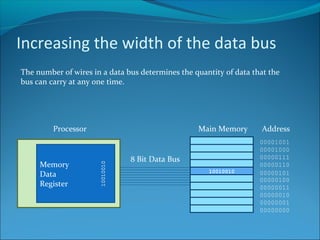
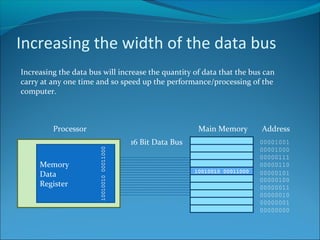
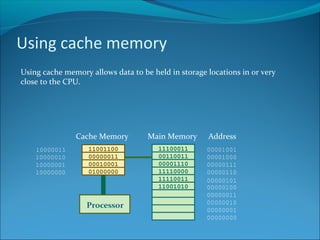
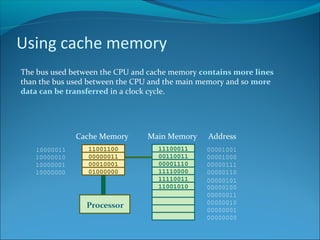
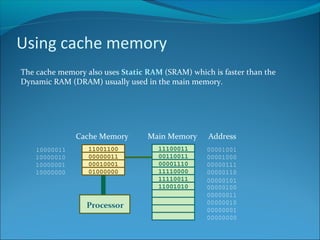
Increasing the width of the data bus allows more data to be transferred at once, speeding up processing. A 32-bit computer has a 32-line data bus and 32-bit word length. Cache memory holds frequently used data close to the CPU, allowing faster access via a wider bus and faster SRAM than main memory DRAM. Peripherals operate slower than the CPU, so increasing interface transfer rates like USB and Firewire versions improves performance. Some peripherals have their own processors and RAM to help speed performance.