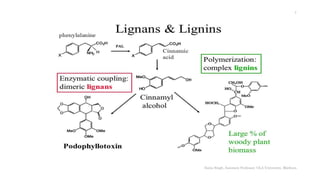
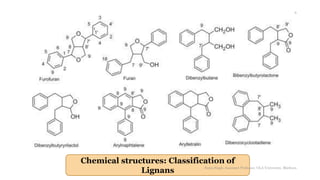
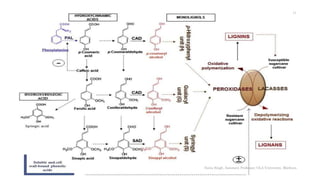
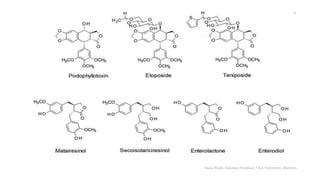
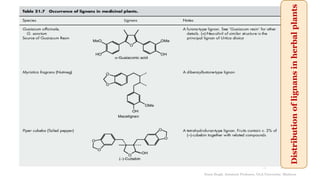
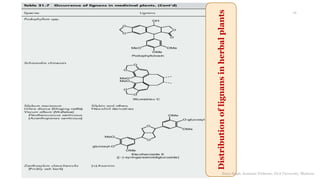
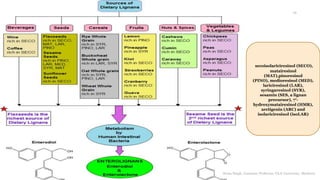
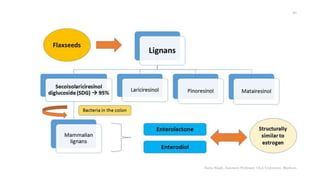
This document discusses lignans, which are non-flavonoid polyphenols found in many plant families. Lignans are dimers of phenylpropane units linked by carbon-carbon bonds and have antioxidant properties. They are classified into subgroups based on their carbon skeleton and cyclization patterns. Lignans are biosynthesized from phenylalanine and hydroxycinnamic acids via the shikimic acid pathway. Food sources of lignans include whole grains, seeds, nuts, fruits and vegetables. Lignans have therapeutic properties such as anticancer and antihypertensive effects. Some lignans are converted by gut bacteria into enterolignans, which may help lower cancer risks.



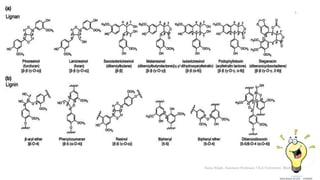
![Lignin is plant polymer acting as
strengthening material for plant cell wall &
matrix for cellulose micro-fibrils
• Represent a large no. of aromatic material
based on C6C3 building unit
• Lignins formed by oxidative coupling of
hyroxycinnamyl alcohol monomers by
peroxidase enzymes [p-coumaryl-, coniferyl-
and sinapyl-alcohol]
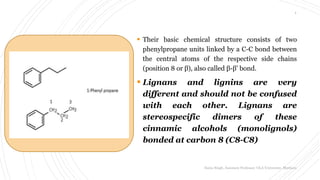
Lignans are dimeric phenylpropanes (C-18)
coupled at the central carbon of the side chain
[via their ß-carbon of the side chain]
Sonia Singh, Assistant Professor, GLA University, Mathura
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lignans-200815185143/85/Lignans-6-320.jpg)