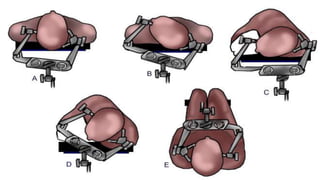
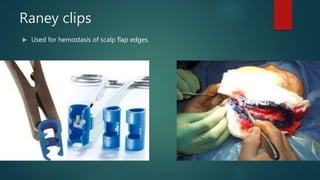
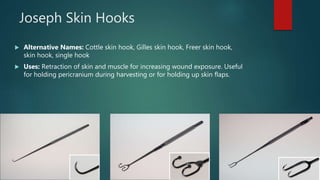
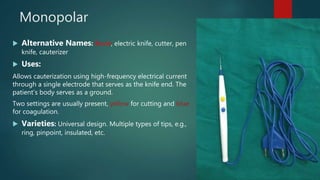
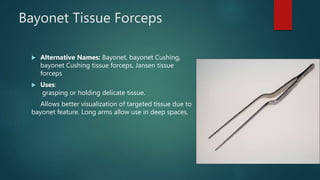
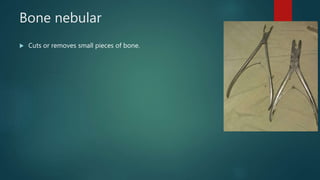
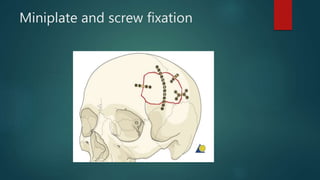
This document lists and describes the essential instruments used in craniotomy procedures. It begins by defining craniotomy as the surgical removal of part of the skull to access the brain. It then lists and provides details on scalpels, suction devices, clips, electrosurgical units, elevators, drills, plate and screw sets, and other instruments used to position, expose, cut, and retract tissues during craniotomy. Positioning involves fixing the head with pins inserted into the skull. Precise cutting and coagulation is enabled by monopolar and bipolar electrosurgical tools. Retractors such as fish hooks and skin hooks are used to improve exposure by retracting skin and bone flaps.