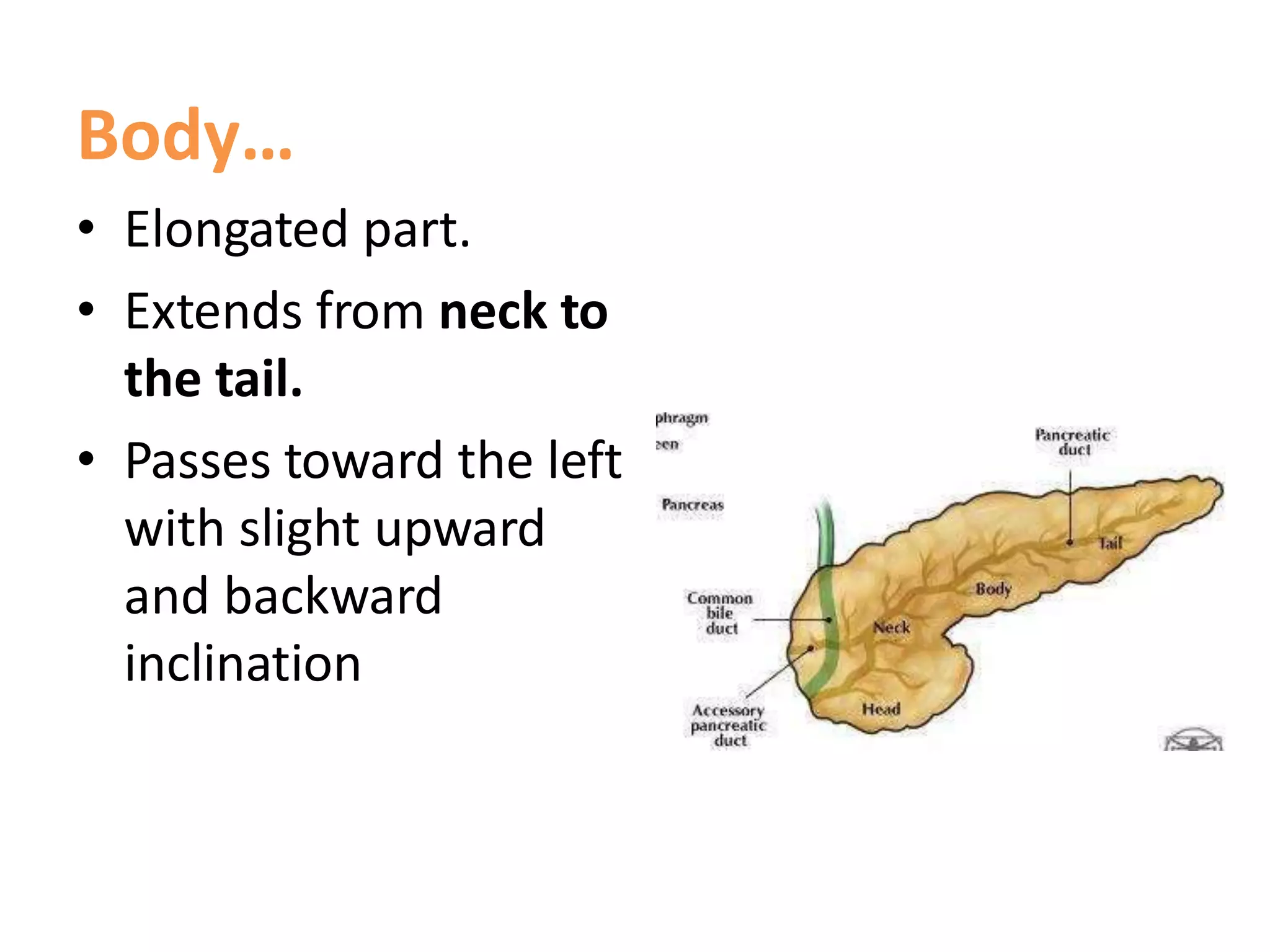
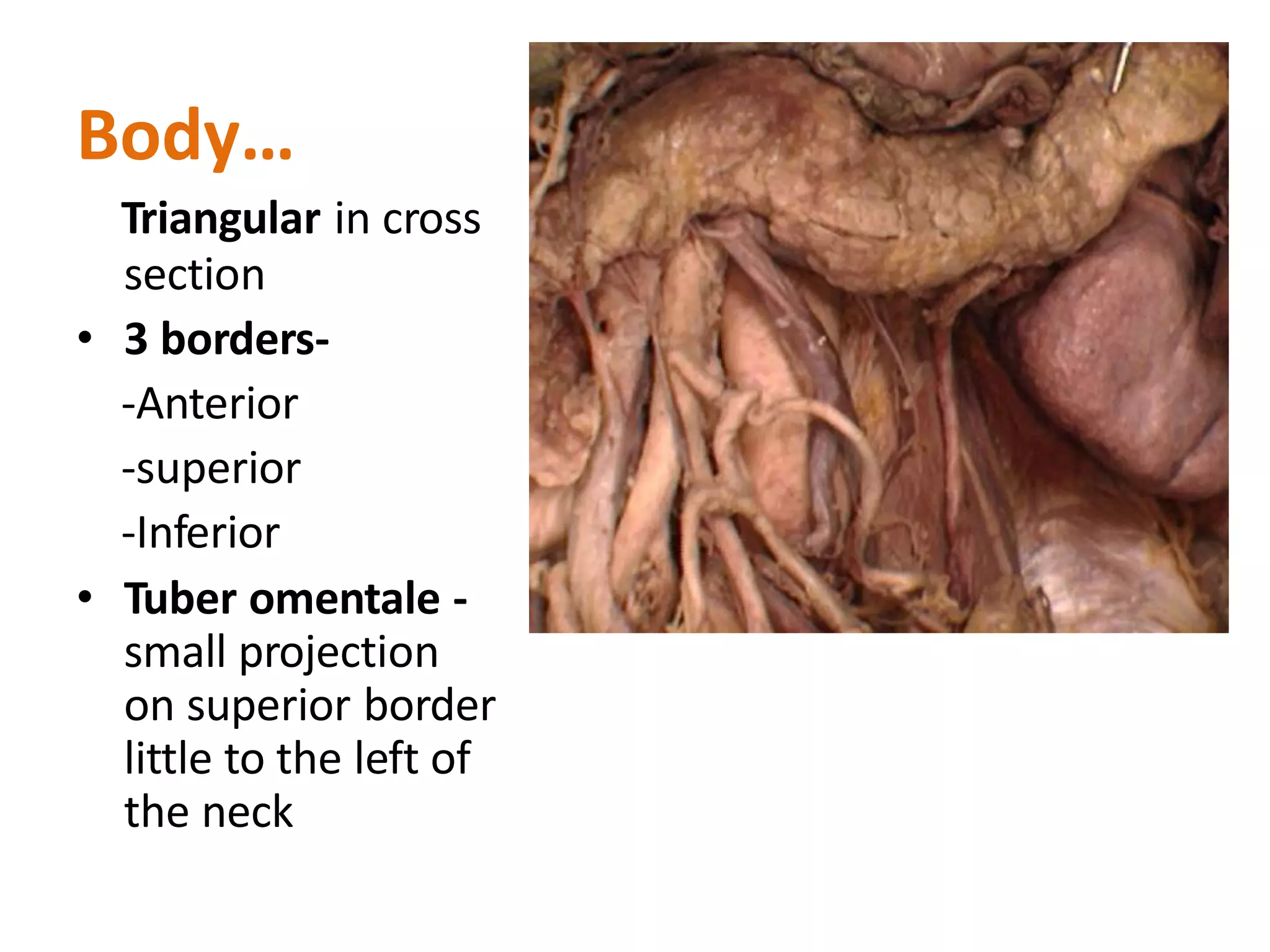
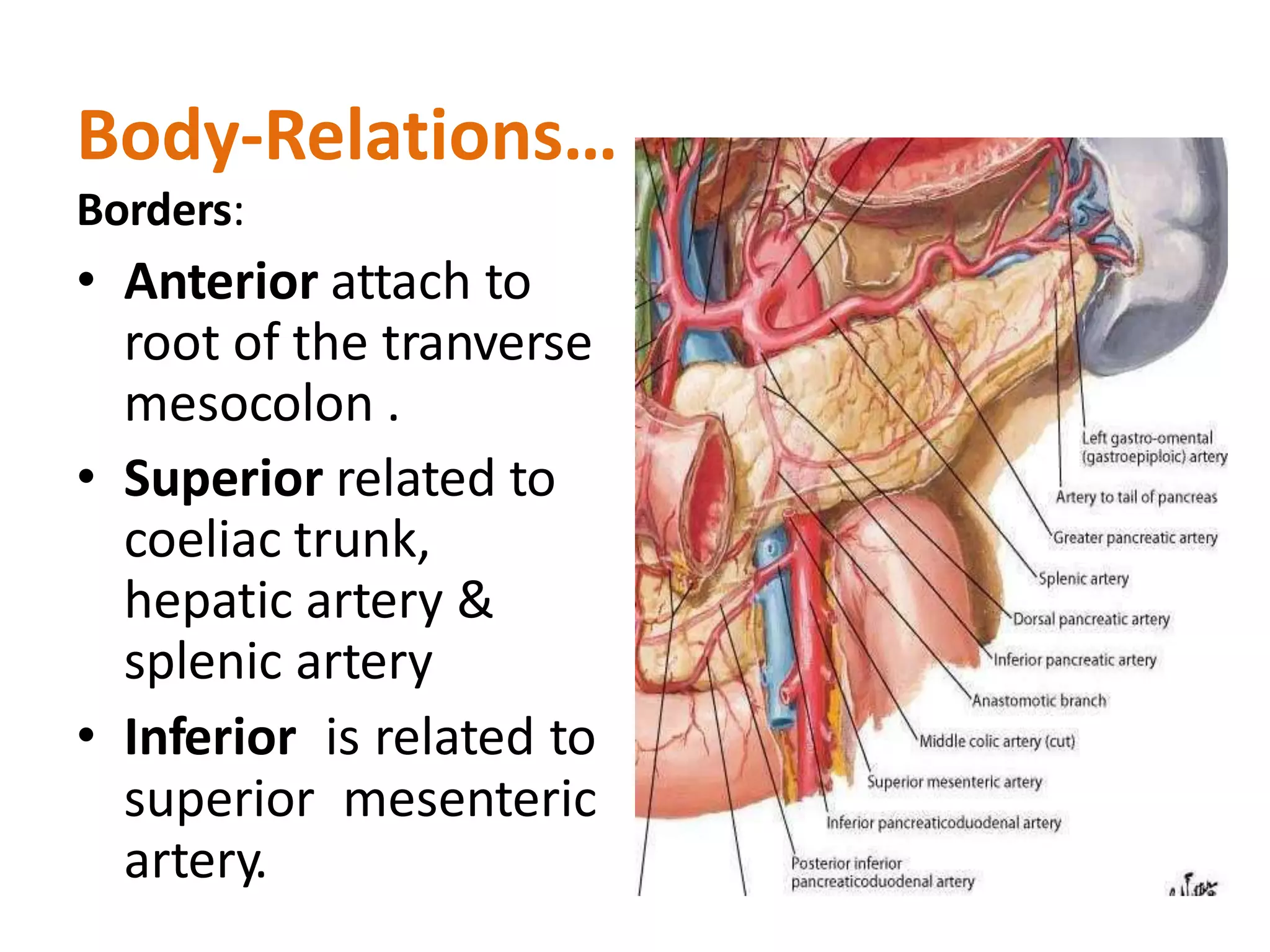
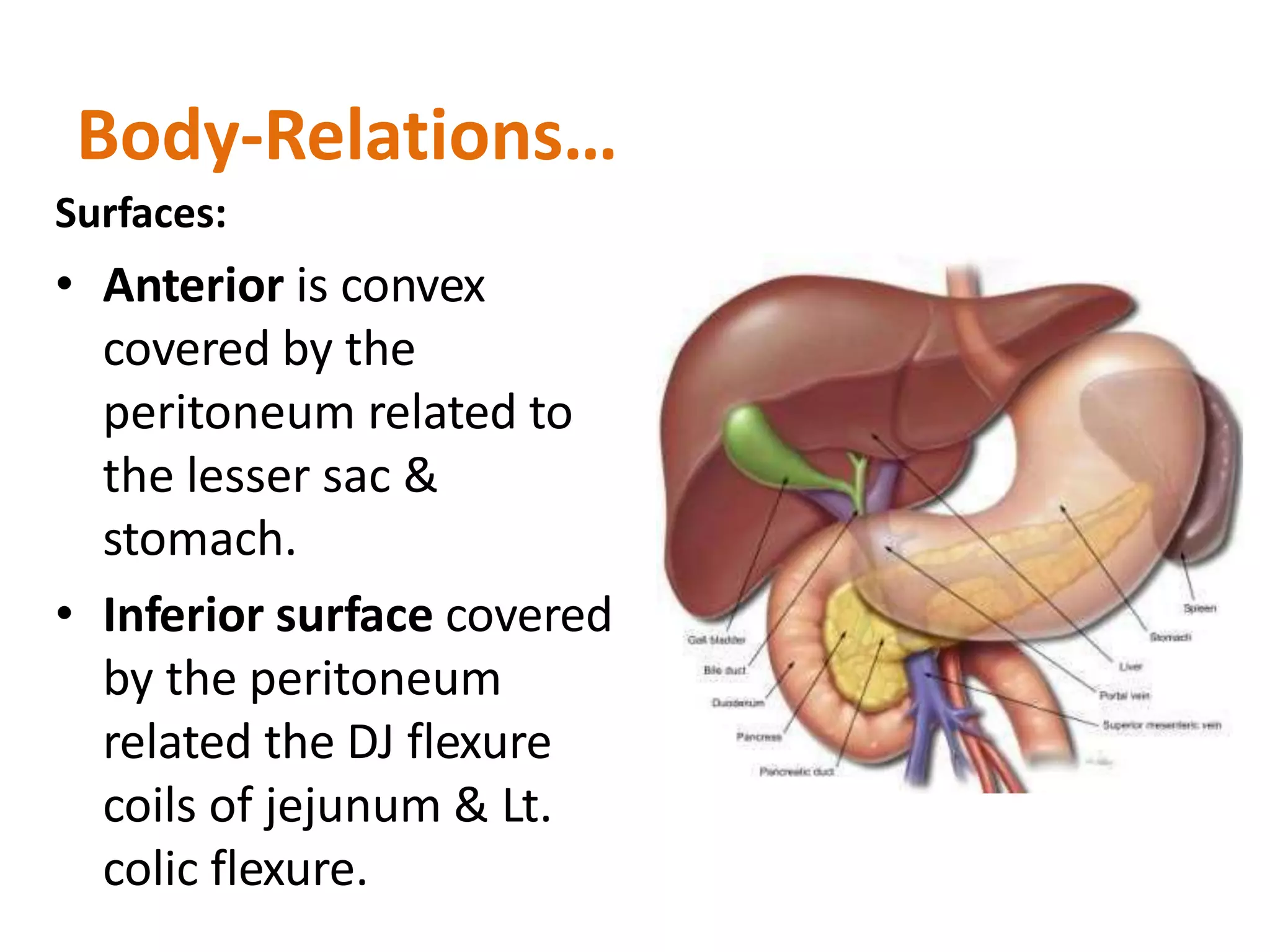
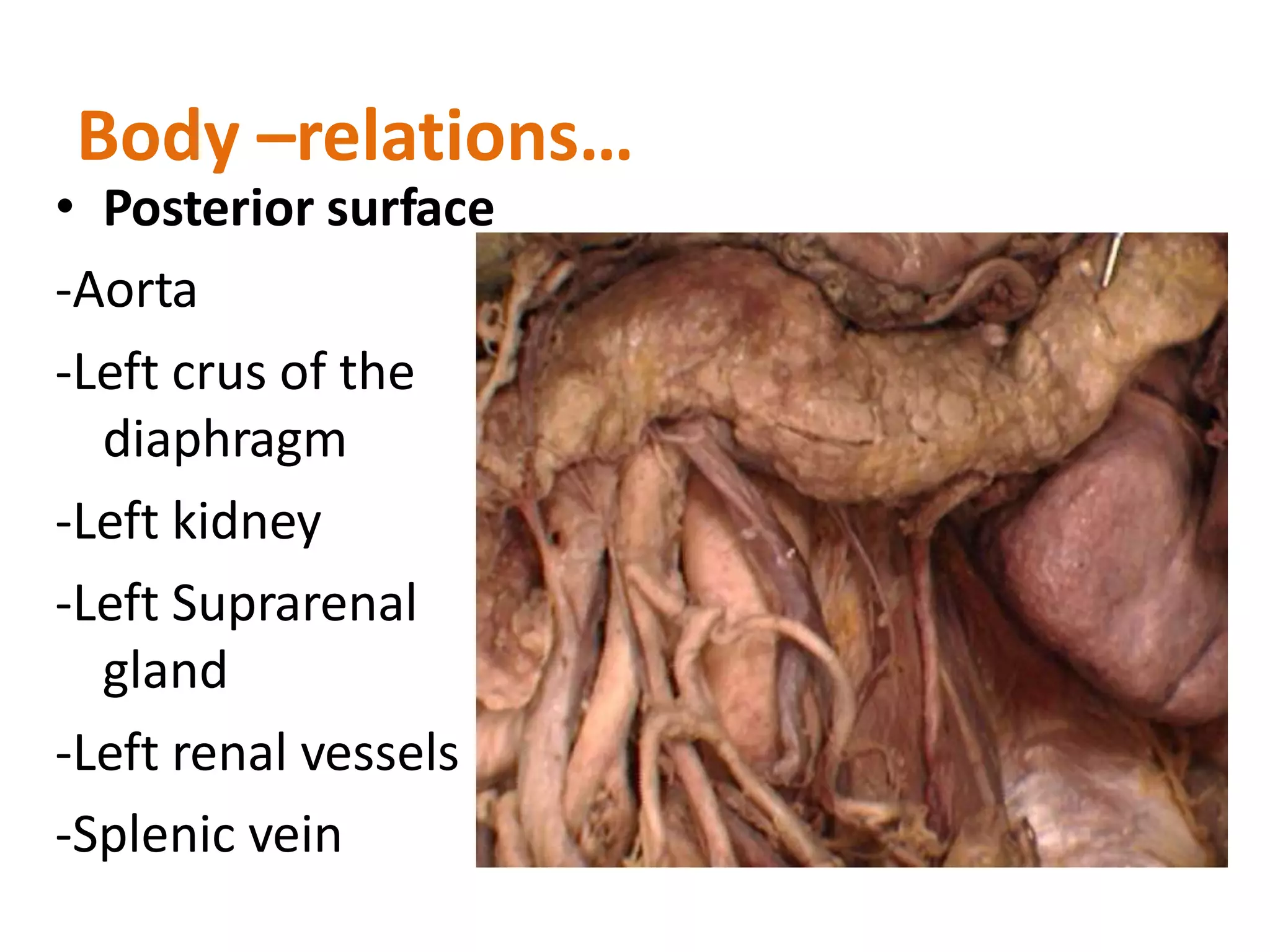
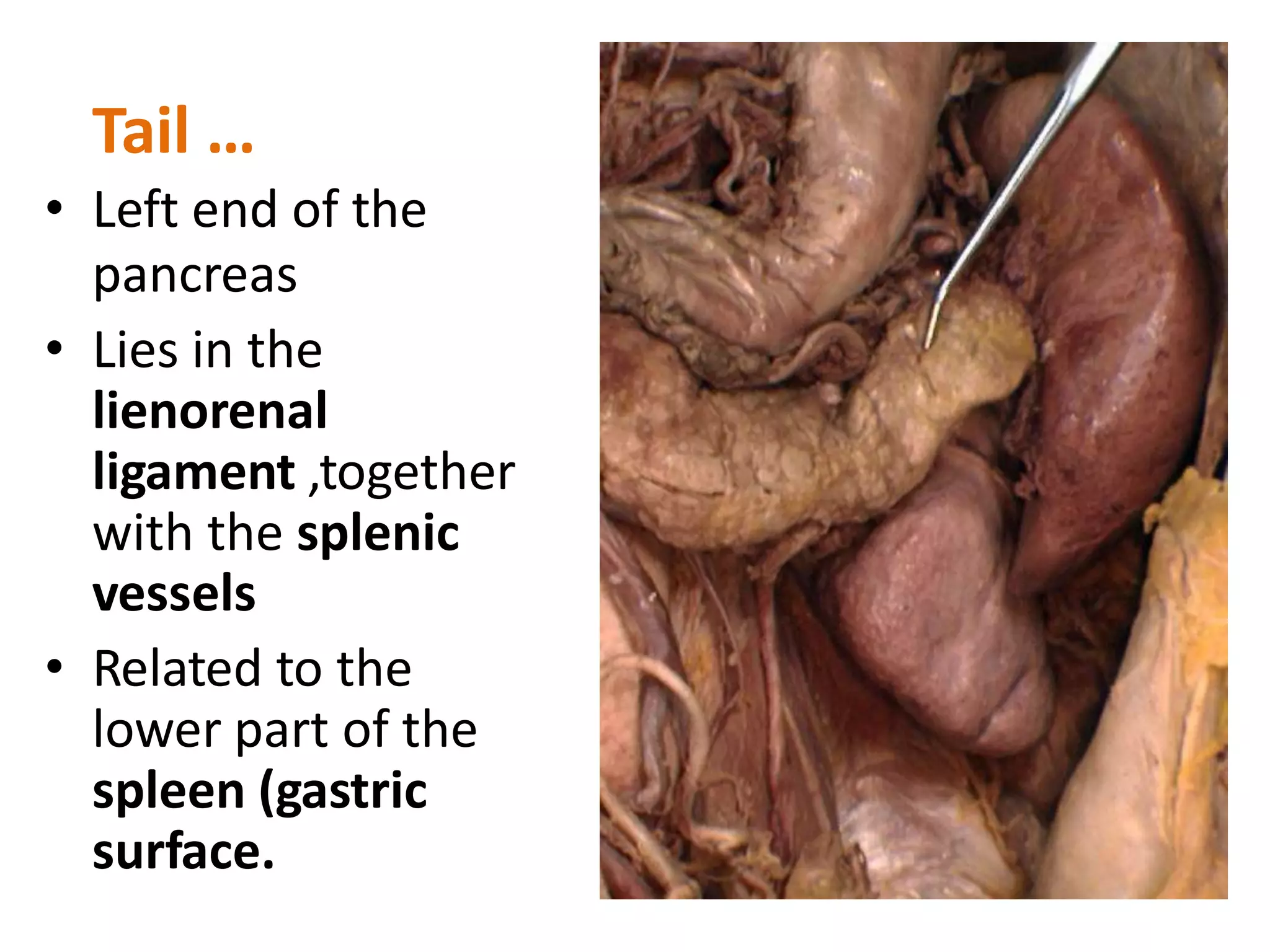
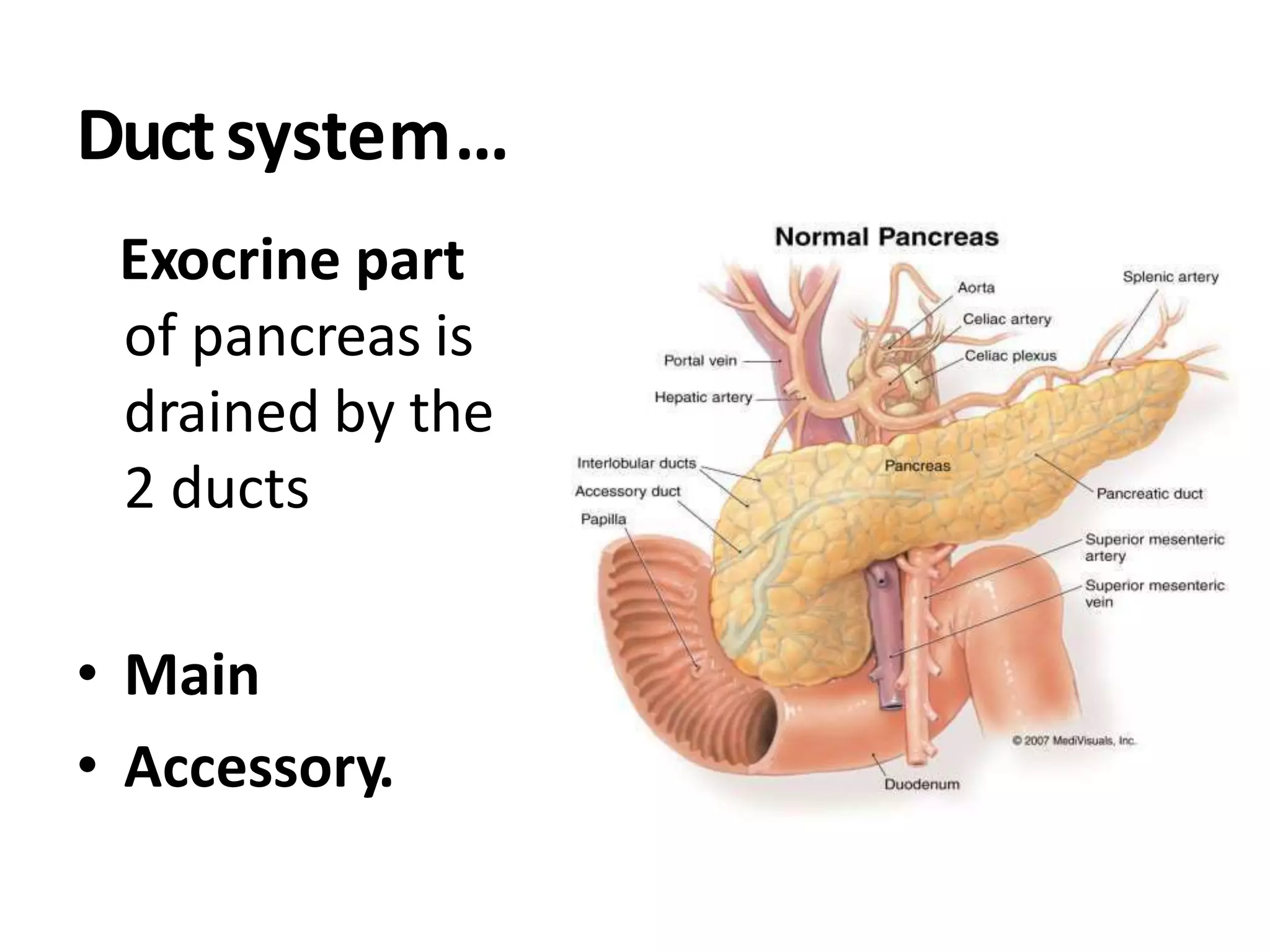
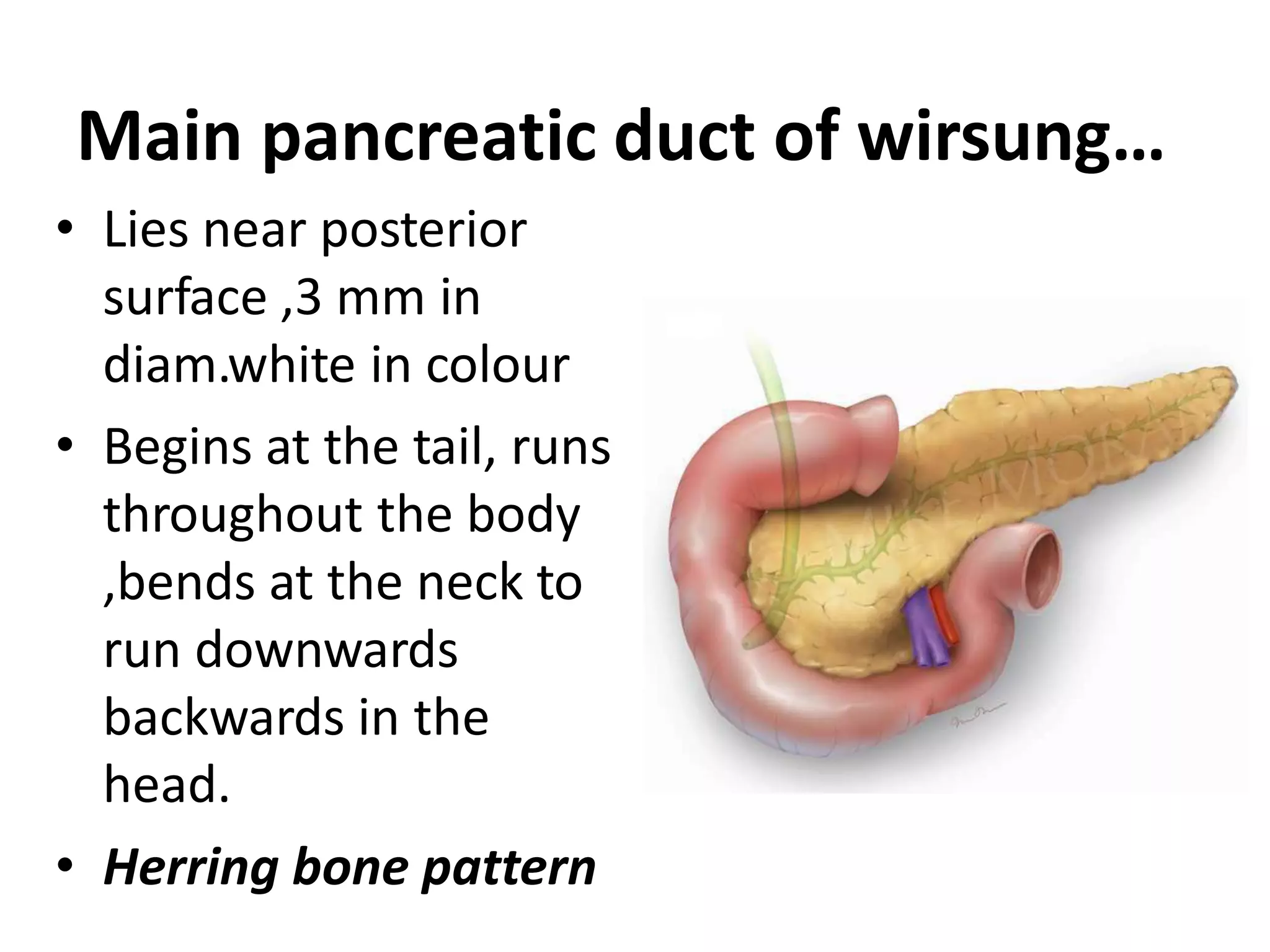
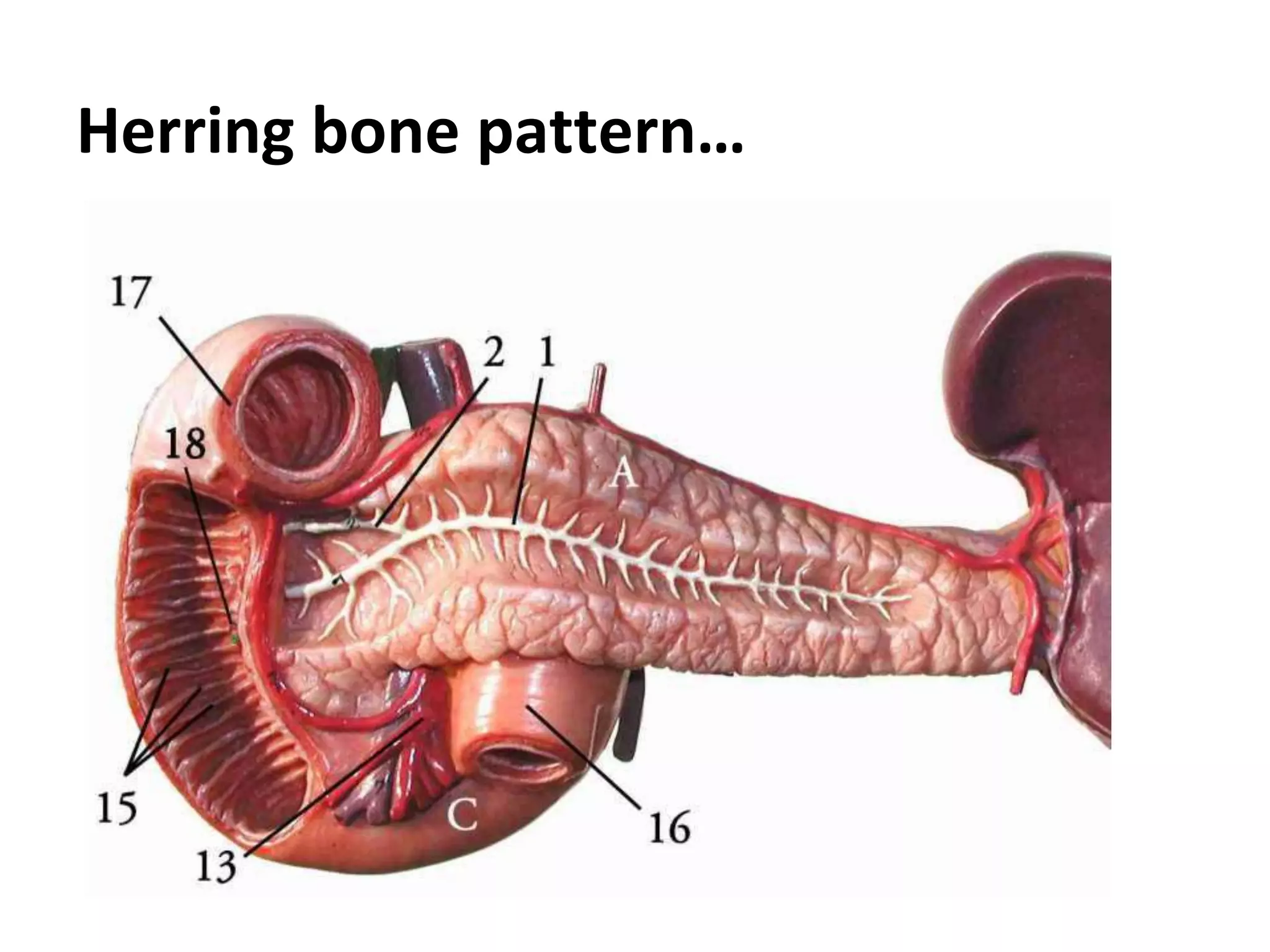
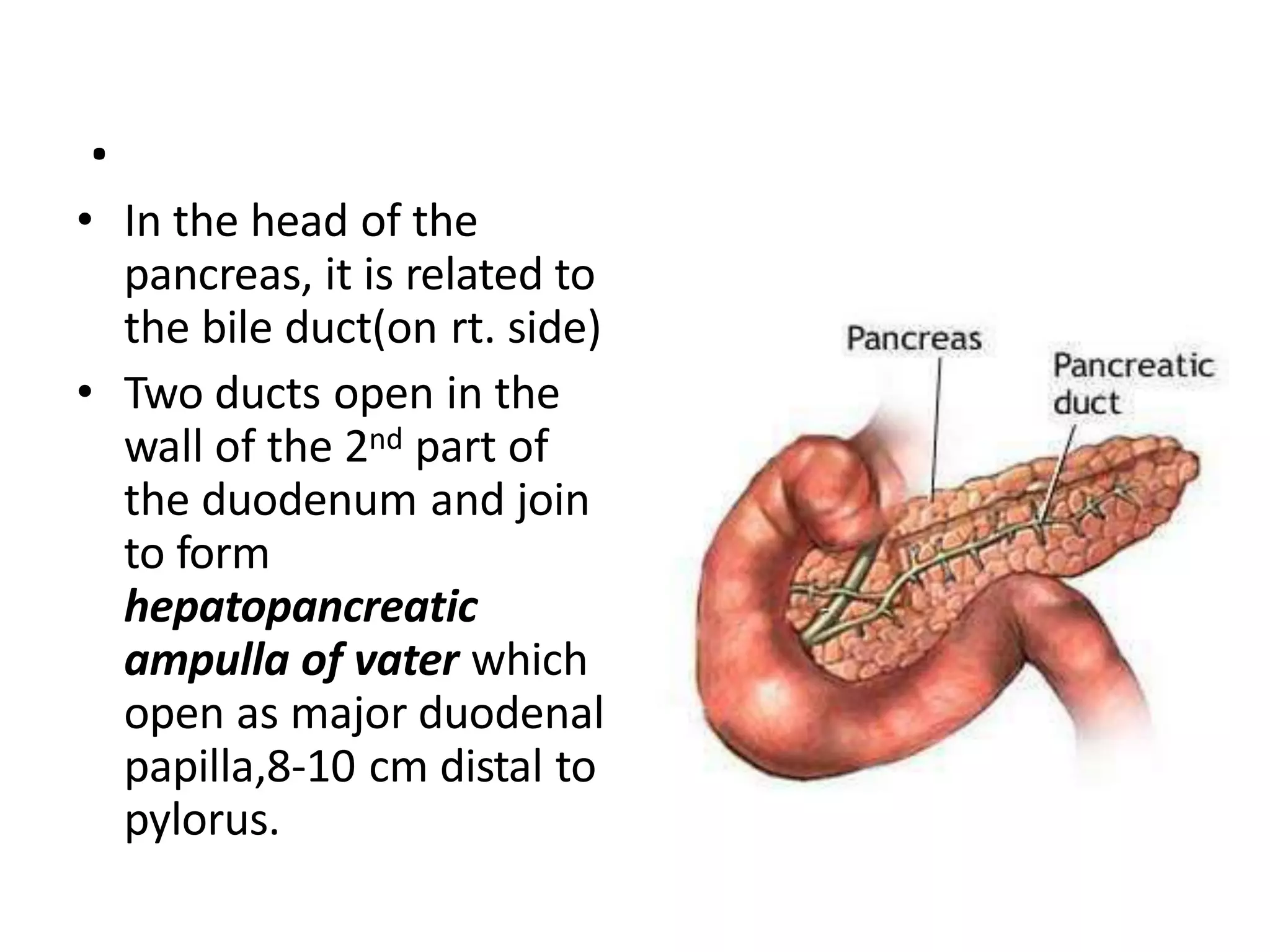
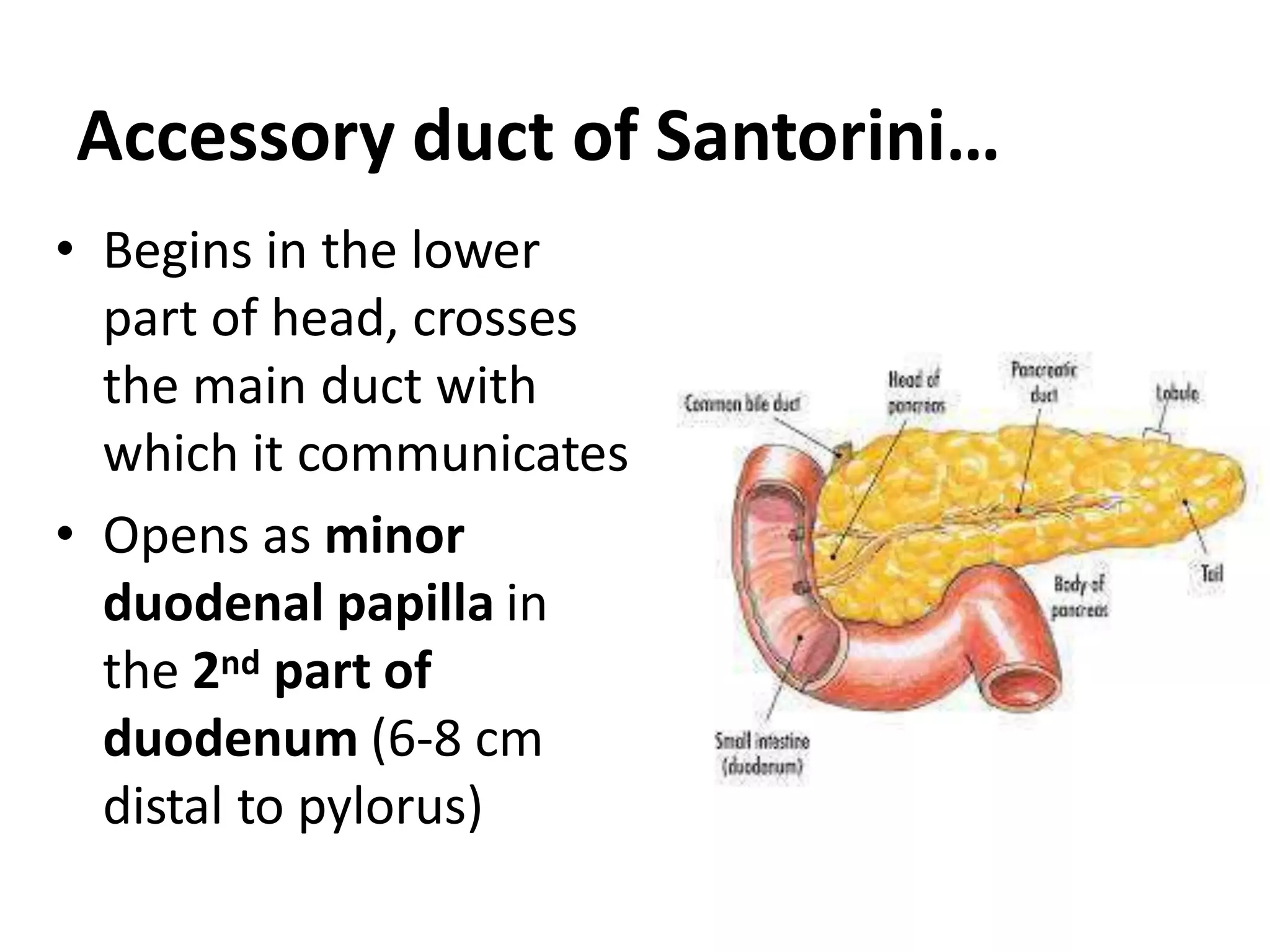
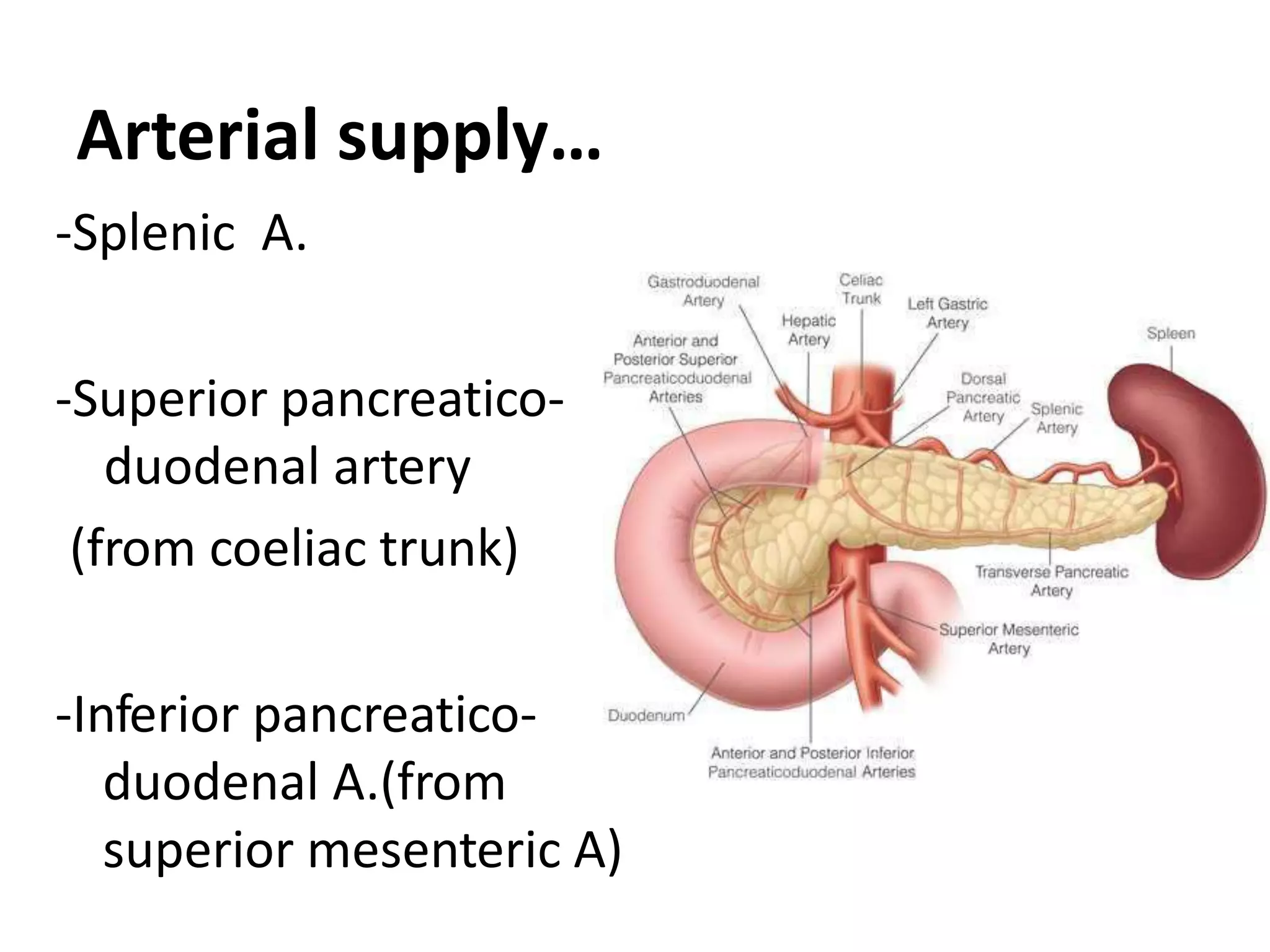
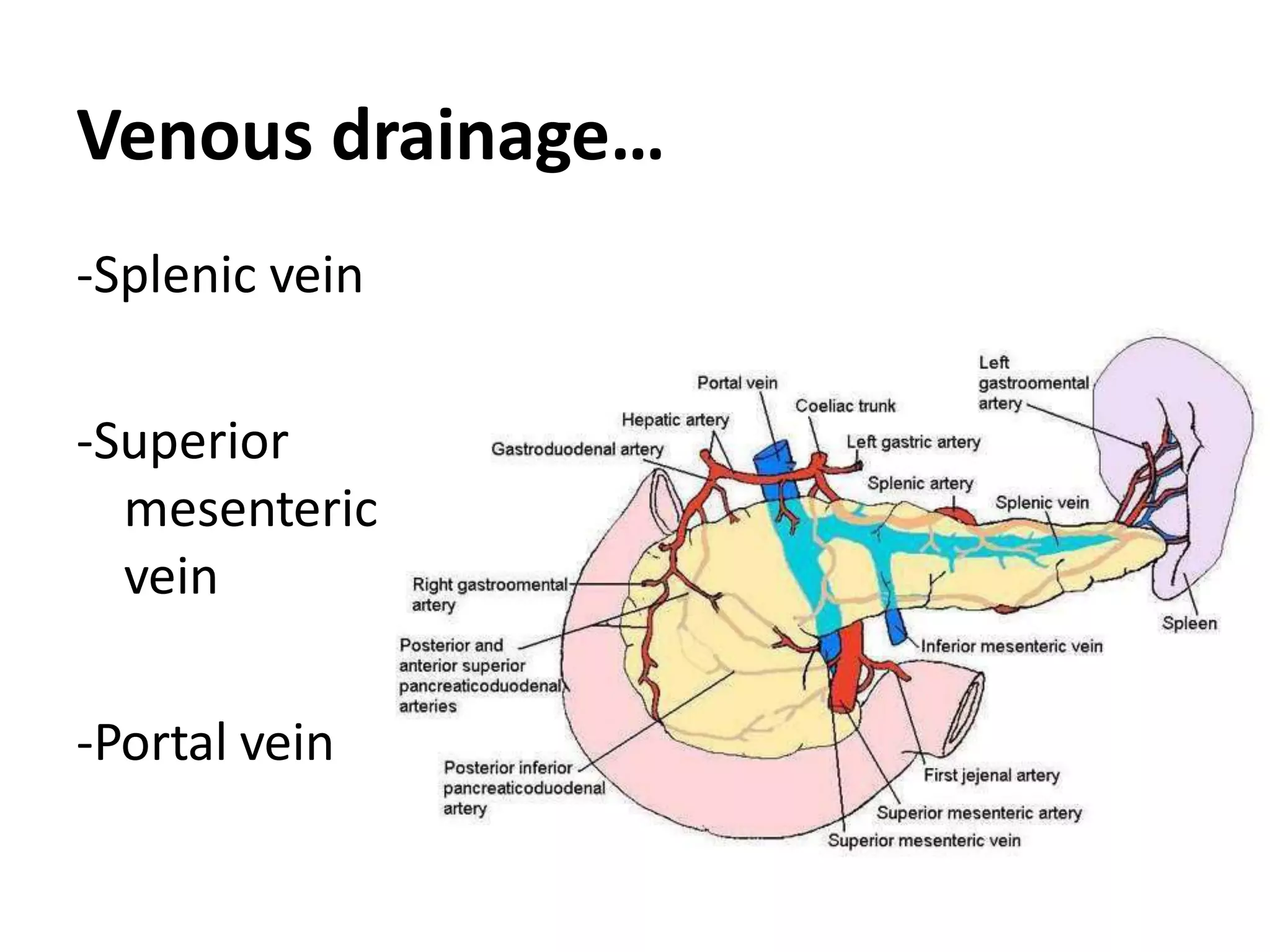
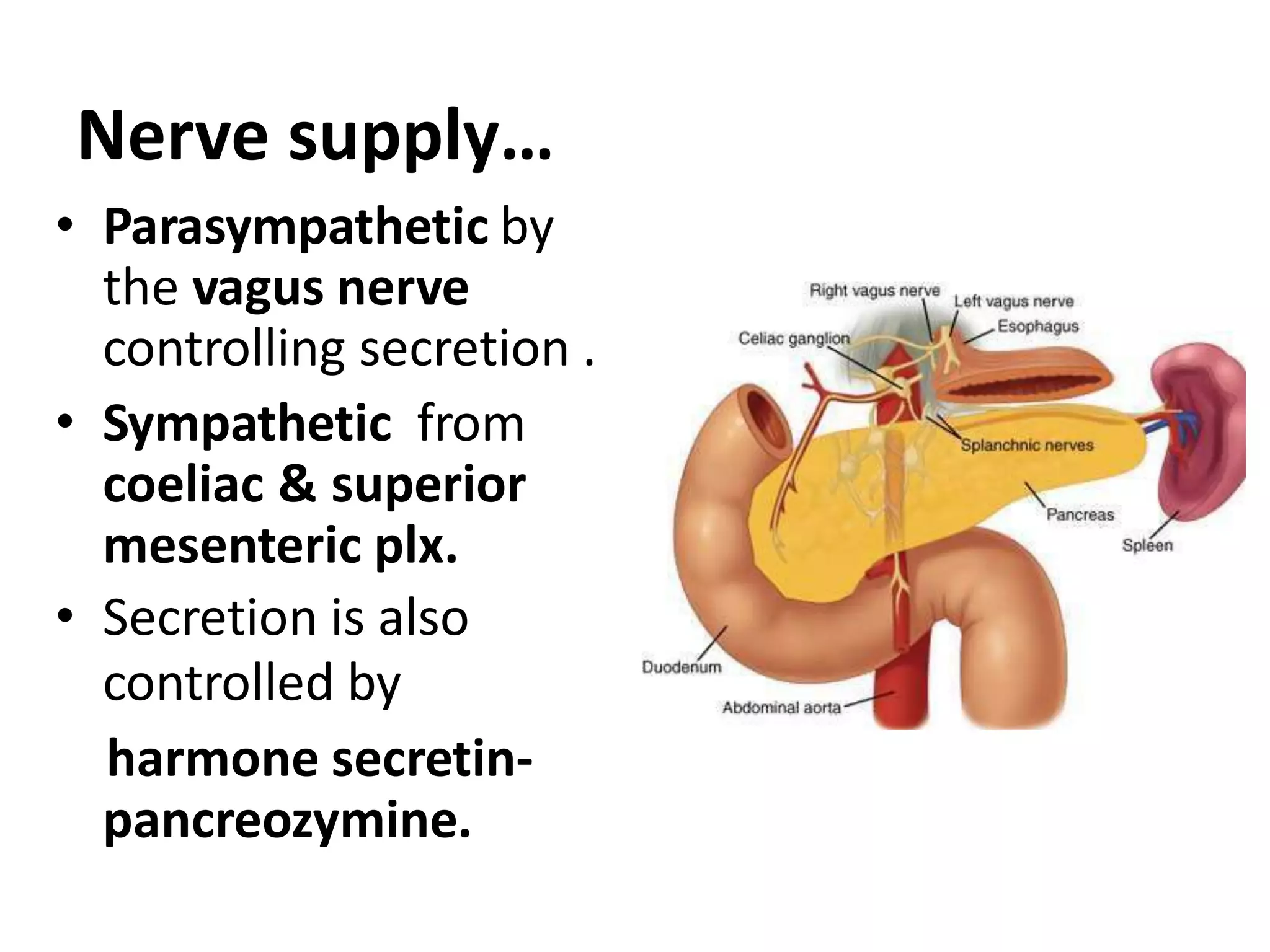
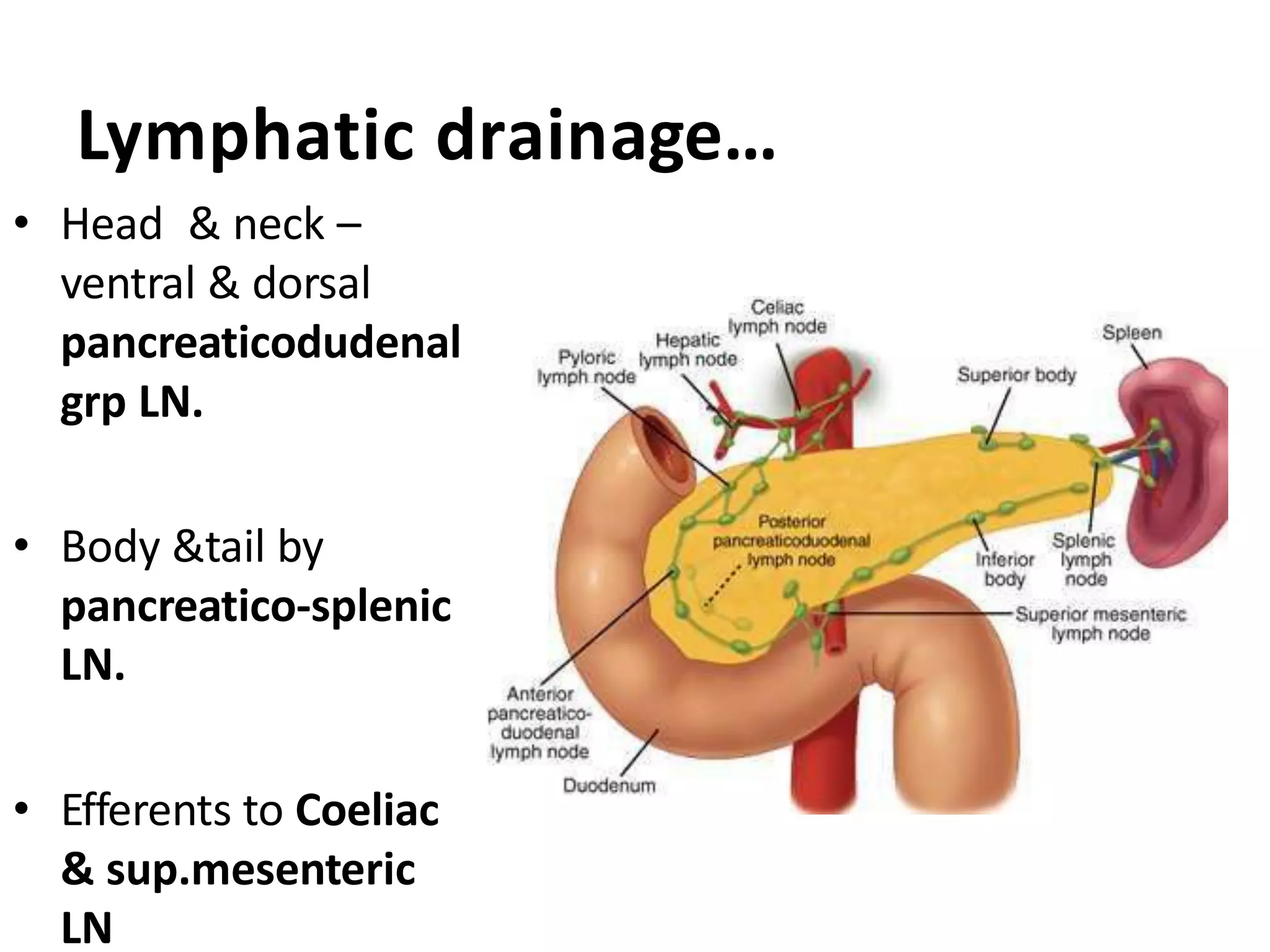
The pancreas develops from dorsal and ventral buds originating in the duodenum. During development, the ventral bud rotates posteriorly to fuse with the dorsal bud. The pancreas is located behind the stomach and has both exocrine and endocrine functions. It has a head, neck, body and tail. The main pancreatic duct drains the exocrine pancreas and opens at the major duodenal papilla along with the common bile duct. Developmental anomalies include pancreatic divisum, annular pancreas, ectopic pancreas, agenesis/hypoplasia, and accessory pancreatic lobes.