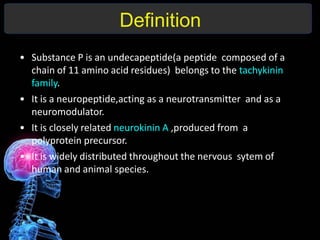
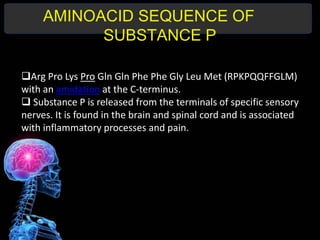
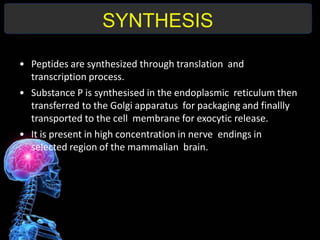
Substance P is an 11-amino acid neuropeptide that acts as a neurotransmitter and neuromodulator. It is widely distributed throughout the nervous system and released from sensory nerve terminals. Substance P binds to neurokinin 1 receptors on cells to trigger various second messenger systems, regulating functions like vasodilation, inflammation, pain, mood, vomiting, and cell growth. Originally discovered in 1931, substance P plays key roles in the body's response to stressors and has clinical significance in conditions involving chronic inflammation, mood disorders, arthritis, cancer, and infections.