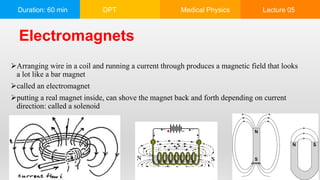
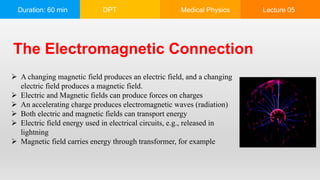
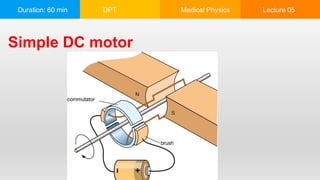
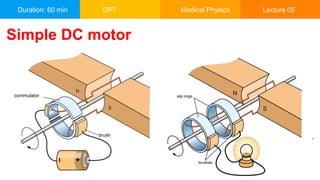
This document is a lecture on electromagnetism covering key historical figures and concepts, such as the relationship between electricity and magnetism, electric motors, and electromagnets. It discusses applications of electromagnetic radiation, including communication systems, medical imaging, and motors in various devices. The lecture emphasizes the fundamental principles of electric and magnetic fields and their interaction, alongside practical examples of their use in technology.