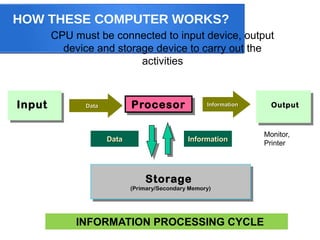
The document provides an overview of the CPU, explaining its role as the brain of the computer responsible for processing instructions and managing input/output operations. It discusses components such as multi-core processors, cache memory, and the control unit, alongside factors affecting processing speed. The document also outlines the connection of the CPU to various devices and presents some examples of CPU models.