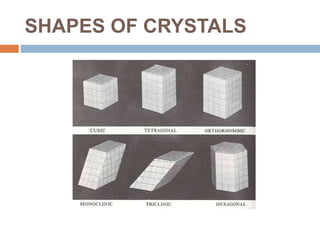
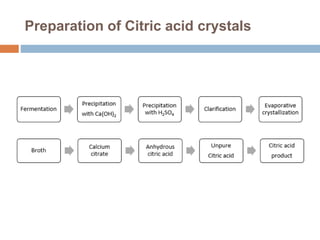
Crystallization is a widely used purification method that relies on a compound's limited solubility in solvents under certain conditions. It involves two stages - formation of nuclei, where clusters reach a critical size to become stable crystals, and crystal growth, where the crystals increase in dimension. Common crystallization types include evaporative, cooling from solution or melt, and reactive/precipitation crystallization. Crystallization produces highly pure solids and has applications in areas like desalination, food processing, and production of materials for electronics and biotechnology.