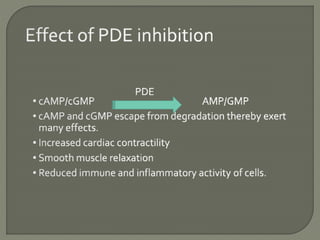
Phosphodiesterase (PDE) enzymes break down cyclic nucleotides like cAMP and cGMP. There are many families of PDEs that regulate these second messenger molecules in different tissues. PDE inhibitors prevent the inactivation of cAMP and cGMP, prolonging their cell signaling effects. Some PDE inhibitors are used to treat conditions like pulmonary hypertension and erectile dysfunction by increasing cyclic nucleotide levels. The document then provides examples of specific PDE inhibitors and their therapeutic applications.