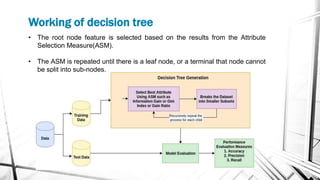
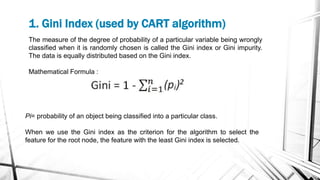
This document discusses decision trees, which are supervised learning algorithms used for both classification and regression. It describes key decision tree concepts like decision nodes, leaves, splitting, and pruning. It also outlines different decision tree algorithms (ID3, C4.5, CART), attribute selection measures like Gini index and information gain, and the basic steps for implementing a decision tree in a programming language.