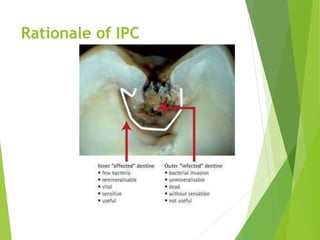
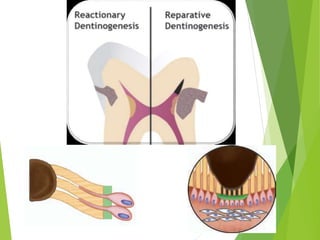
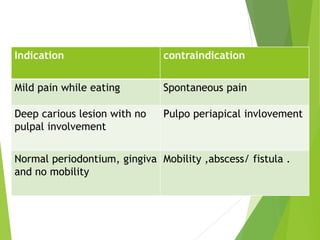
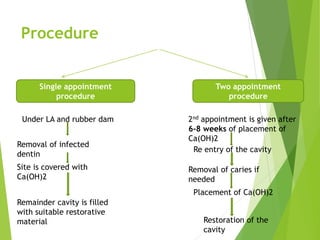
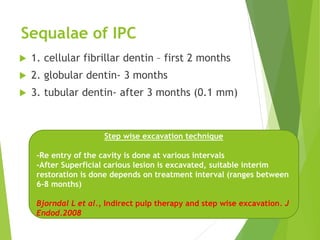
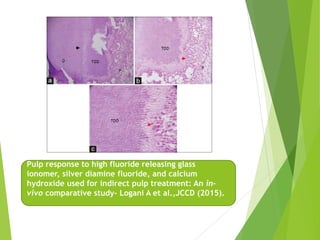
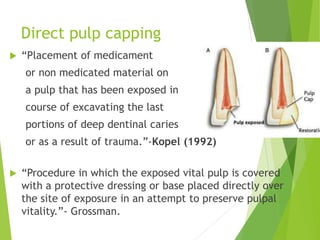
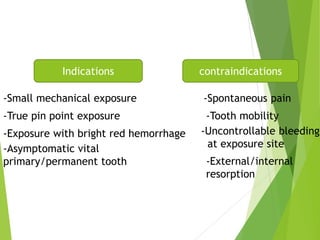
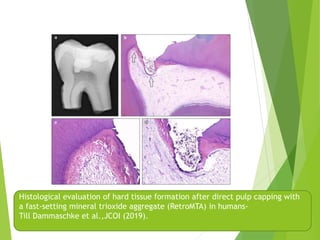
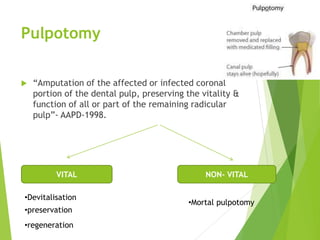
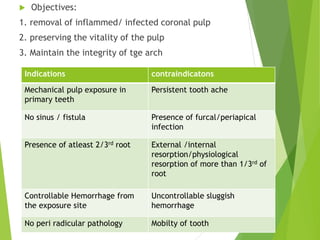
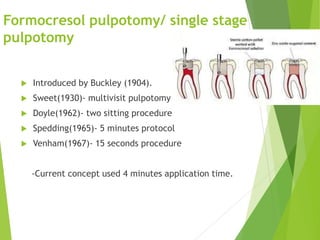
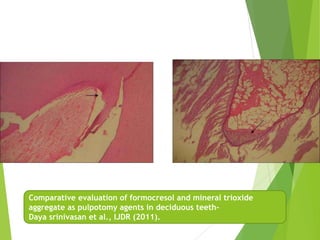
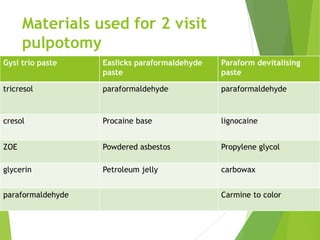
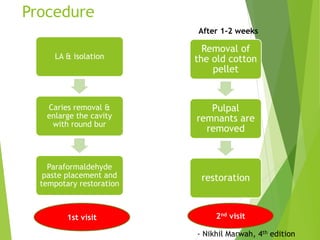
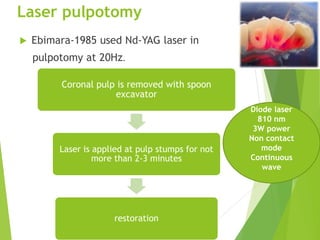
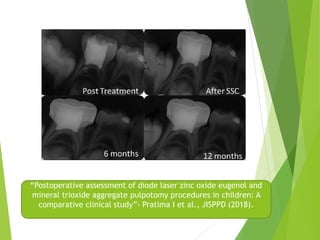
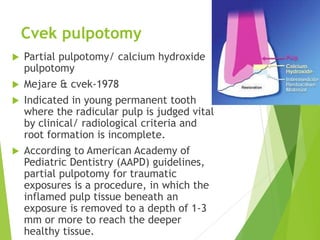
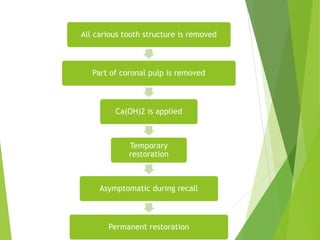
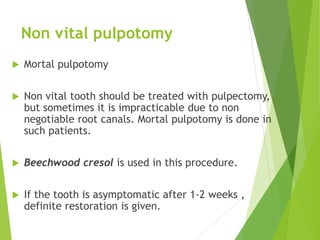
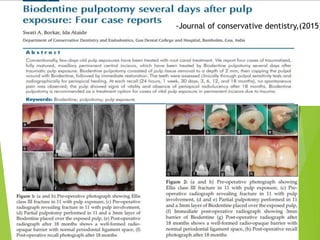
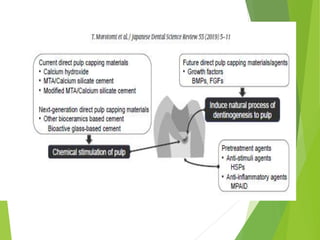
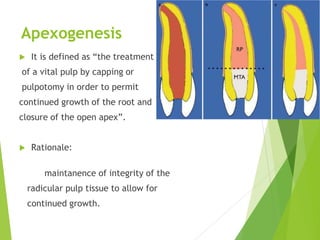
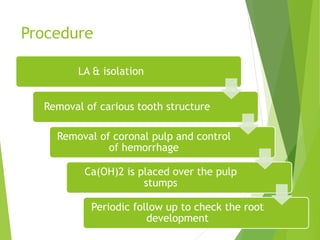
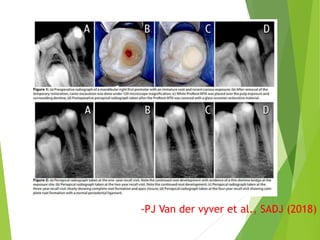
Vital pulp therapy is a procedure to treat exposed pulp, aiming to repair and maintain pulp vitality to prevent infection and enhance tooth function. The document outlines various methods including indirect pulp capping, direct pulp capping, pulpotomy, and apexogenesis, describing their indications, contraindications, procedures, materials used, and expected outcomes. Additionally, it discusses the histological changes and limitations associated with each method, emphasizing the importance of proper case selection and follow-up in pediatric dentistry.