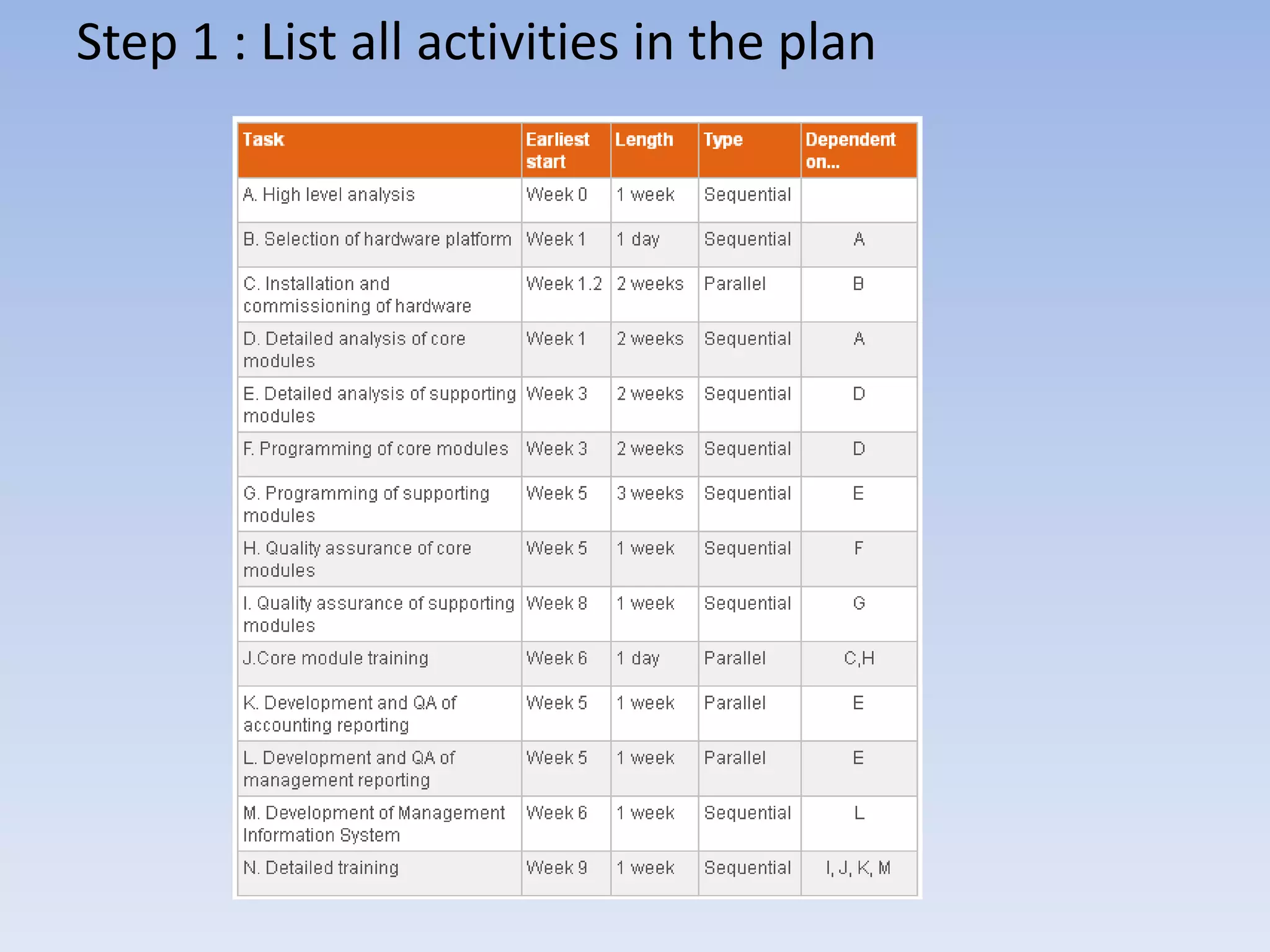
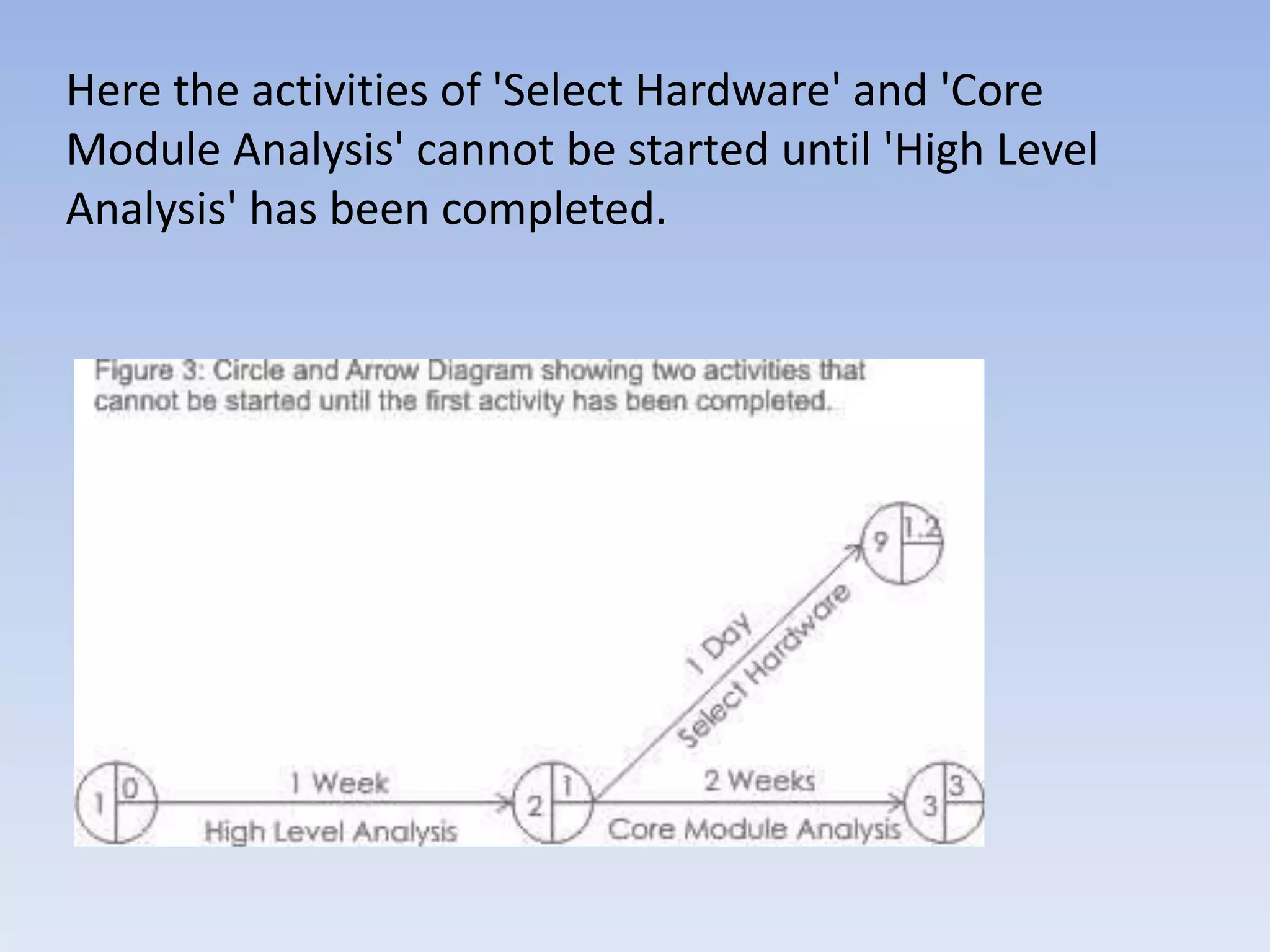
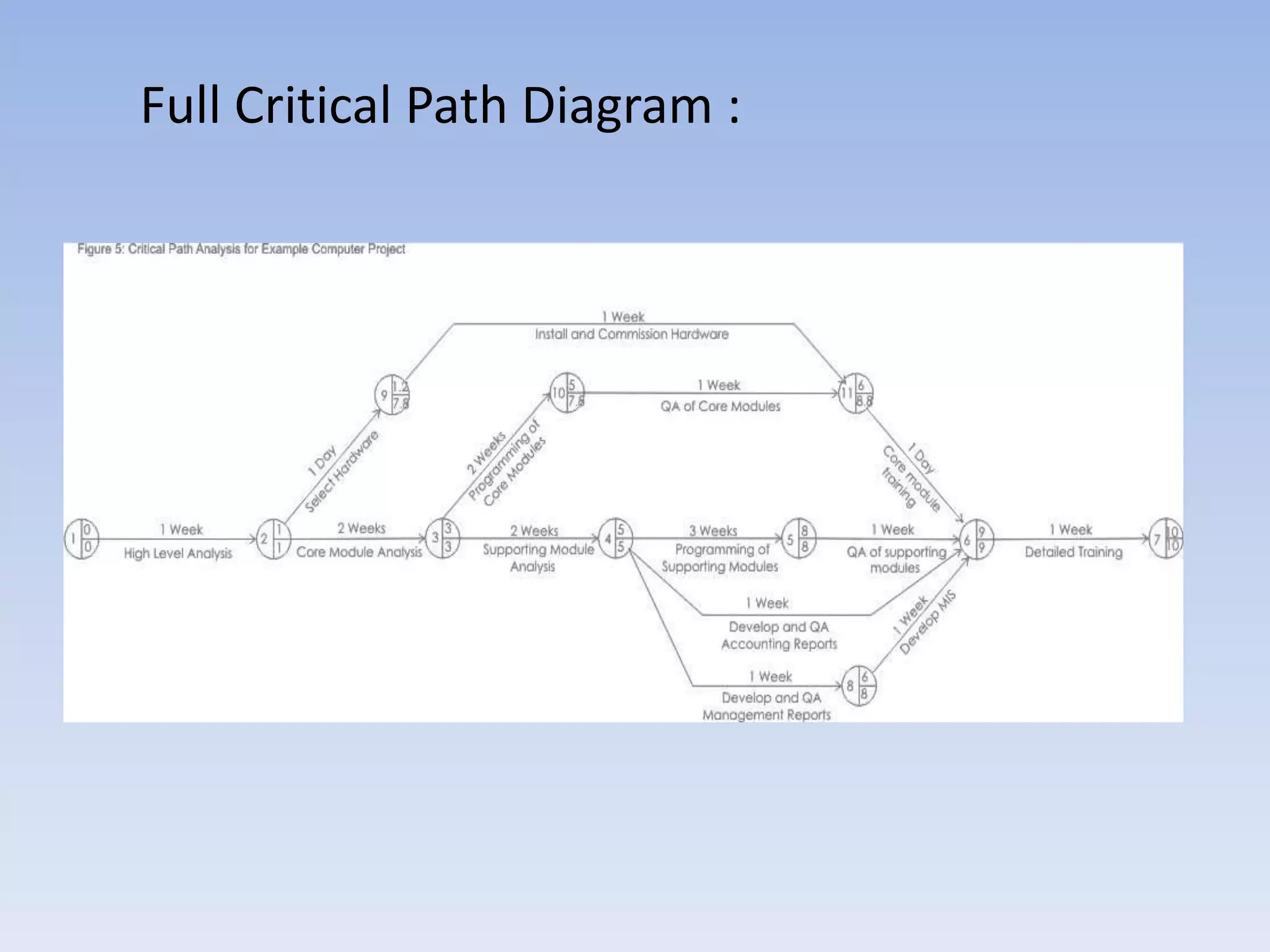
Critical Path Analysis (CPA) and Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) are project management tools used to schedule complex projects. CPA identifies the critical path of tasks that must be completed on time for the project to finish on time. It also identifies non-critical parallel tasks. PERT is similar but takes a more conservative approach to estimating task durations. Both help project managers monitor progress and determine where to take remedial action if the project falls behind schedule.