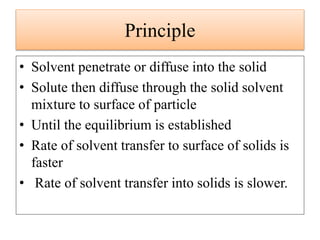
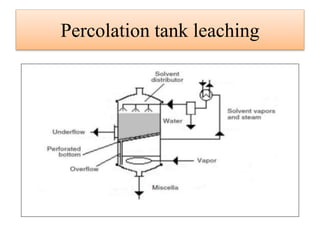
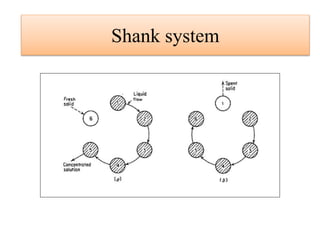
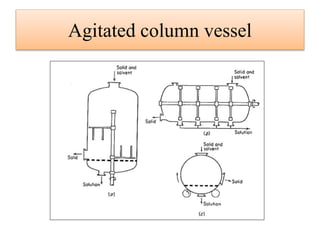
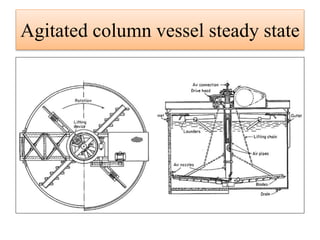
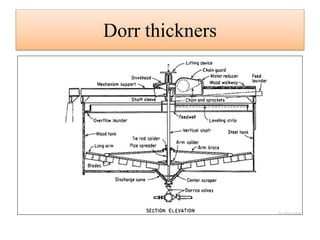
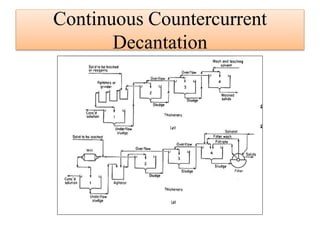
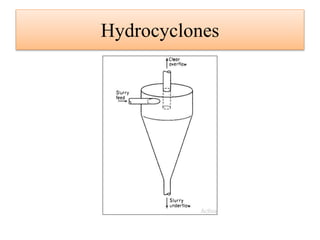
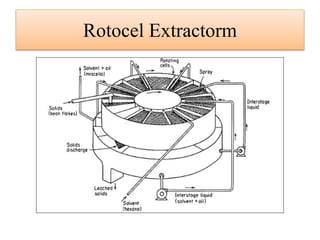
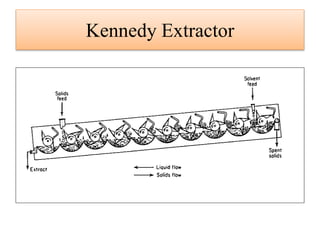
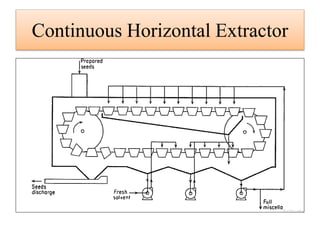
Leaching is a solid-liquid extraction process where one or more constituents of a solid mixture are separated by contact with a liquid solvent. It works on the principles of solvent penetrating the solid, the solute then diffusing through the solid-solvent mixture to the particle surface until equilibrium is established. There are two types - unsteady state processes like in situ leaching and heap leaching, and steady state processes using agitated vessels or continuous countercurrent decantation. Various equipment is used for leaching like percolation tanks, shank systems, agitated column vessels, thickeners, hydrocyclones, and various extractors.