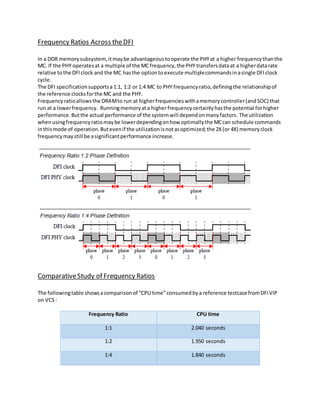
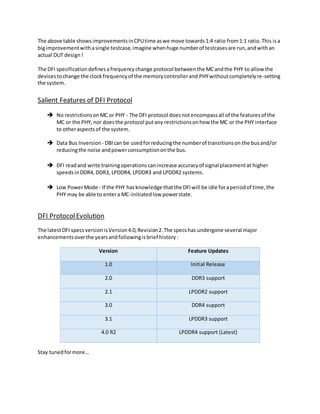
The DDR PHY Interface (DFI) defines the signals, timing parameters, and programmable parameters required to transfer control information and data between the memory controller (MC), PHY, and DRAM devices. DFI allows MC and PHY IP cores developed by different companies to interoperate. It also provides a standardized interface for MC and PHY designs developed by different engineering groups within the same company. The DFI specification supports operating the PHY at higher frequencies than the MC, up to 4x, to enable higher DRAM frequencies and potential performance improvements for the system.