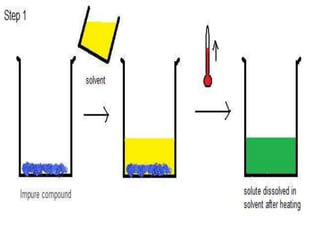
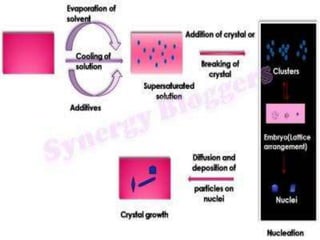
Crystallization is a process where a solid forms from a liquid solution as the atoms or molecules organize into a crystal structure. It involves warming a solution to dissolve the solid, then cooling it in an open container to allow solvent evaporation. This leaves a saturated solution from which crystals will form and grow as it cools further. The size of crystals depends on the cooling rate - fast cooling yields many small crystals, while slow cooling produces fewer but larger crystals. Crystallization is used to purify drugs and improve properties like stability and bioavailability.