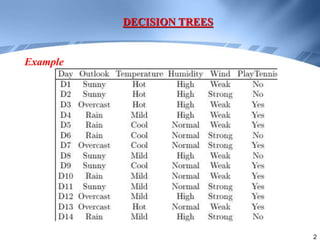
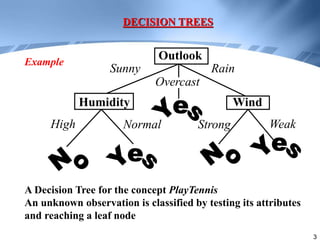
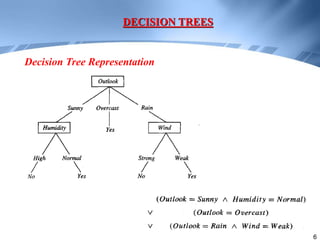
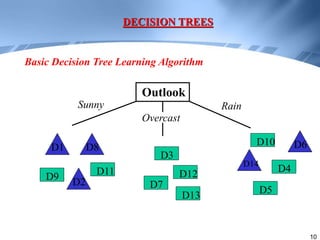
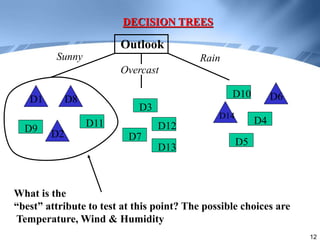
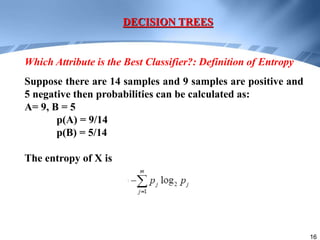
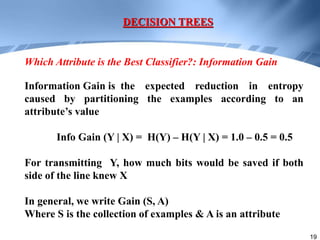
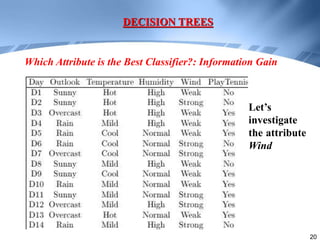
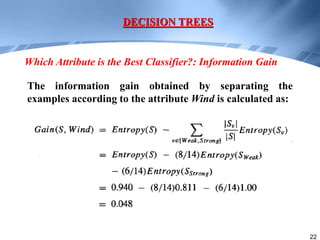
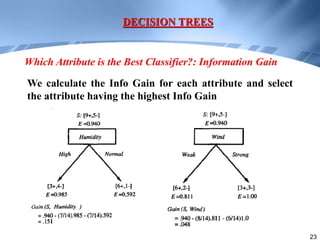
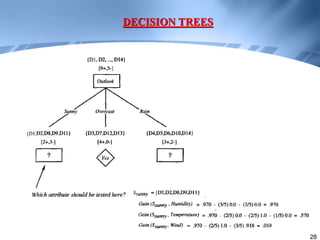
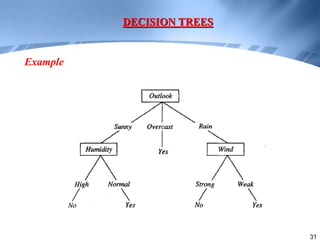
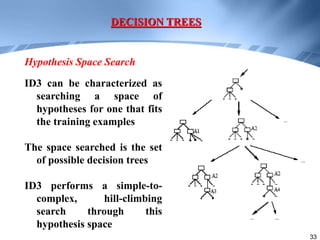
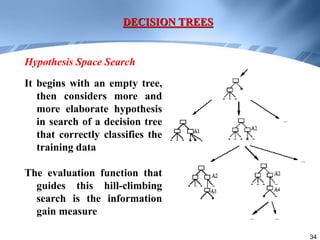
Decision trees are a supervised learning method that represents concepts as decision trees to classify data. The algorithm works by selecting the best attribute to test at each node using information gain, which measures the reduction in entropy from partitioning data by an attribute. It builds the tree in a top-down greedy manner, recursively selecting the attribute that best splits the data until the leaf nodes are pure or no further information gain is possible. The tree can then be converted to classification rules by tracing paths from the root to leaf nodes.