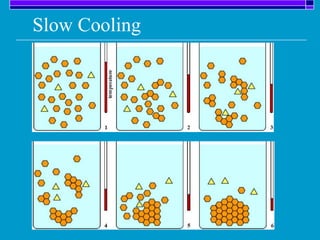
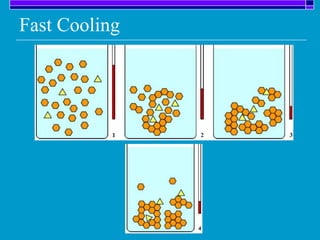
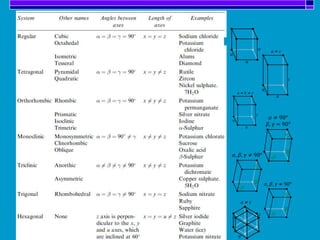
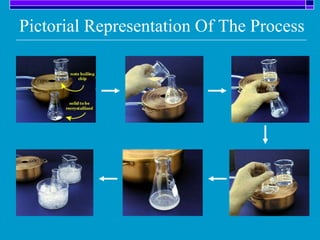
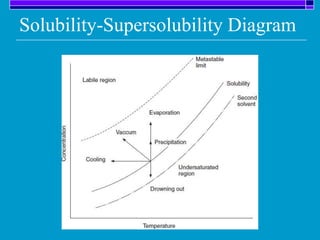
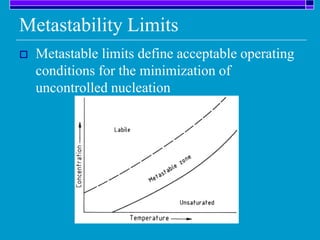
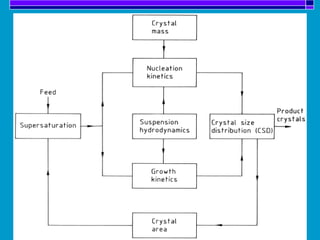
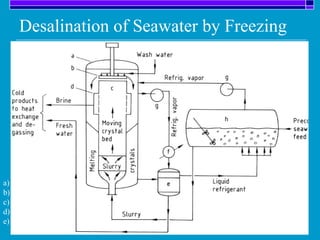
Crystallization is a technique used to purify solid compounds from a homogeneous solution by controlling the formation of solid crystals. It involves two main stages - crystal nucleation where small particles or nuclei form, and crystal growth where the nuclei grow in size. The process is based on principles of solubility where impurities are excluded from the growing crystals which can then be separated. Proper control of factors like cooling rate, agitation, supersaturation, and impurities is important to control crystal size and yield. Various types of crystallizers exist that employ different cooling and agitation methods for continuous crystallization in industrial applications like detergents, fertilizers, foods, and pharmaceuticals.