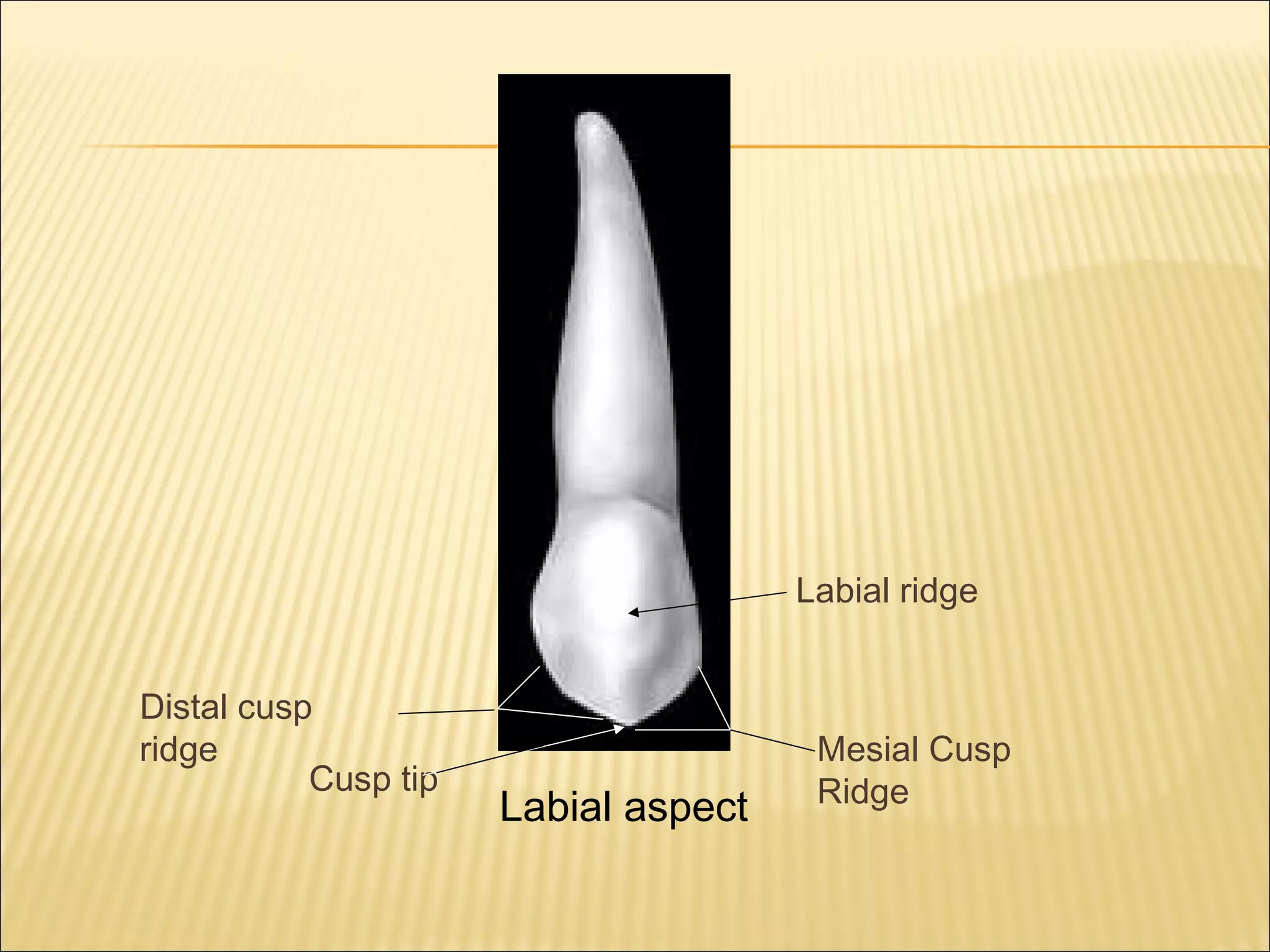
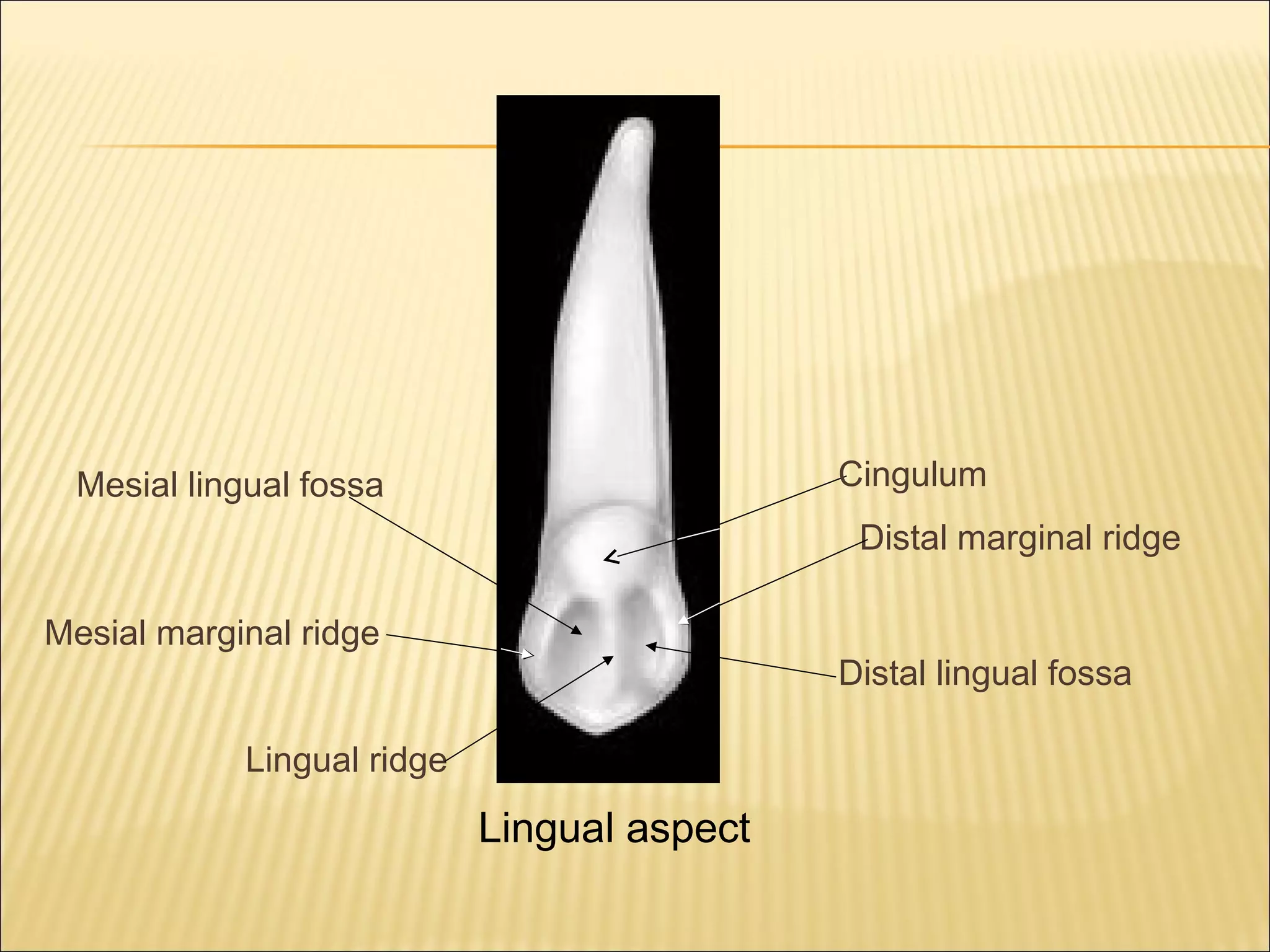
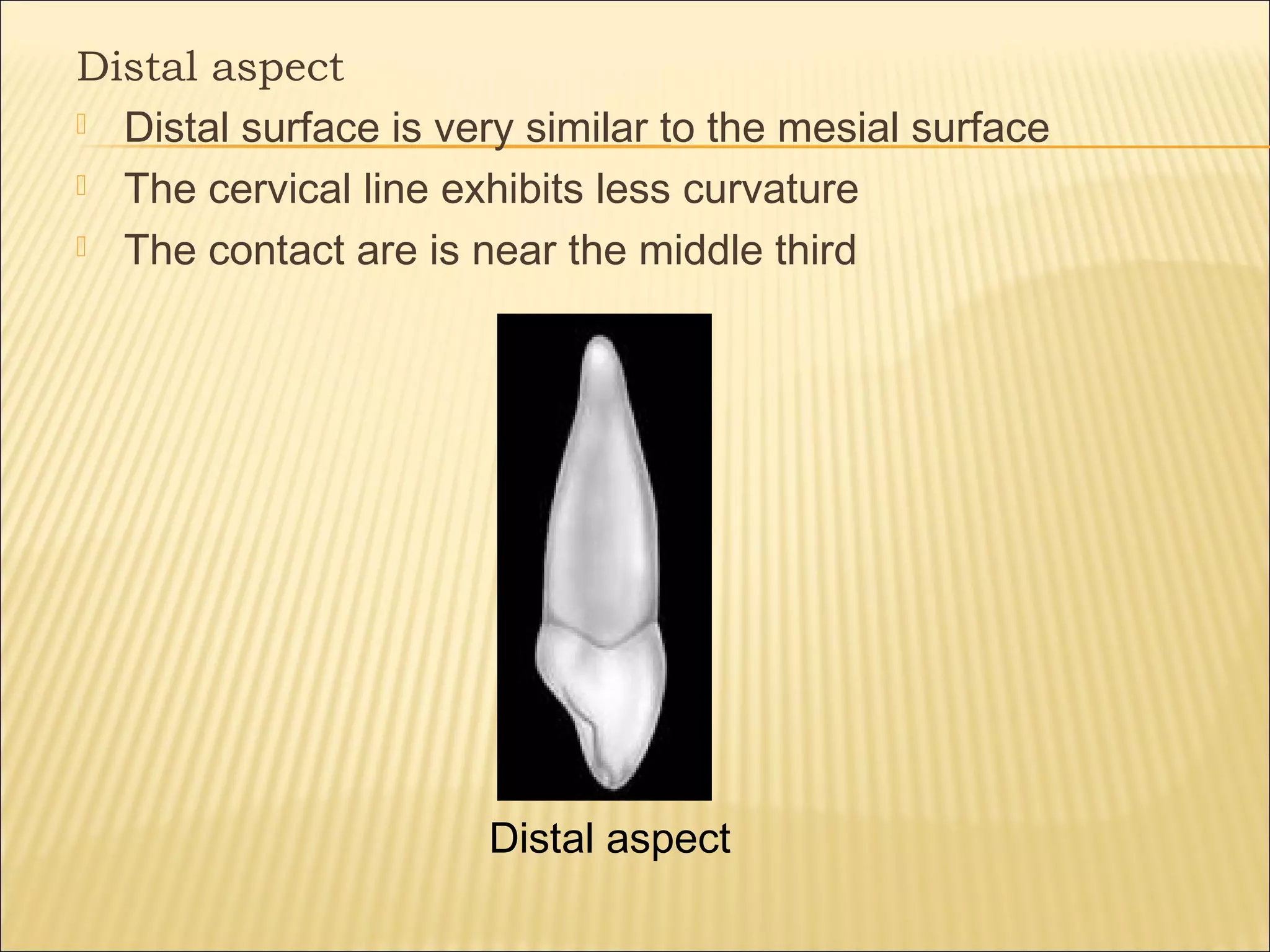
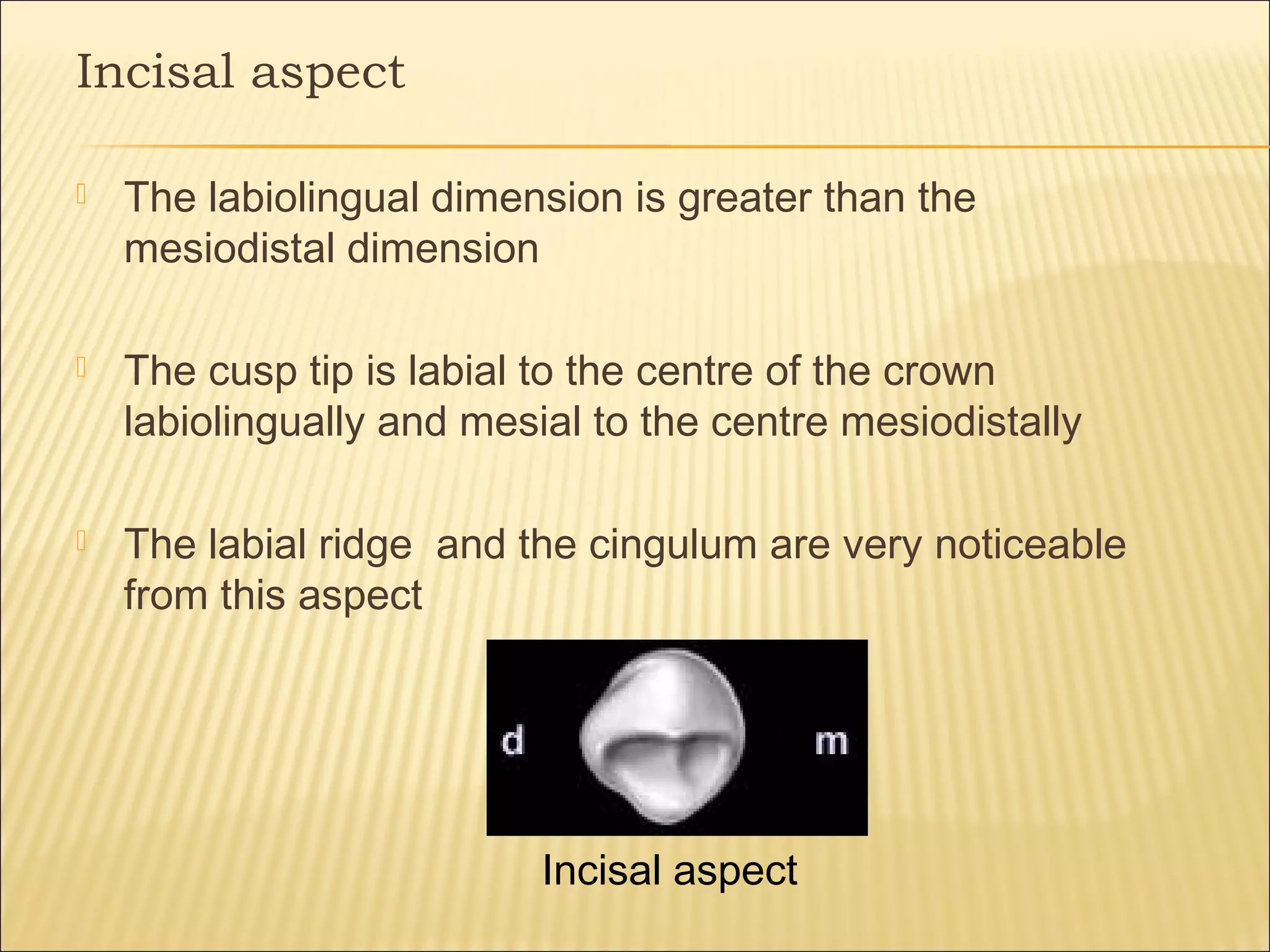
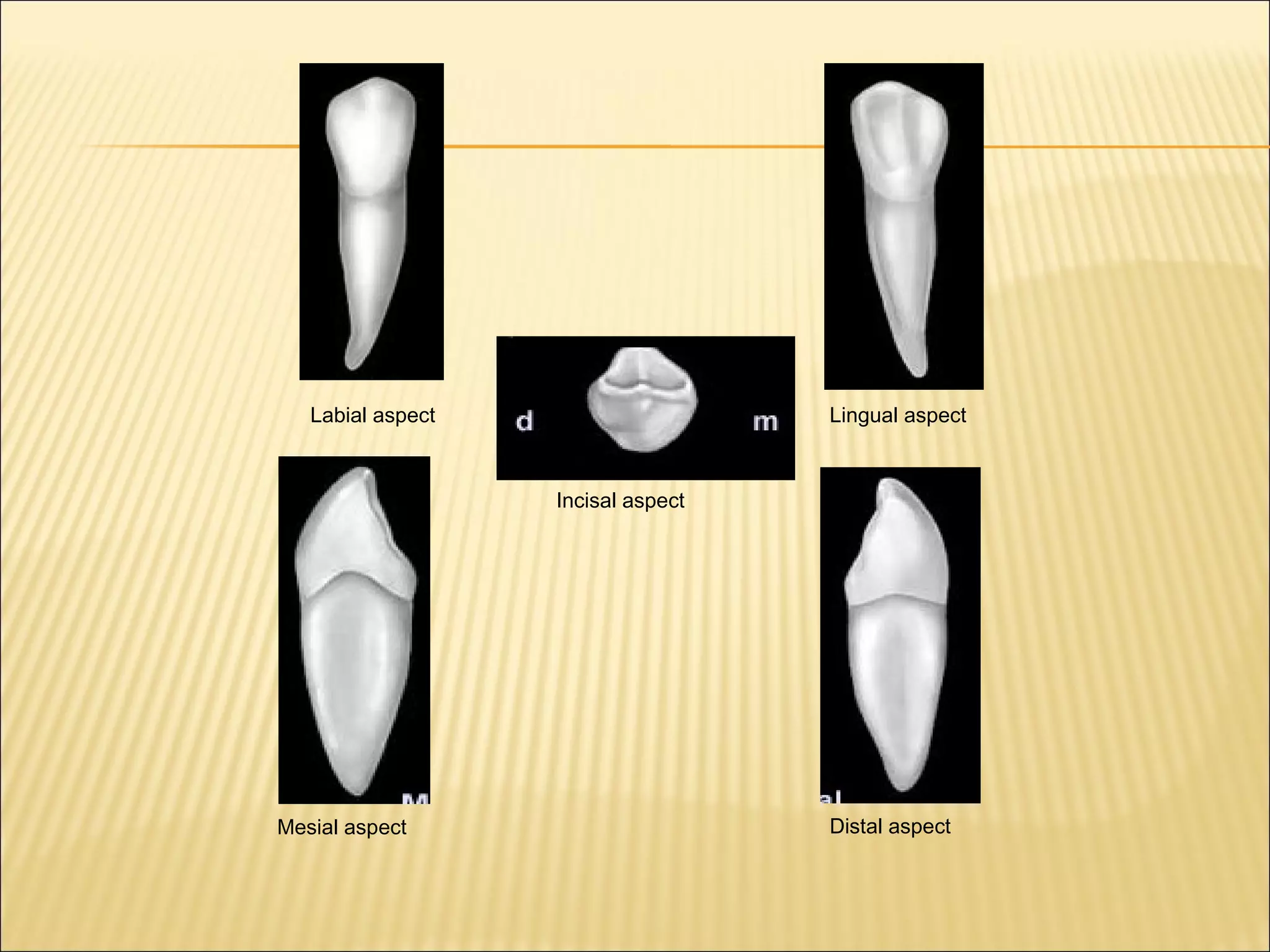
This document describes the morphology of permanent canine teeth. It details the features of maxillary and mandibular canines, including their crowns, roots, and various aspects. The maxillary canine has a prominent cusp with sloping ridges, a bulky labial ridge, and the longest, strongest root. The mandibular canine is slightly narrower with a smoother lingual surface and shorter root. Key distinguishing features of canines are described for clinicians to identify their shape and position.