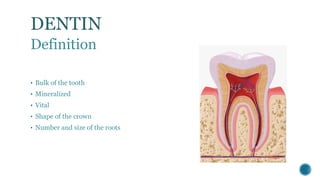
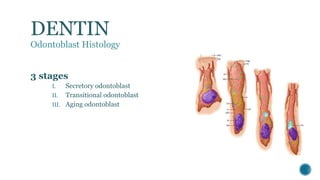
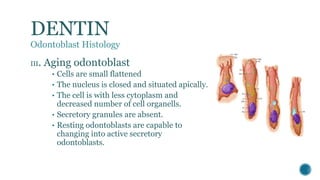
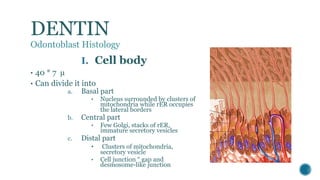
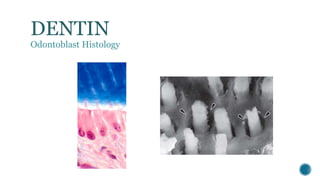
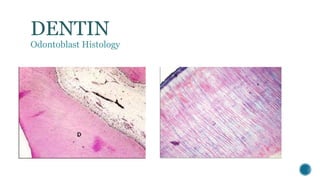
The document provides a detailed overview of dentin, covering its definition, properties (physical and chemical), and formation through odontoblast differentiation and histology. It discusses dentinogenesis, including matrix formation and mineralization, along with the structure and arrangement of dentinal tubules. Additionally, it highlights the differences between mantle dentin and circumpulpal dentin, including fiber types, thickness, and mineralization processes.