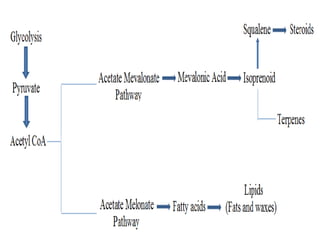
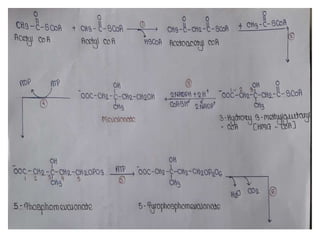
The acetate pathway, also known as the mevalonate or HMG-CoA reductase pathway, is an essential metabolic pathway that produces isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) from acetyl-CoA. It begins with two acetyl-CoA molecules condensing to form acetoacetyl-CoA, which then condenses with another acetyl-CoA to form HMG-CoA. HMG-CoA is reduced to mevalonate, which is then converted through a series of phosphorylation and decarboxylation steps into IPP and DMAPP. This pathway is targeted by statin drugs for lowering