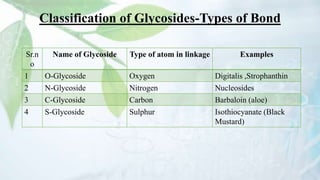
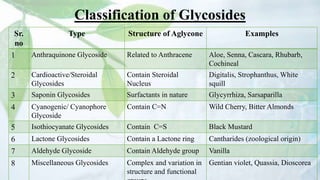
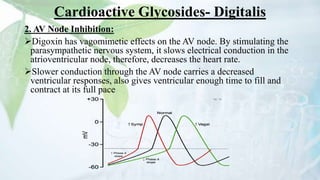
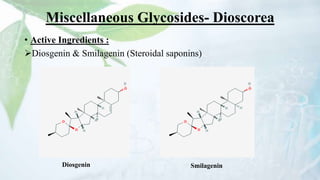
Glycosides are organic compounds found in many plants and animals that contain a sugar and non-sugar portion. They are classified based on the type of bond between the sugar and non-sugar parts. Some important examples of glycosides discussed in the document include digitalis containing cardioactive glycosides, aloe containing anthraquinone glycosides, licorice root containing saponin glycosides, and black mustard containing isothiocyanate glycosides. Glycosides have various pharmacological properties depending on their non-sugar portions, such as laxative, antiviral, antimicrobial, or cardiac effects.