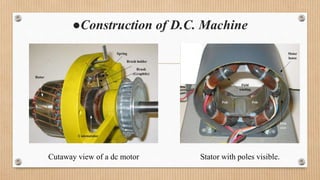
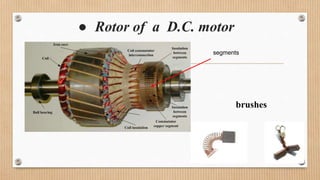
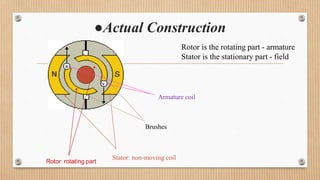
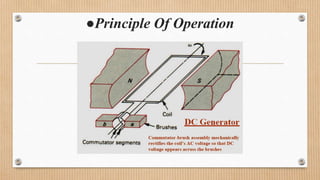
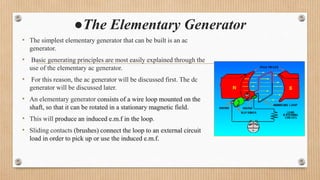
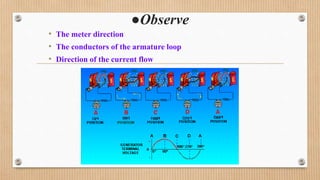
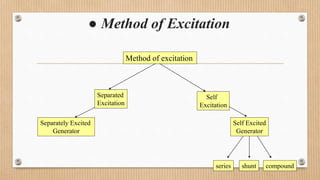
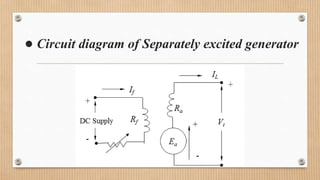
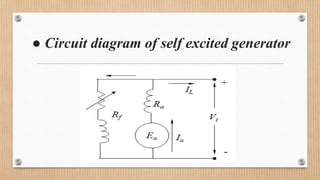
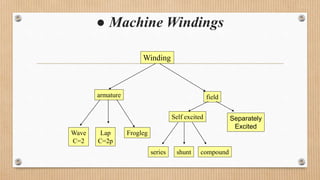
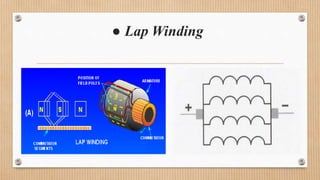
The document outlines a presentation on d.c. machines and transformers, covering topics such as construction, working principles, and excitation methods. It details different types of generators including separately and self-excited generators, as well as armature winding types like simplex lap and wave winding. The principles of operation and the effects of magnetic fields on voltage generation are also discussed.