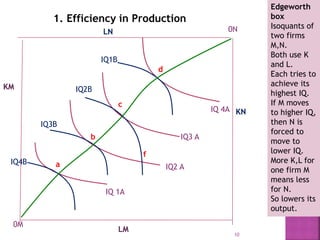
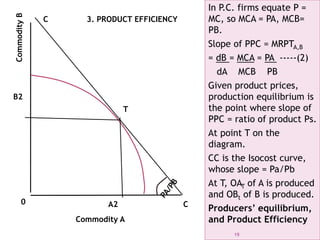
The document discusses general equilibrium theory and its key assumptions and implications. It addresses the following points in 3 sentences:
General equilibrium theory posits that all markets, including both product and factor markets, will reach equilibrium simultaneously. This equilibrium will be Pareto optimal, meaning no individual can be made better off without making another worse off due to optimal resource allocation. The model assumes perfect competition, constant returns to scale, and that equilibrium is determined by price adjustments across interconnected markets.