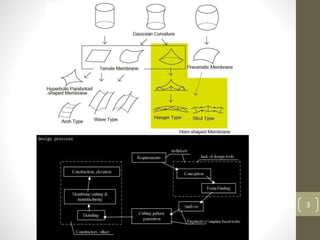
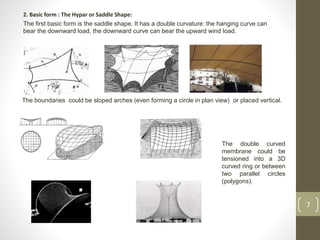
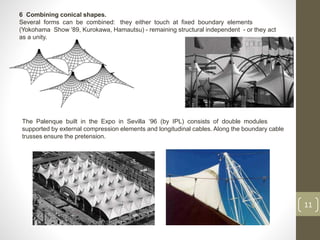
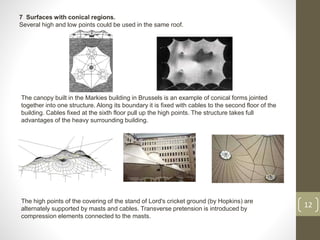
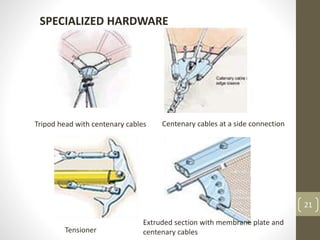
The document discusses membrane structures, which are tensile surface structures made from coated fabrics like PVC and PTFE, offering lightweight, flexible designs with minimal support. It categorizes these structures into pneumatic, tensile membrane, and cable domes, highlighting their unique forms and advantages such as high strength and environmental sensitivity, while also addressing misconceptions about their durability and stability. Additionally, the document covers various architectural forms, material choices, and the evolution of membrane structures within civil engineering and architecture.