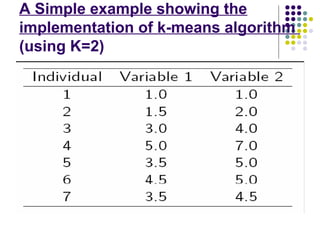
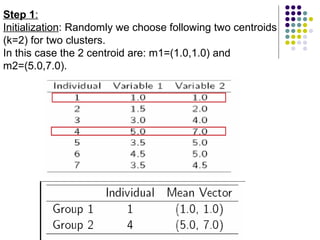
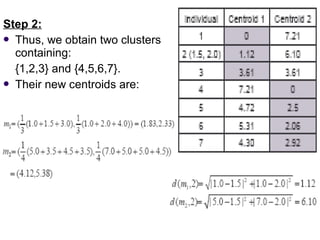
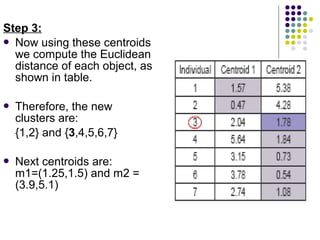
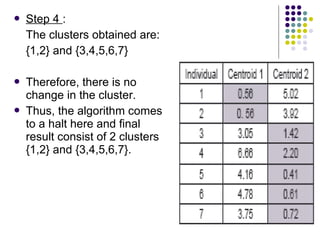
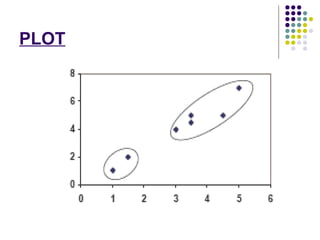
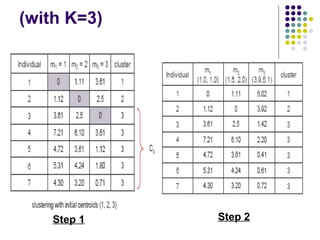
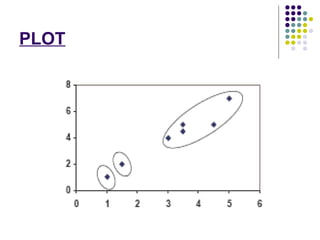
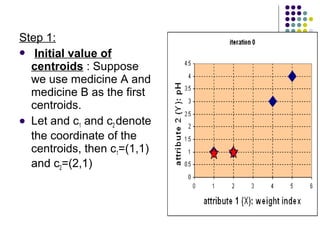
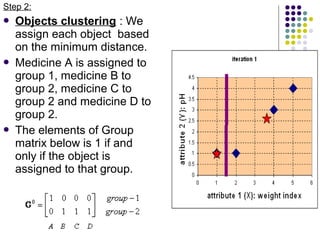
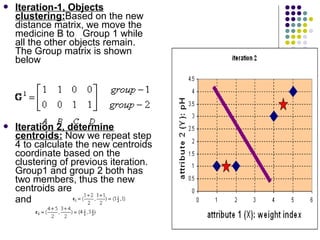
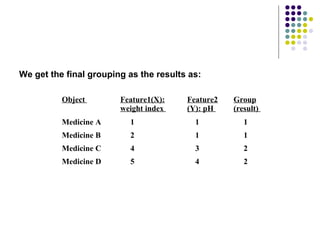
K-means clustering is a method for partitioning a dataset into k distinct groups based on attributes, seeking to minimize the sum of squared distances between data points and their respective cluster centroids. The process involves initializing centroids, assigning data points to clusters based on proximity, updating centroids, and iterating until no changes occur. While efficient and widely used in various fields, k-means has limitations, including sensitivity to initial conditions and the requirement of specifying the number of clusters in advance.