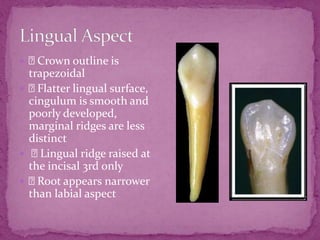
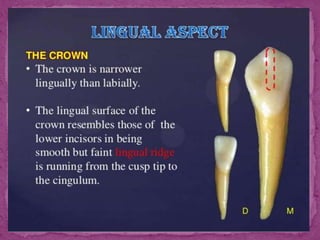
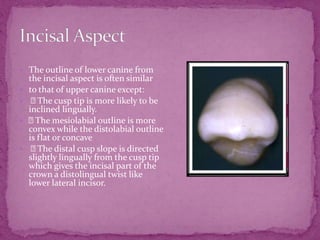
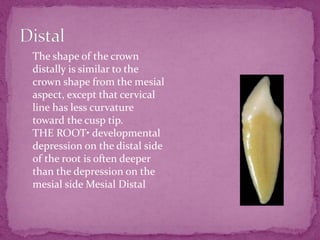
This document describes the anatomical features of lower canine teeth. It notes that lower canines have a narrower crown than upper canines, with variations including bifurcated roots. The crown outline is trapezoidal with mesiodistal dimensions less than upper canines. Contact areas are near the incisal angle mesially and distal junction of middle and incisal thirds distally. The root is shorter than upper canines by 1-2mm with a more sharply pointed apex. Lingual surfaces are flatter with a smooth, poorly developed cingulum and less distinct marginal ridges.