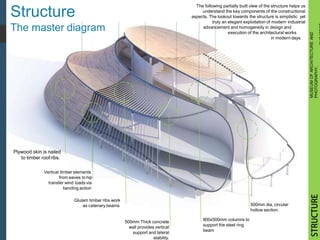
The document presents a case study on the catenary structures used in the design of the Museum of Architecture and Photography in Budapest, highlighting its architectural concept, construction, and material details. Key focus areas include the development process, structural components, and spatial planning to create a seamless integration between the museum's interior and the surrounding park. It concludes with a summary of the design's form development, spatial qualities, and execution details.