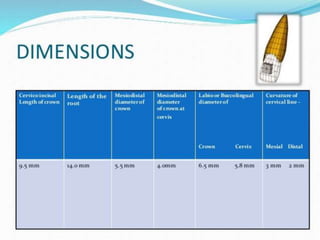
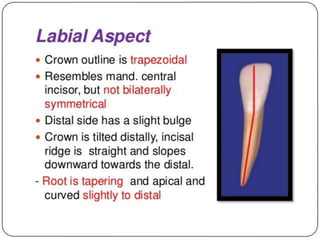
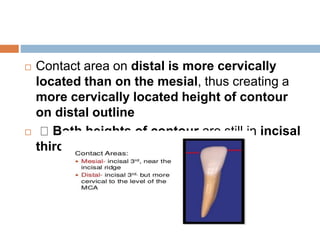
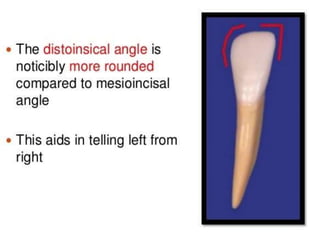
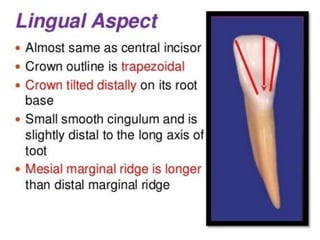
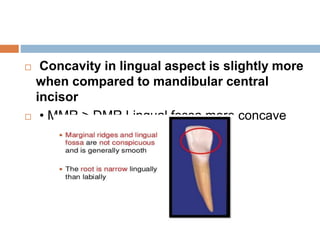
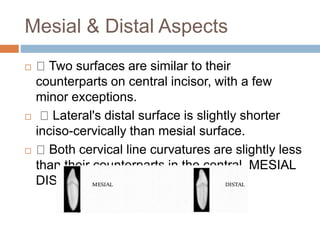
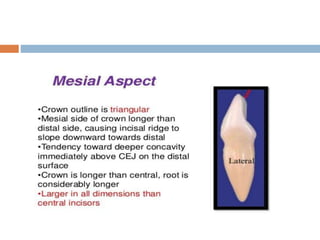
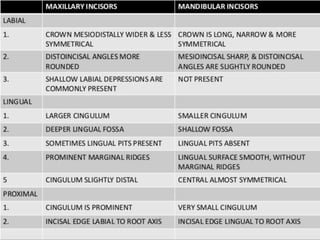
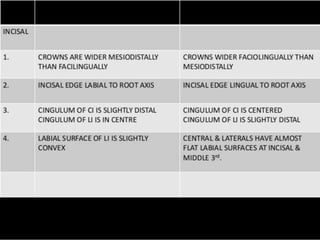
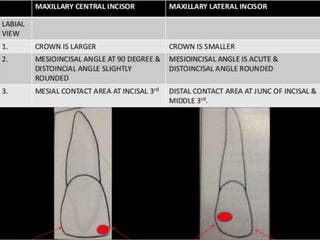
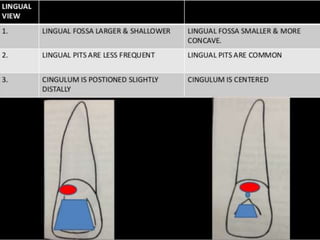
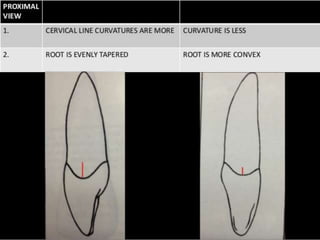
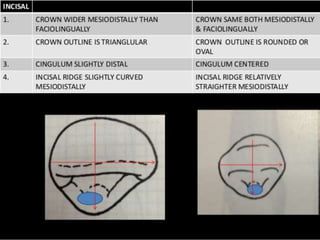
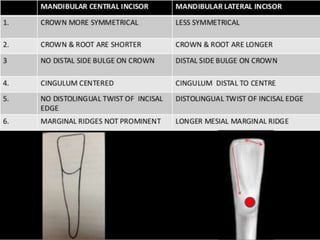
This document provides information about the mandibular lateral incisor tooth. It describes the anatomy and morphology of the mandibular lateral incisor, including its size, shape, root structure, and variations compared to the central incisor. Key details include that the lateral incisor is slightly wider than the central incisor, has a more rounded distoincisal angle, and a more cervically located height of contour and distal contact area. The document also discusses tooth numbering systems and the chronology of lateral incisor development.