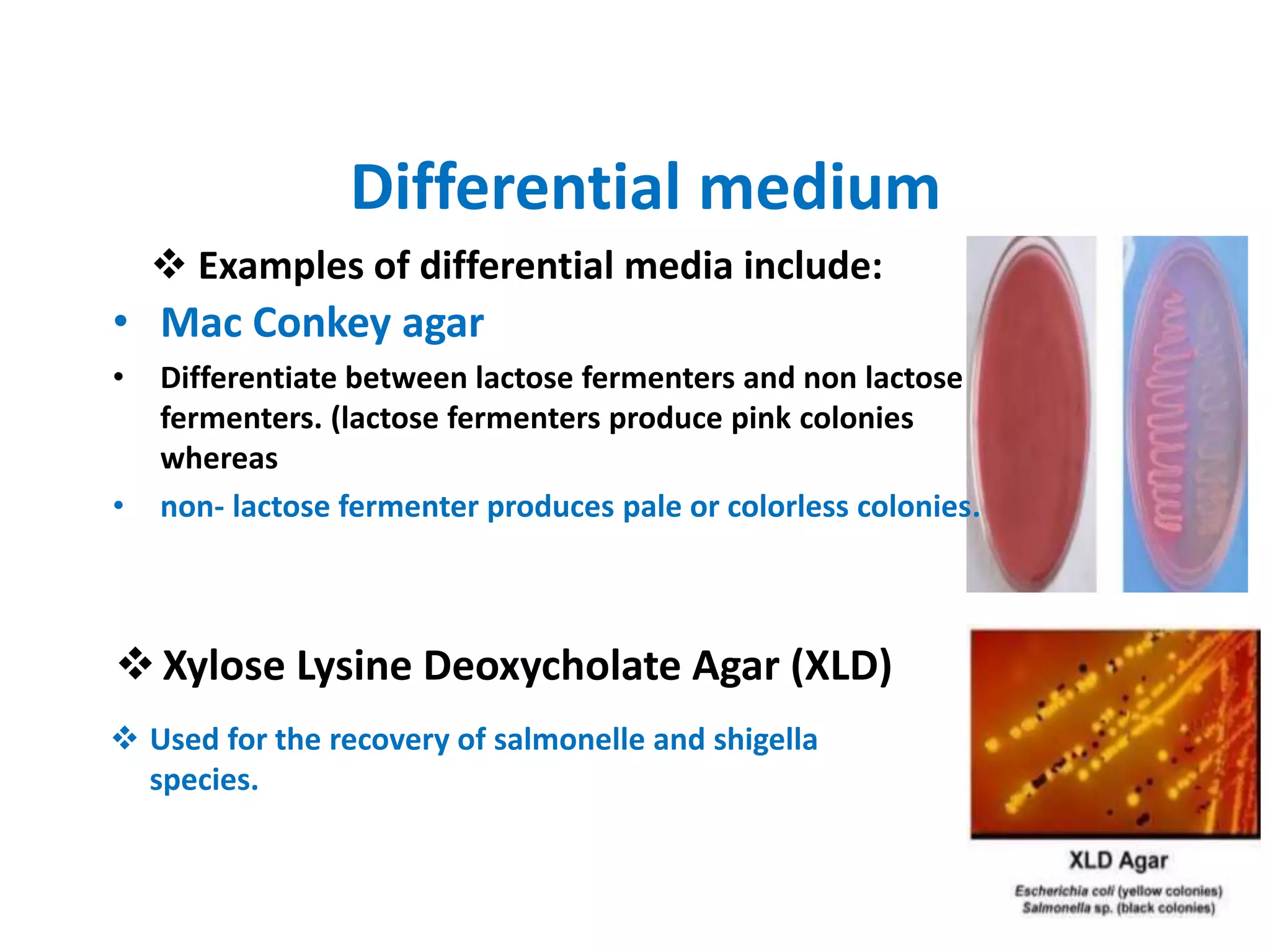
Culture media are used to grow microorganisms outside the body. There are many types of culture media based on their physical state (solid, semi-solid, liquid), chemical composition (synthetic/defined, non-synthetic/undefined), and purpose (general, enriched, selective, differential). Solid media contain agar and allow microbes to grow as colonies. Selective media inhibit unwanted bacteria to recover pathogens. Differential media distinguish bacteria based on colony color. Culture media allow identification and study of microorganisms.