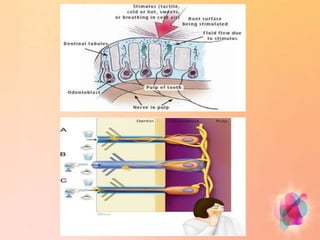
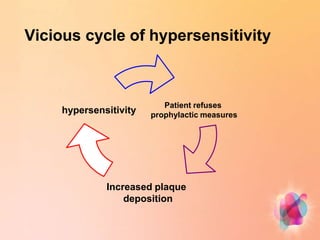
Dentin hypersensitivity is a common condition characterized by short, sharp pains in response to stimuli like hot, cold, sweet or acidic foods. It affects 14-98% of adults and is caused by exposure of dentin, usually due to gum recession. The hydrodynamic theory is the most accepted explanation, where stimuli cause rapid fluid movement in dentinal tubules, stimulating nerve fibers. Treatment focuses on blocking tubules with agents like potassium nitrate, strontium chloride or oxalate. Placement of restorations or periodontal procedures may also help. Patients are advised on controlling factors that exacerbate sensitivity.