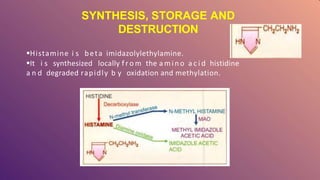
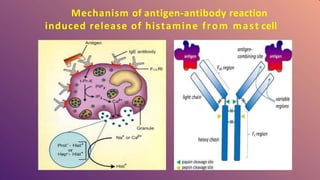
Histamine is a compound involved in local immune responses and regulating various physiological functions. It is produced by basophils and mast cells and released during allergic reactions. Histamine binds to H1, H2, and H3 receptors throughout the body, causing effects like vasodilation, increased capillary permeability during allergic responses, regulation of the sleep-wake cycle as a neurotransmitter, stimulation of gastric acid release, and involvement in conditions like schizophrenia and multiple sclerosis. Histamine plays an important role in many physiological processes through its ability to interact with different receptor types in various tissues and organs.