This document discusses sequences and their limits. Some key points:
- A sequence is a list of numbers written in a definite order. It can be thought of as a function with domain the positive integers.
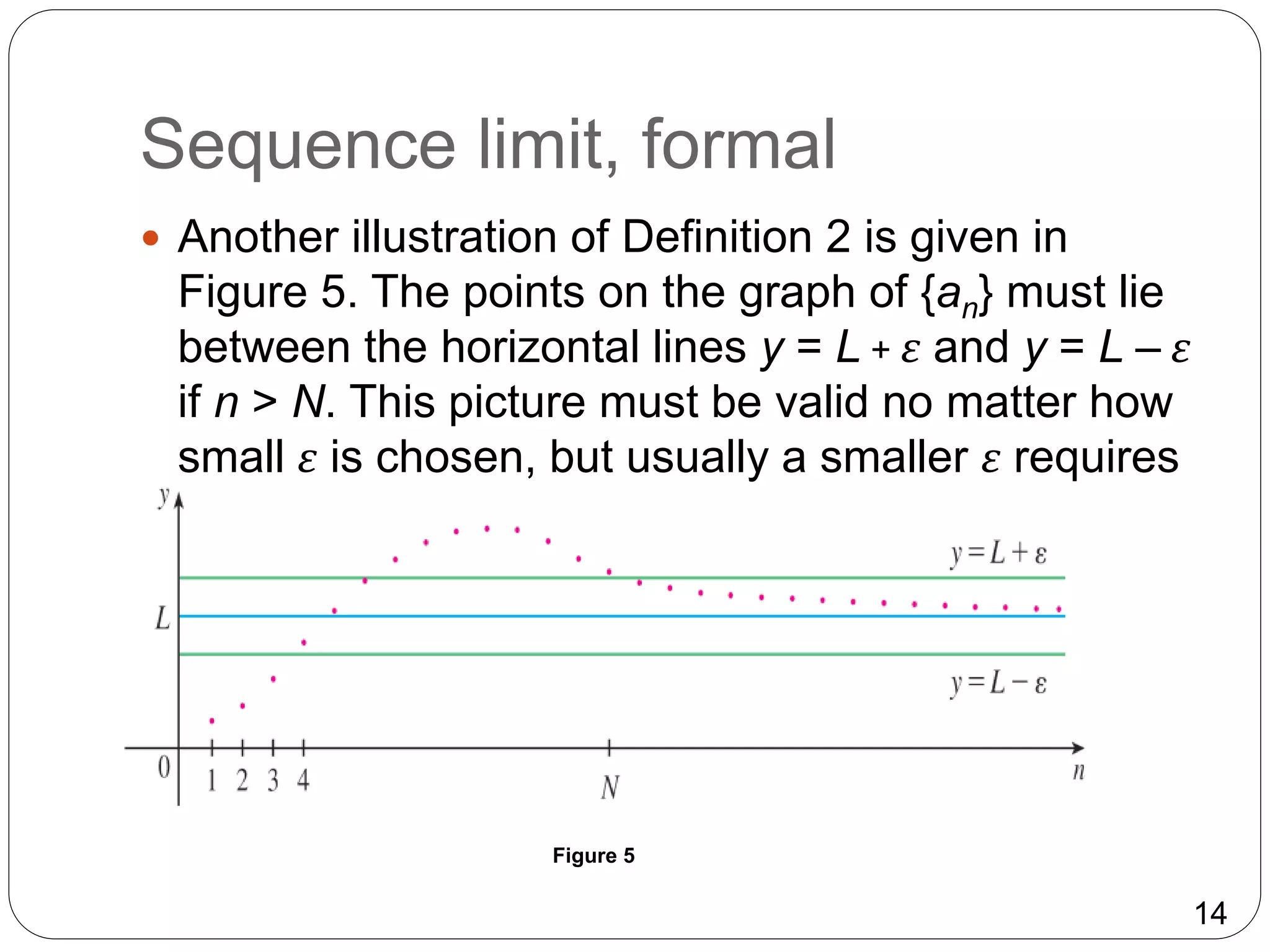
- The limit of a sequence is defined as the number L such that the terms of the sequence can be made arbitrarily close to L by choosing a sufficiently large term.
- A sequence converges if it has a finite limit, and diverges if its terms approach infinity. Bounded monotonic sequences are guaranteed to converge.
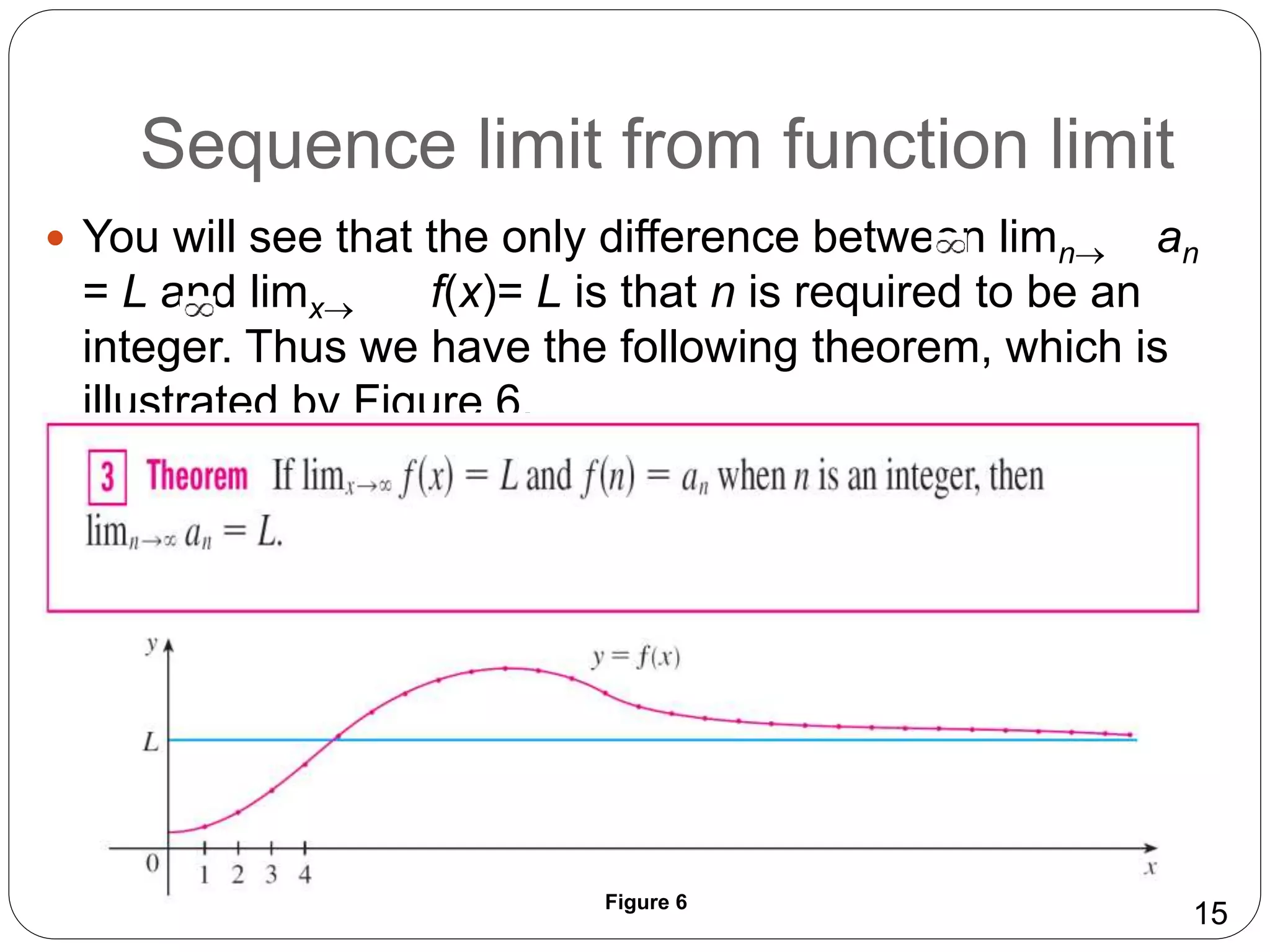
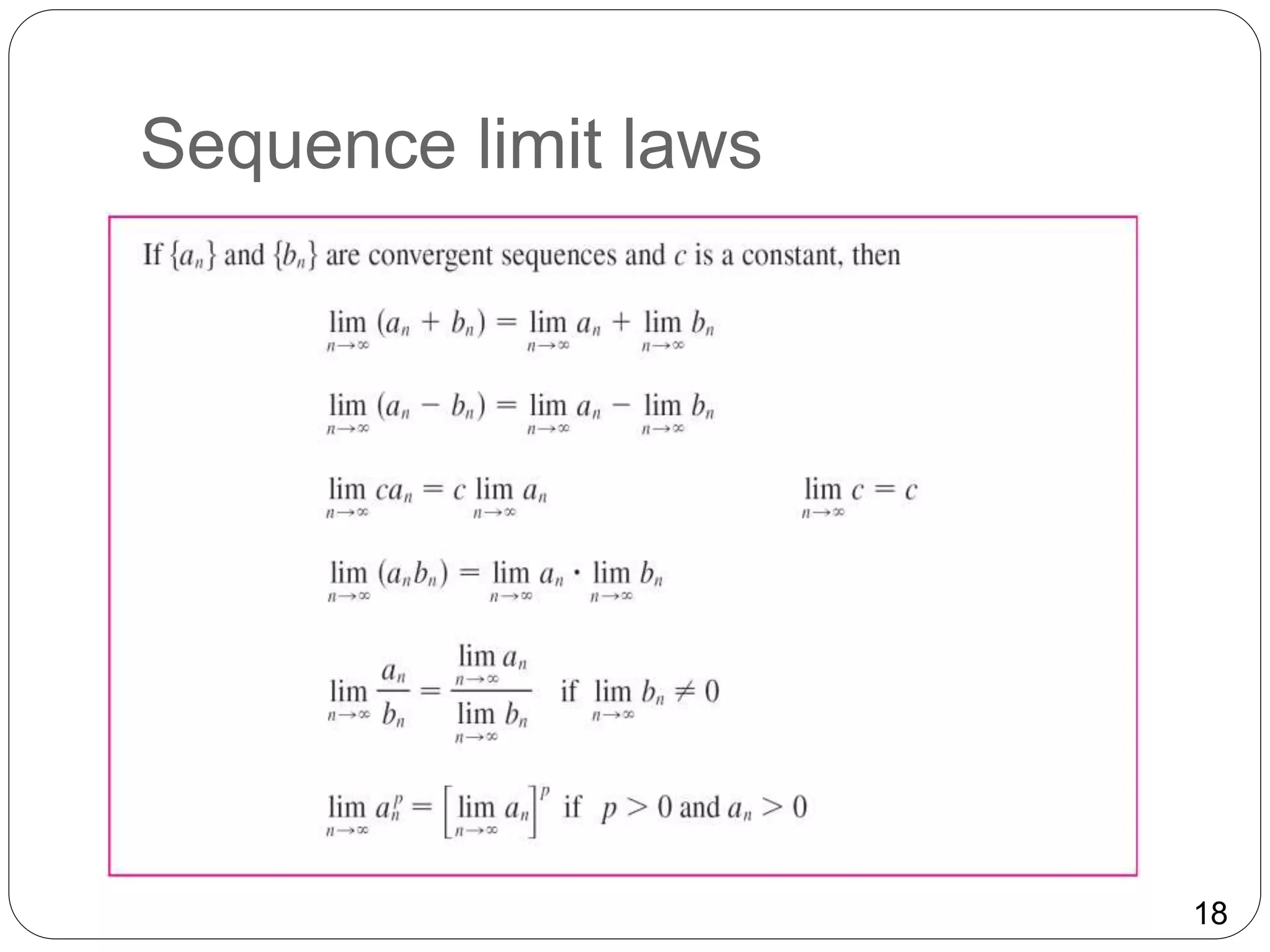
- Properties of sequence limits parallel those of limits of functions, including laws of limits and the ability to pass limits inside continuous functions.


















![25
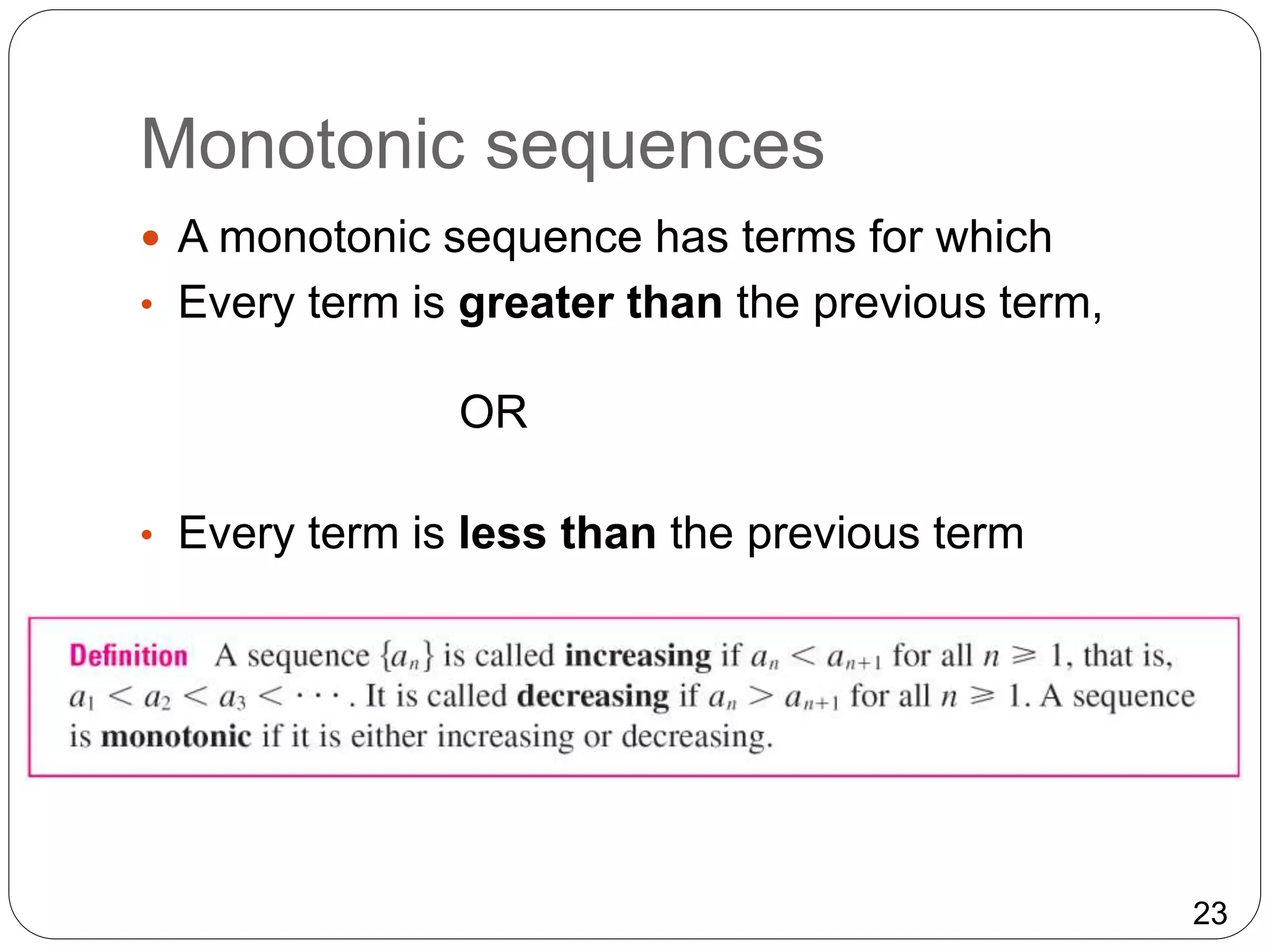
Bounded monotonic sequences
We know that not every bounded sequence is
convergent [for instance, the sequence an = (–1)n
satisfies –1 an 1 but is divergent,] and not
every monotonic sequence is convergent (an = n
).
But if a sequence is both bounded and
monotonic, then it must be convergent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iib-191030041635/75/Sequences-and-Series-25-2048.jpg)

