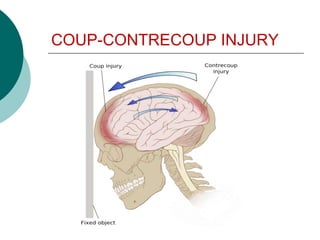
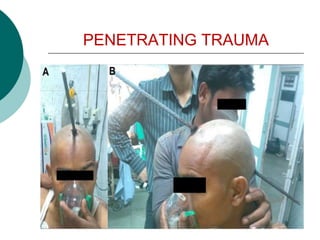
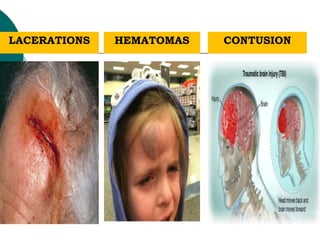
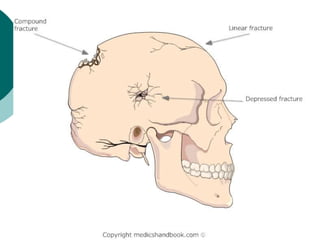
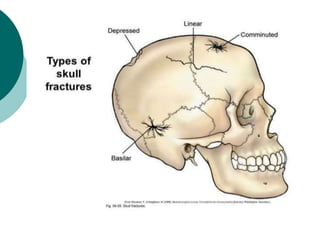
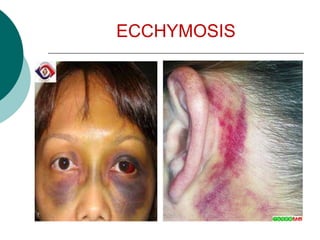
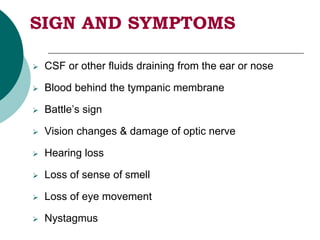
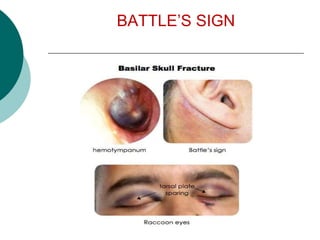
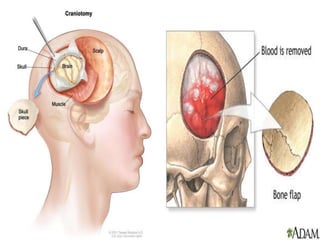
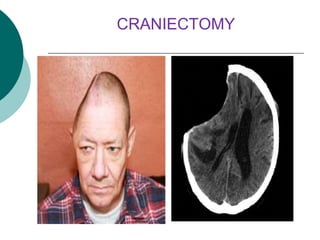
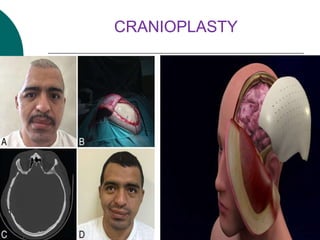
This document discusses head injuries, including traumatic brain injury caused by external forces. Common causes are motor vehicle accidents, falls, assaults, and sports injuries. Mechanisms of injury include coup-contrecoup injuries where impact causes injury on both sides of the brain. Skull fractures and brain injuries like concussions and contusions can occur. Signs and symptoms include headache, vomiting, seizures and loss of consciousness. Diagnostic tests include CT scans, MRI and X-rays. Management focuses on ABCs, controlling intracranial pressure, oxygenation and surgery if needed. Nursing diagnoses address issues like impaired mobility, anxiety and knowledge deficits.