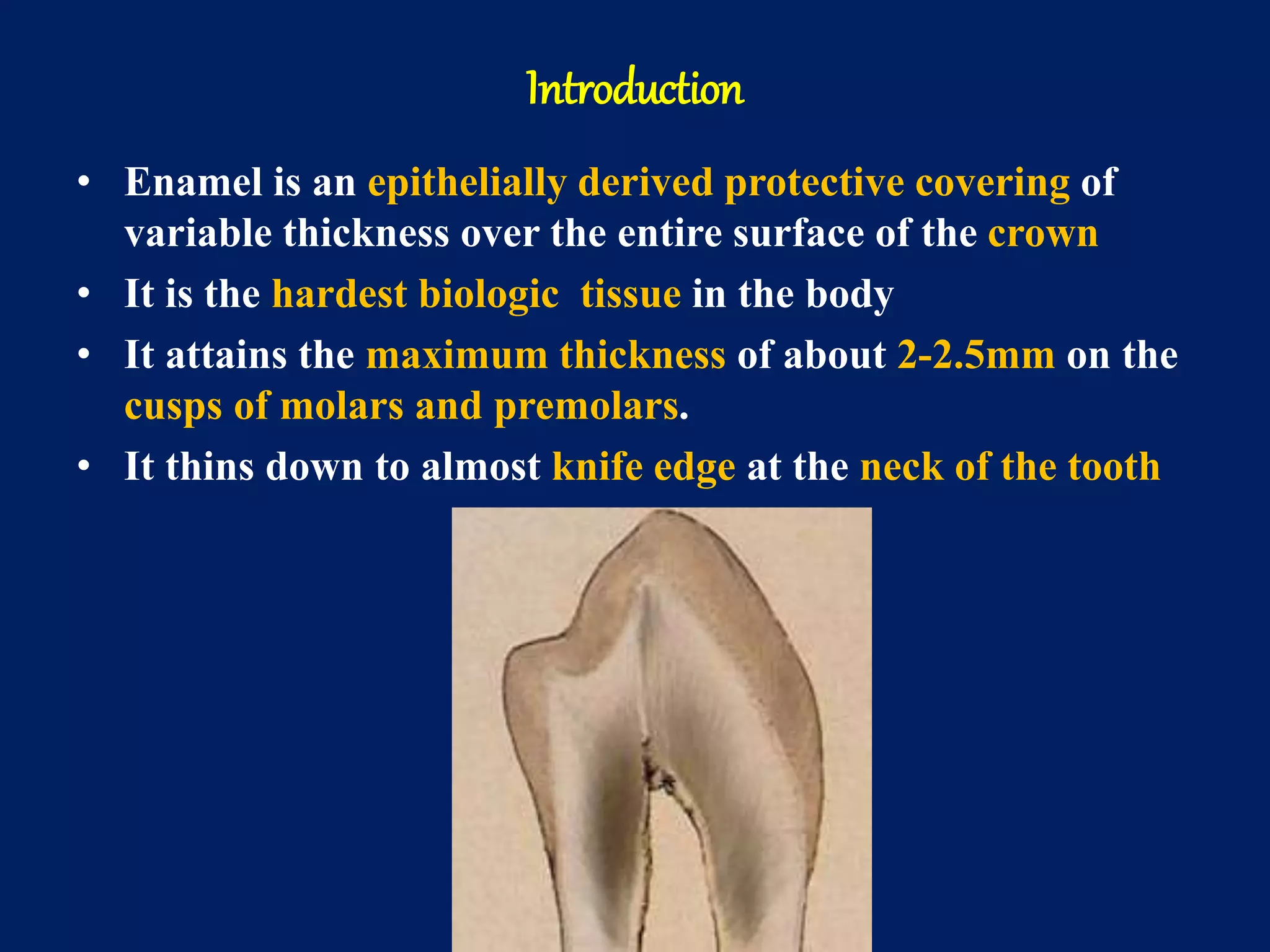
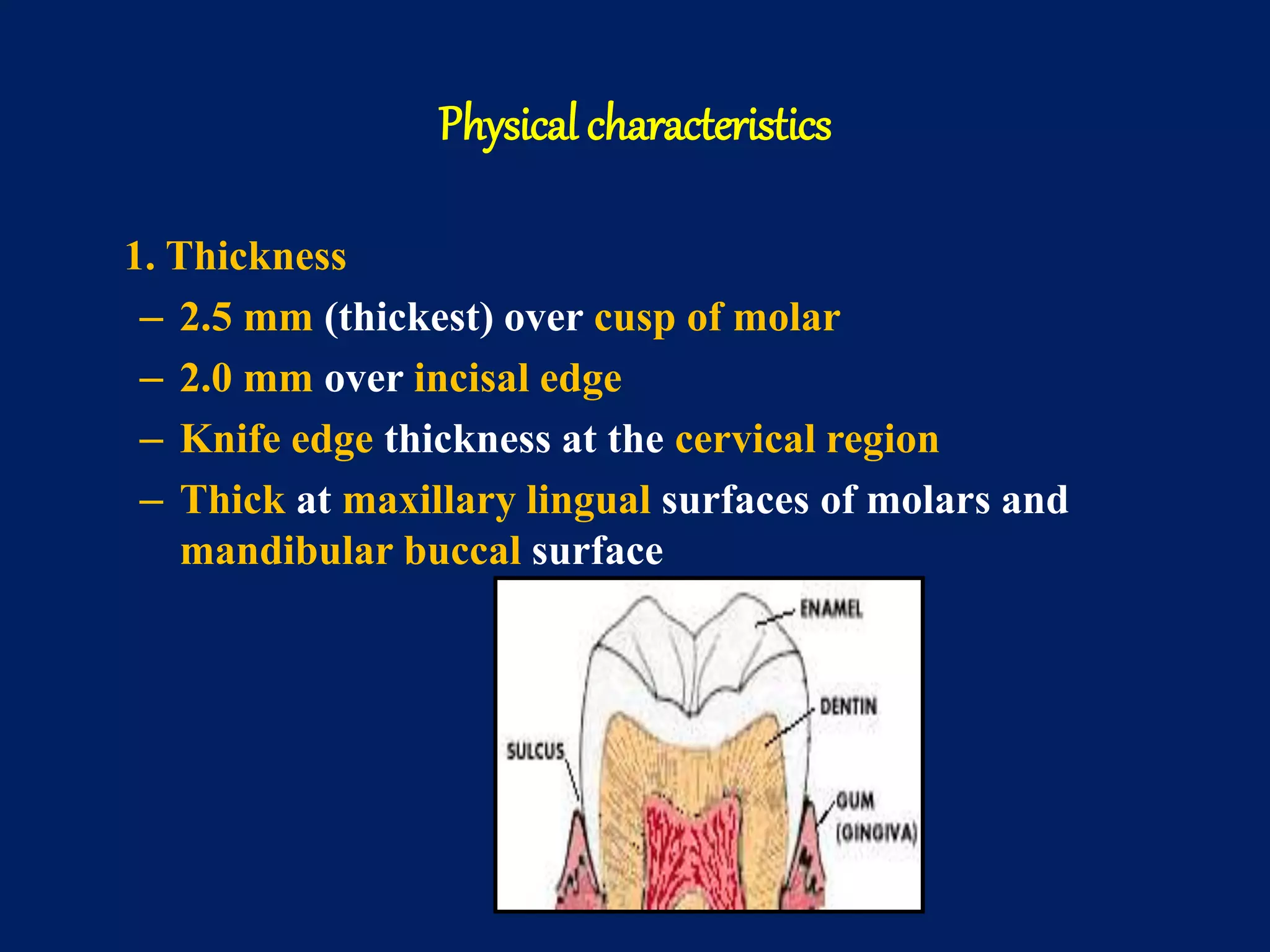
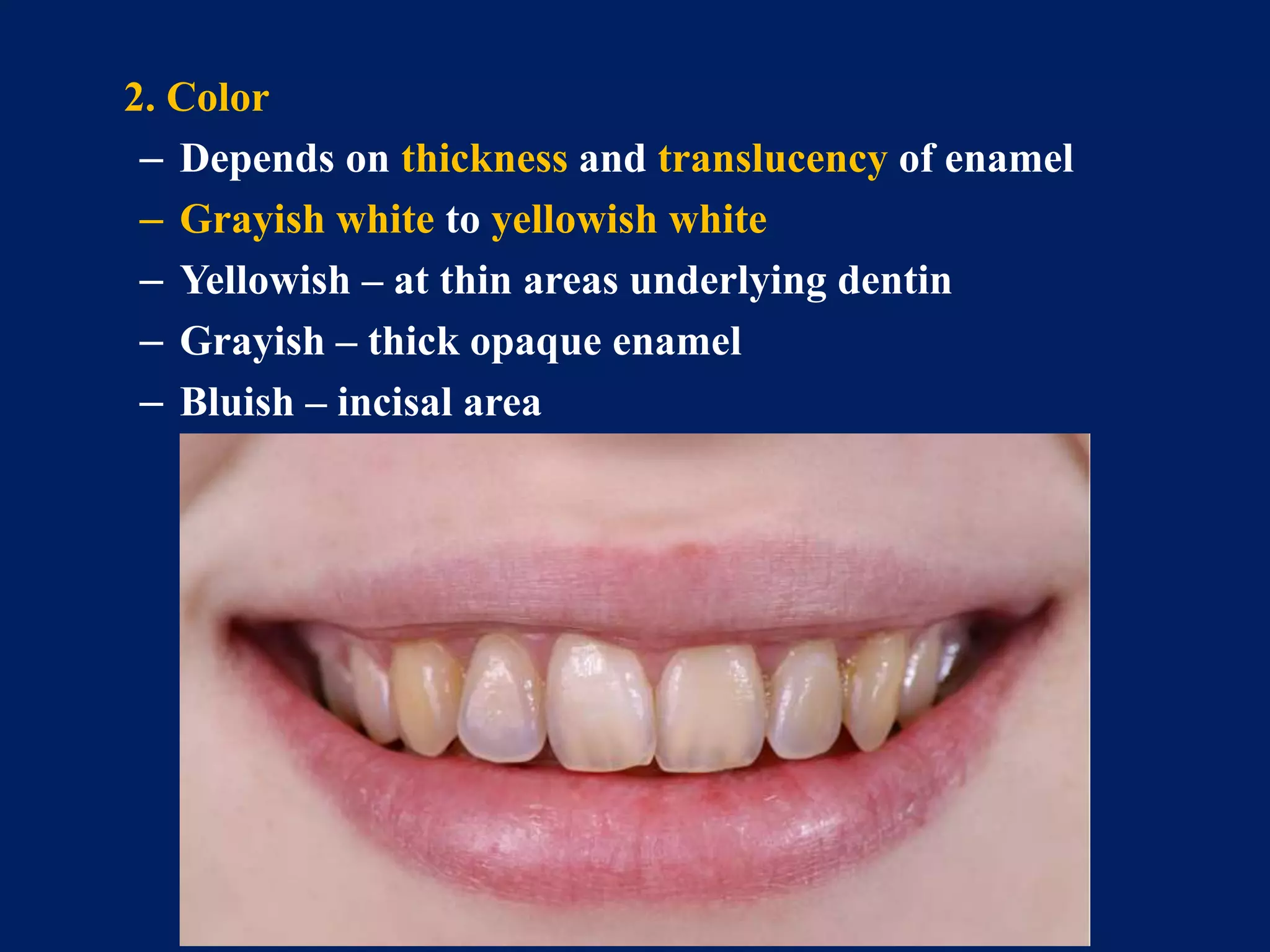
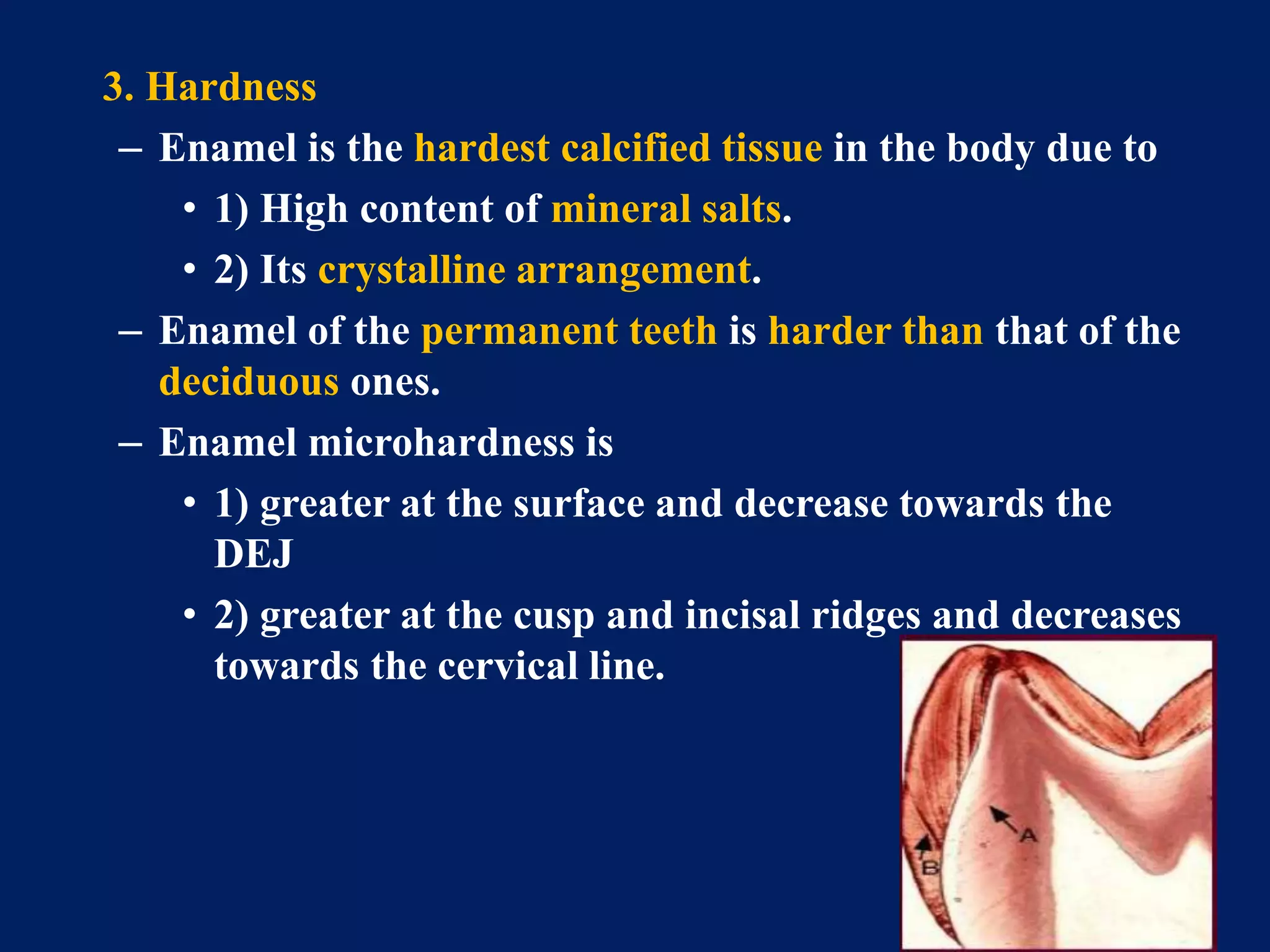
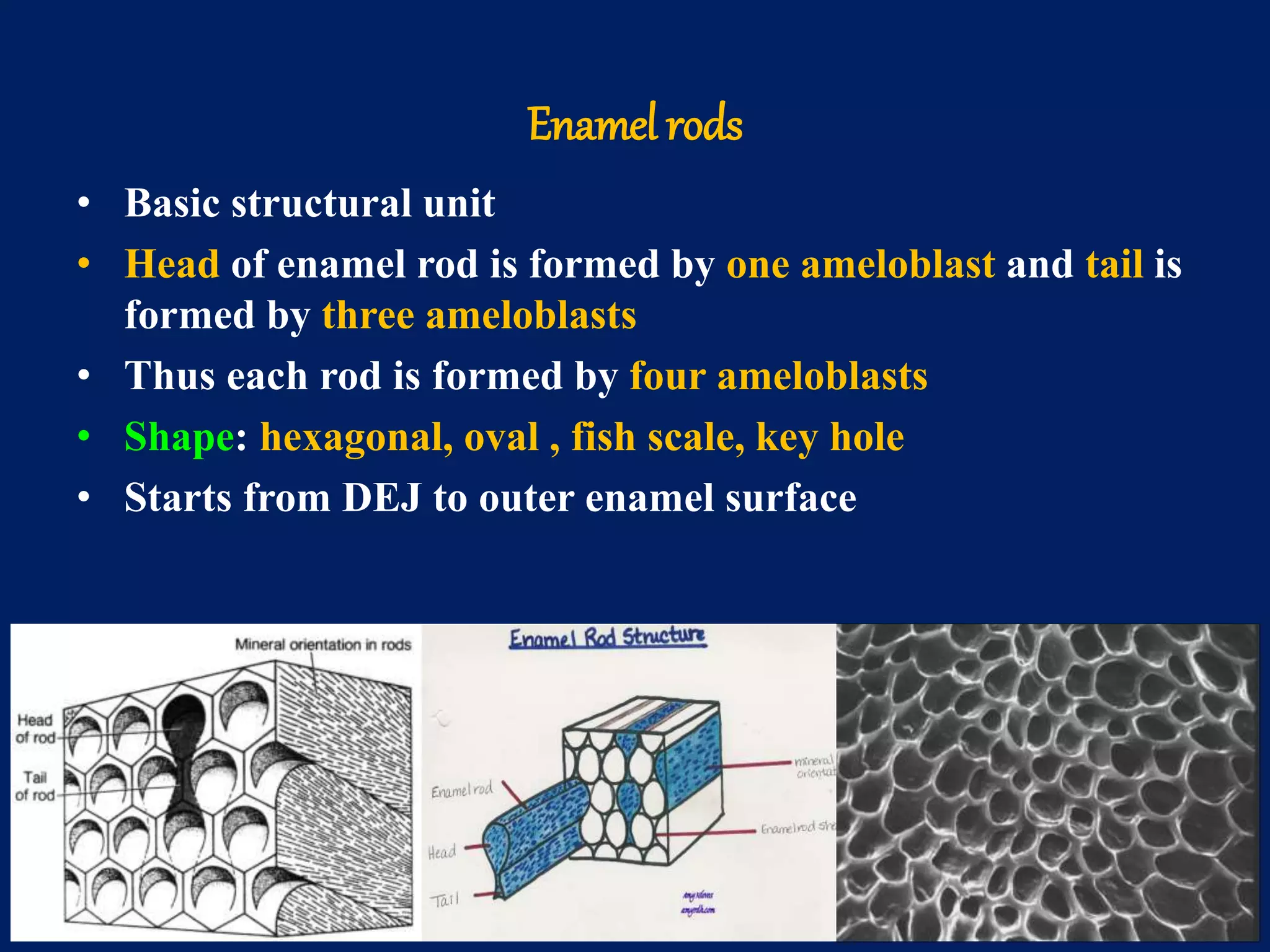
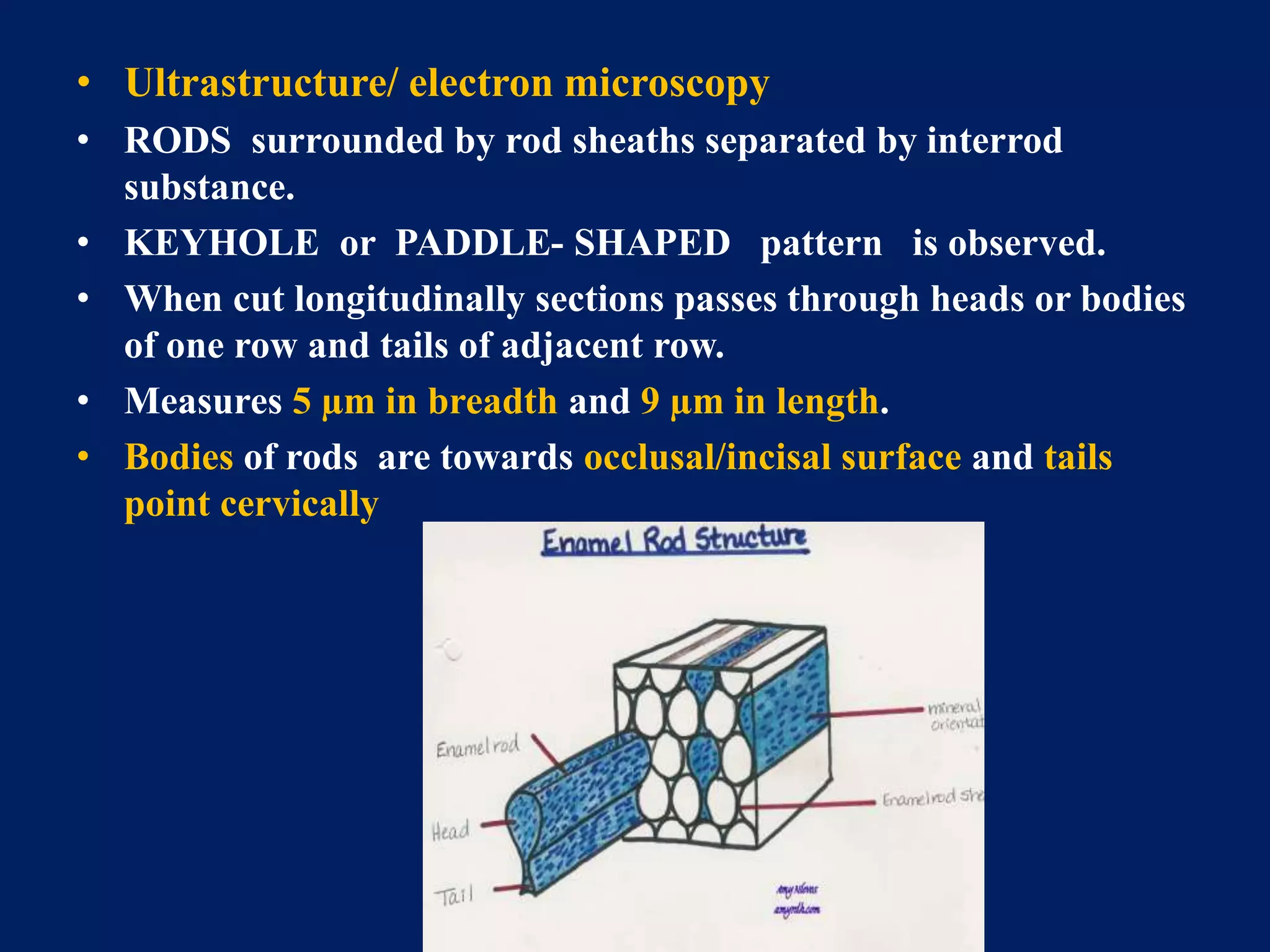
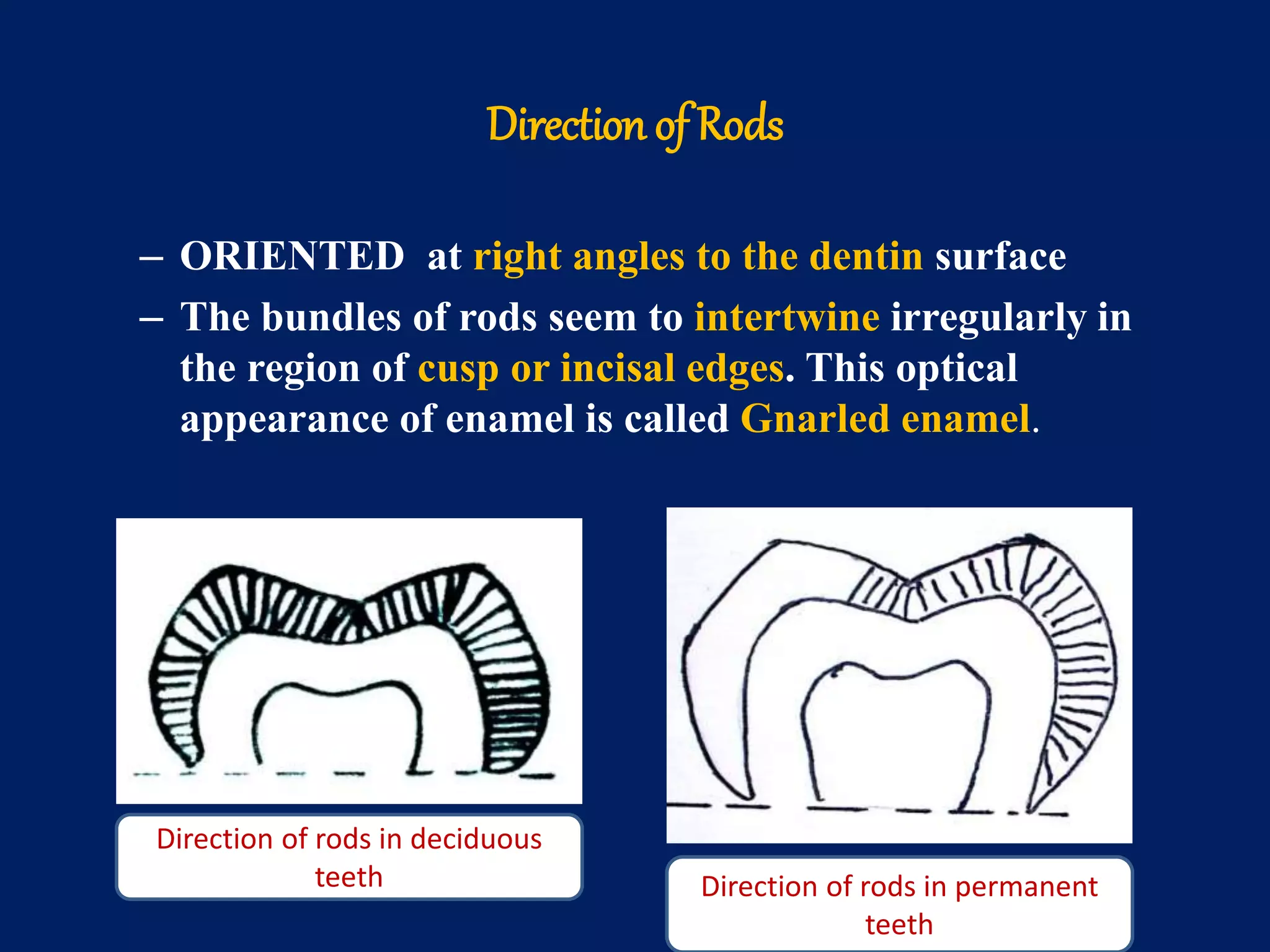
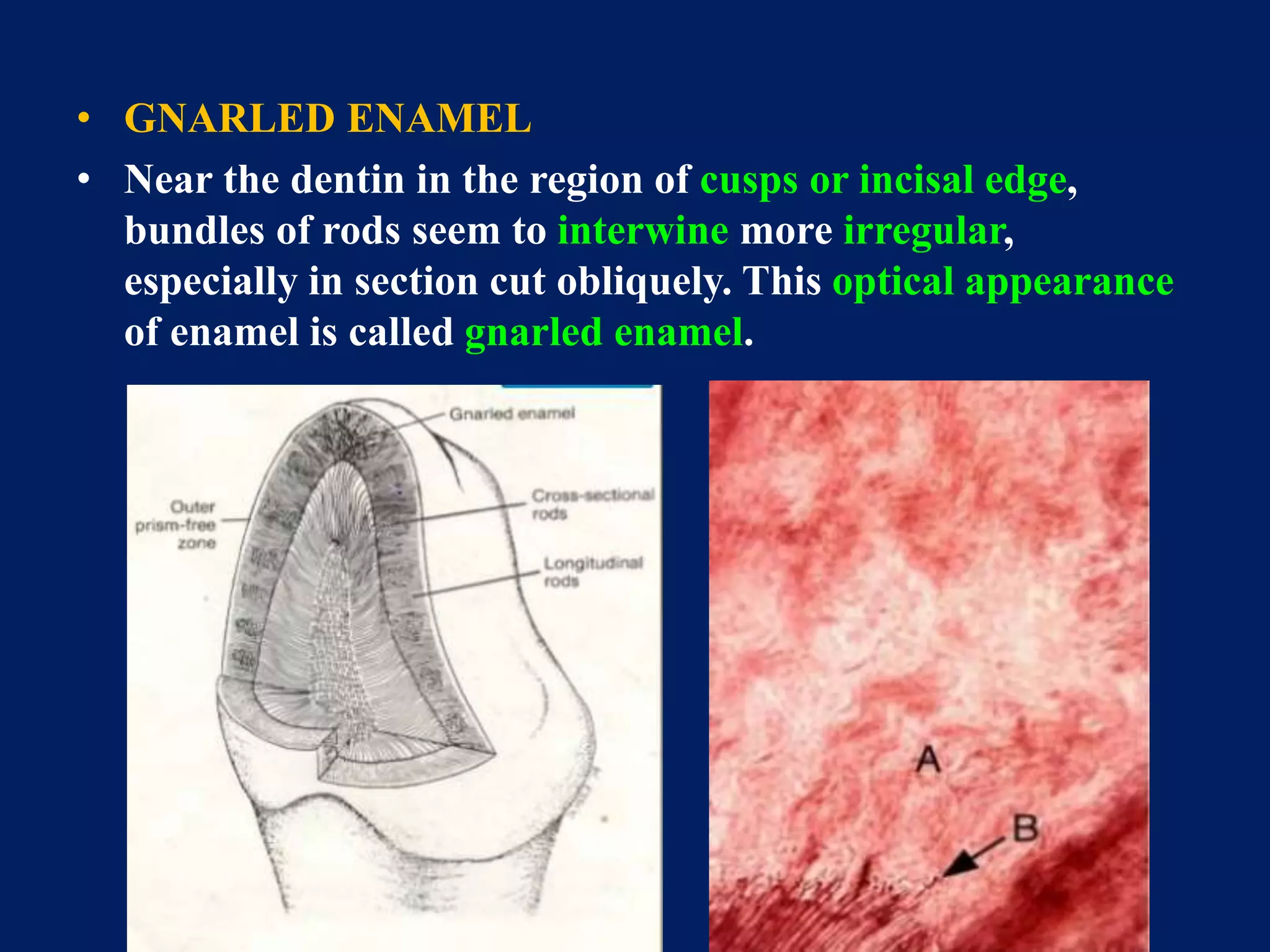
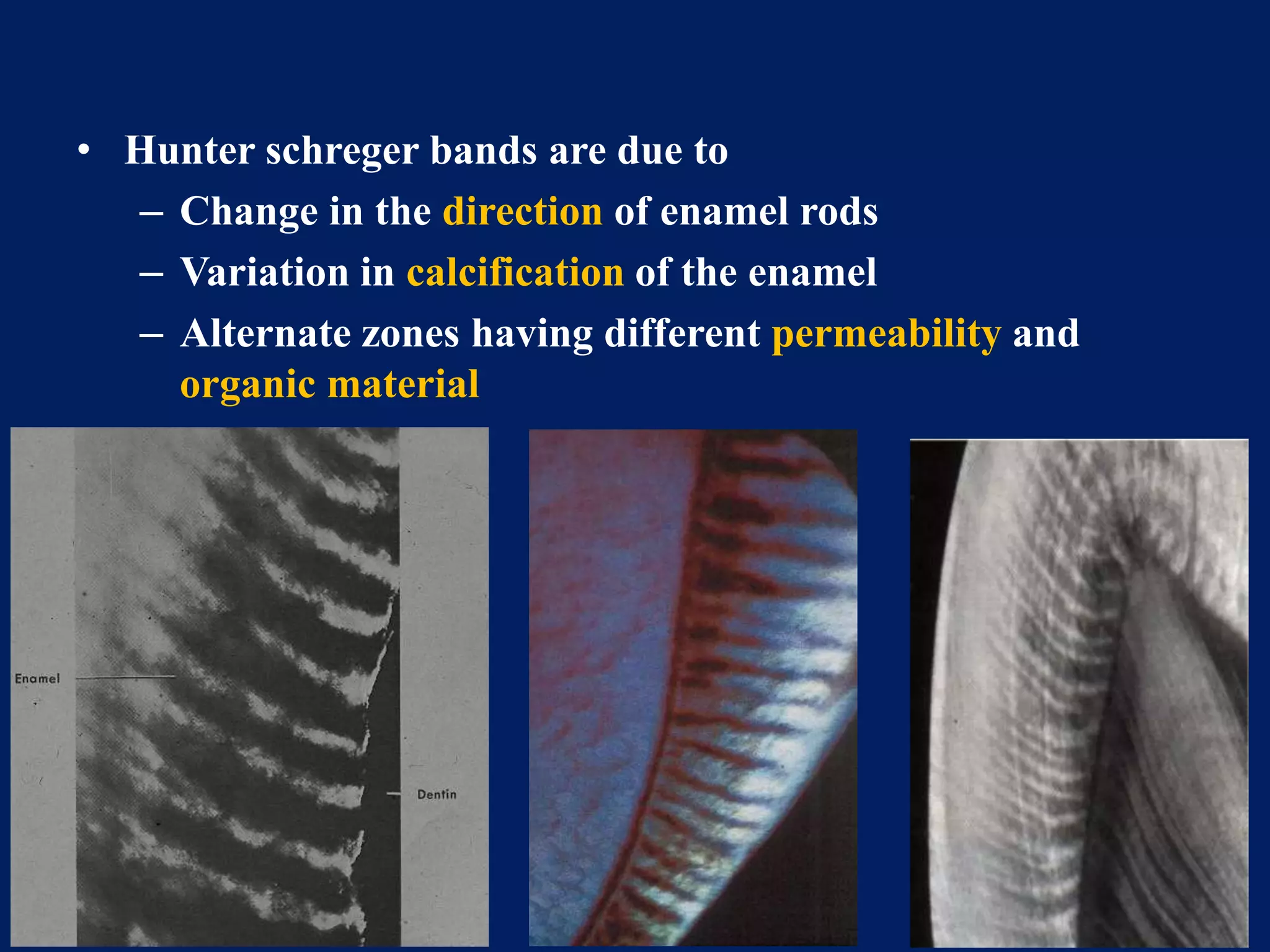
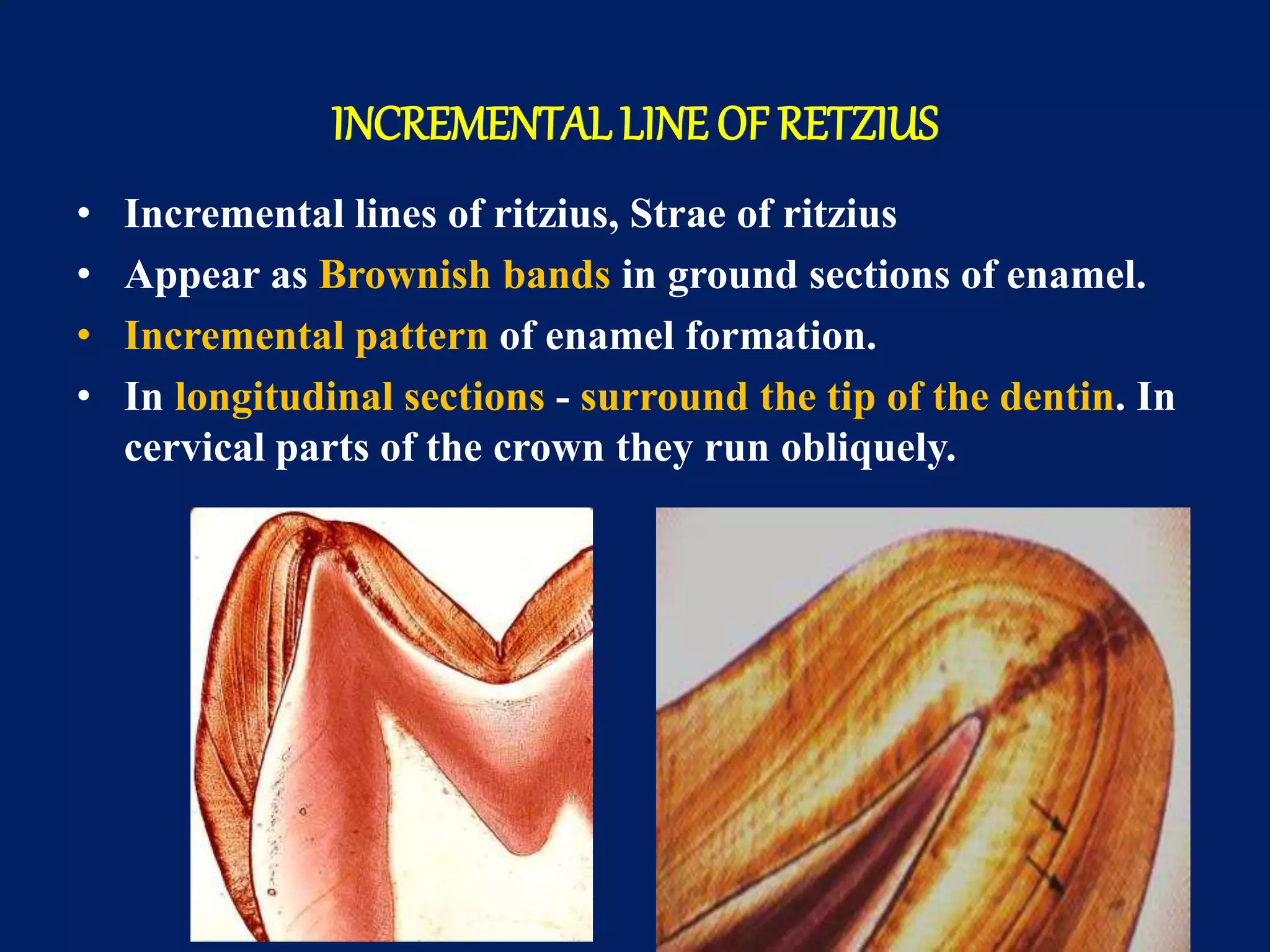
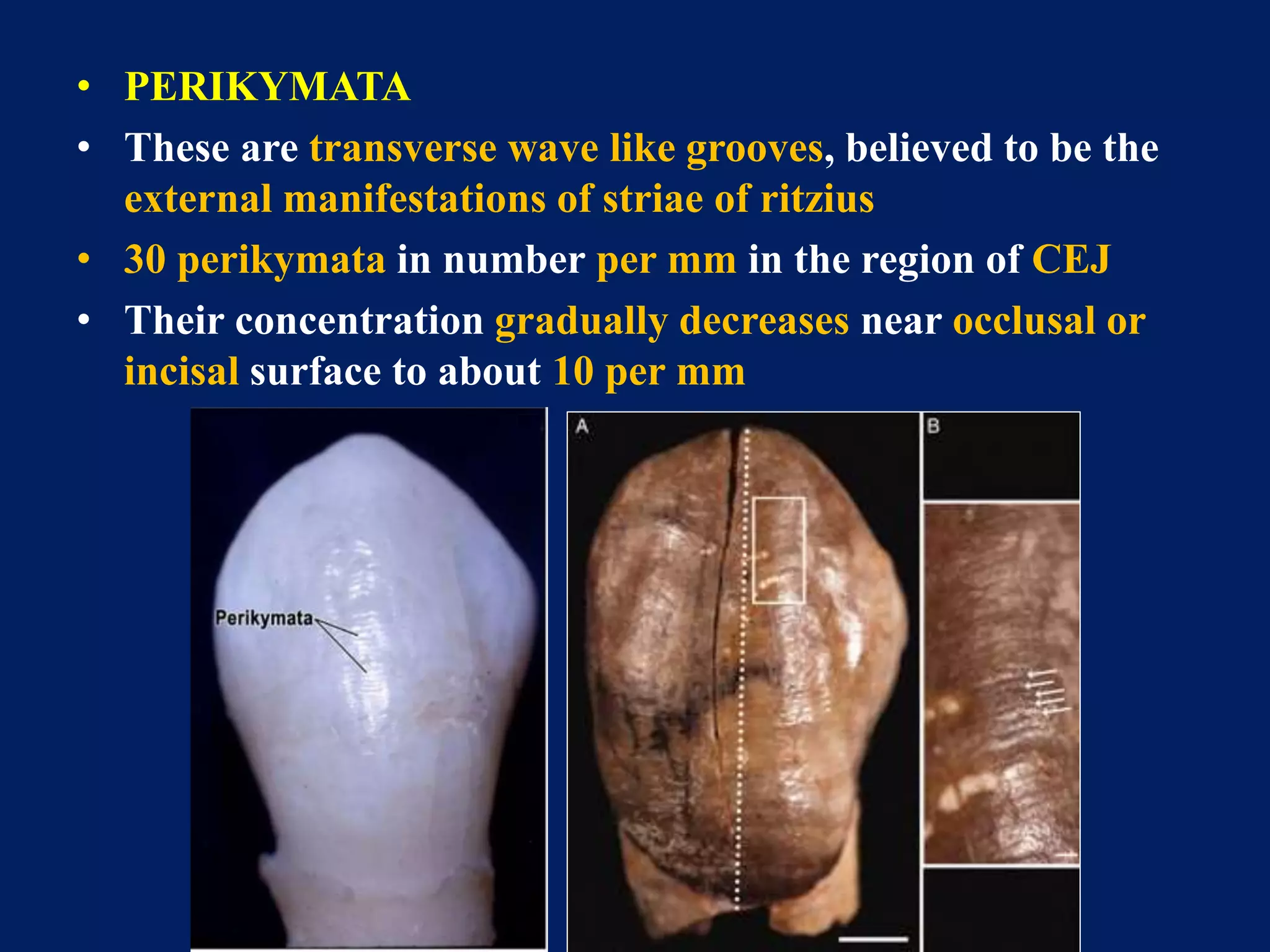
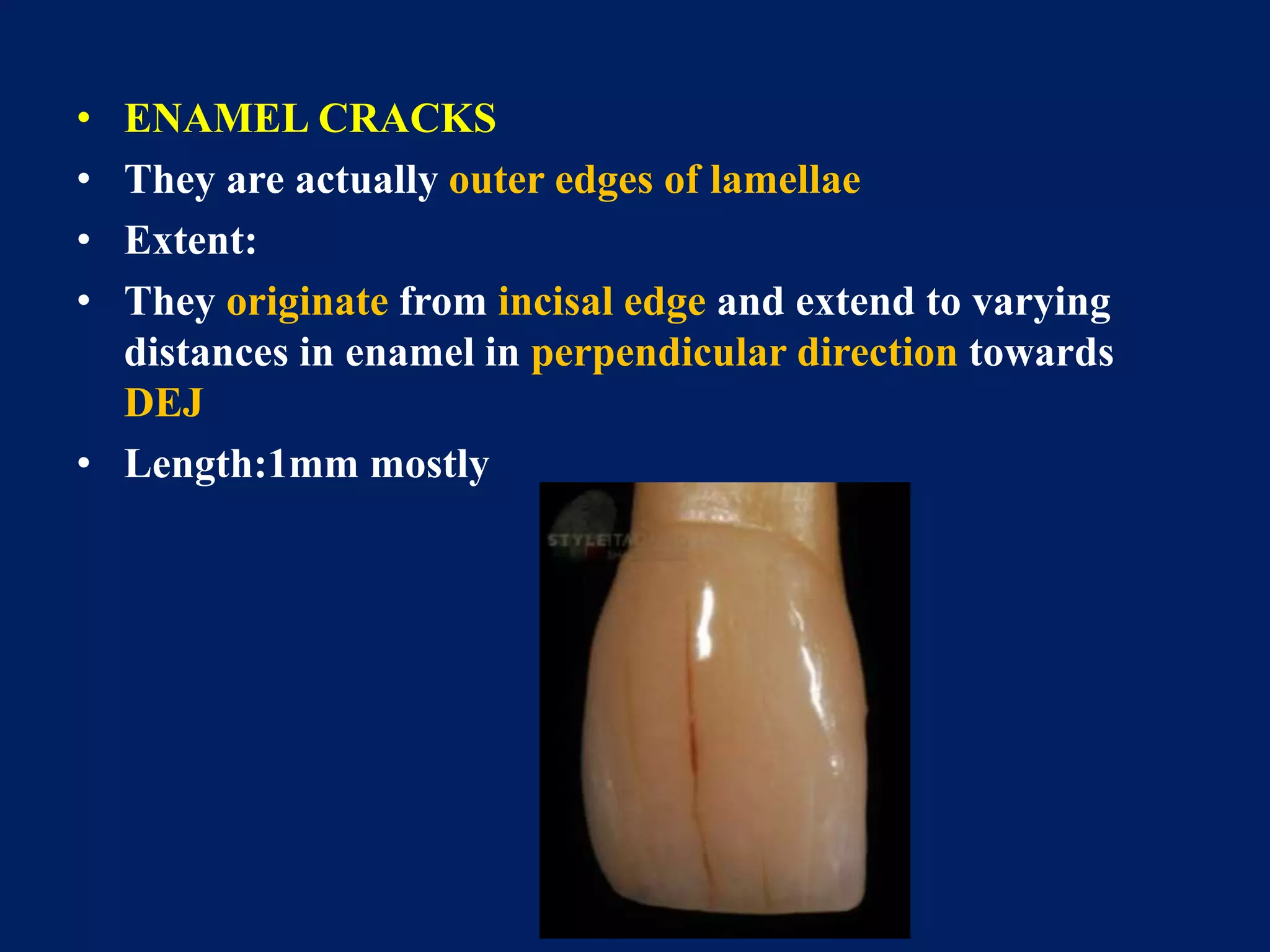
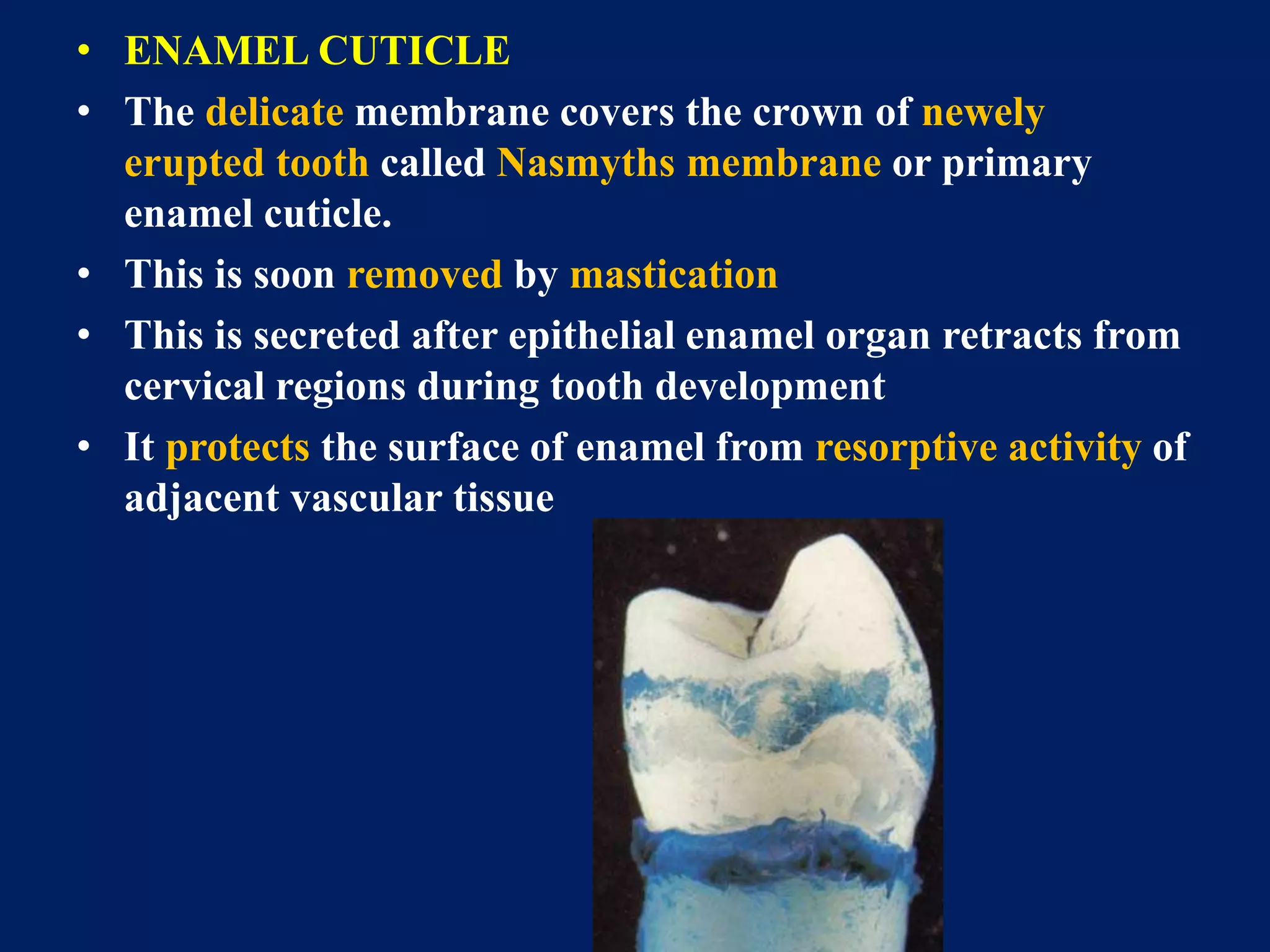
The document provides an in-depth examination of dental enamel, detailing its characteristics, structure, development, and clinical implications. Enamel is recognized as the hardest biological tissue, with its properties influenced by its composition, thickness, and translucency. The breakdown of enamel structures and age-related changes highlight its susceptibility to caries and the importance of clinical interventions like fluoride treatment.