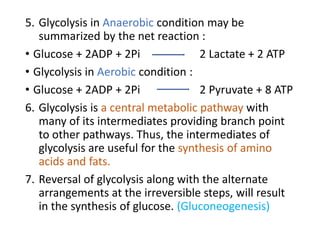
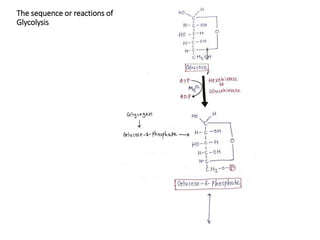
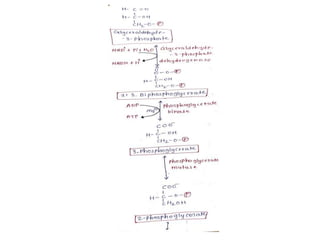
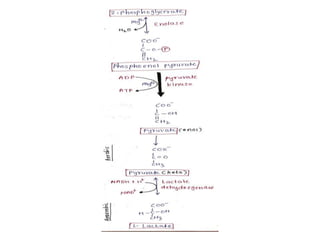
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate or lactate, producing ATP in the process. This pathway occurs in all cells, can function under both anaerobic and aerobic conditions, and is crucial for energy in tissues lacking mitochondria, particularly the brain. The reaction sequence of glycolysis is divided into three phases: energy investment, splitting, and energy generation, involving key enzymes that facilitate ATP production and metabolic intermediates for other biosynthetic pathways.