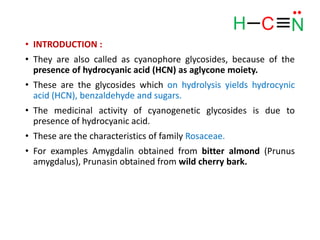
Cyanogenic glycosides, including amygdalin from bitter almonds, release hydrocyanic acid upon hydrolysis, contributing to their medicinal properties. Bitter almonds, distinct from sweet almonds, contain amygdalin and are cultivated in various regions including Italy and Spain. The oil from bitter almonds is used in skin lotions, while their consumption is limited due to their toxic properties.