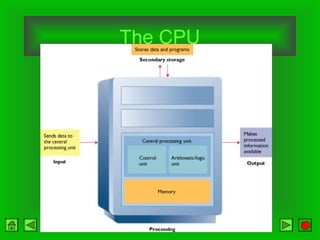
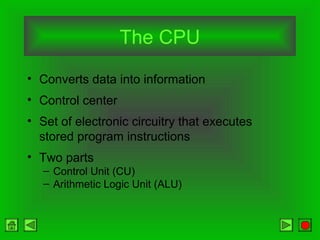
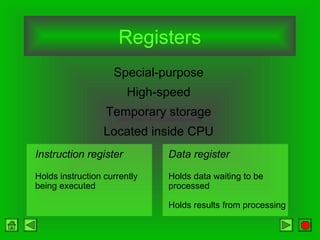
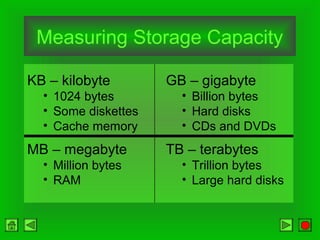
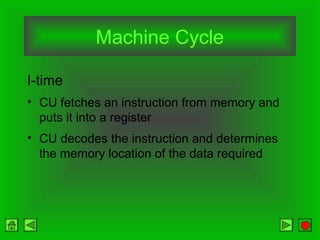
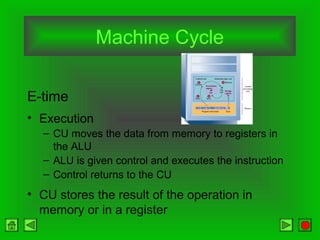
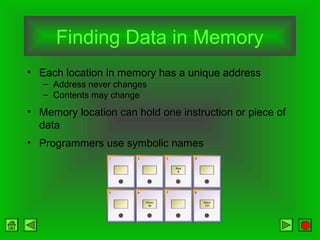
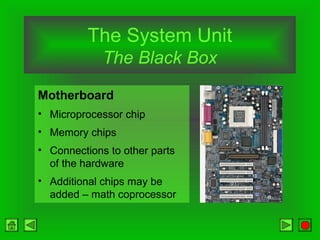
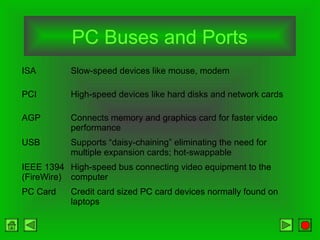
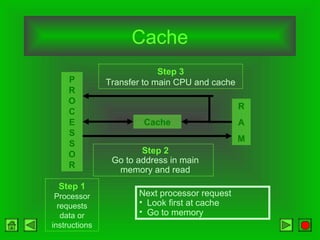
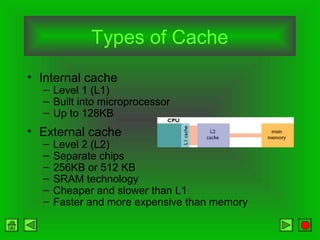
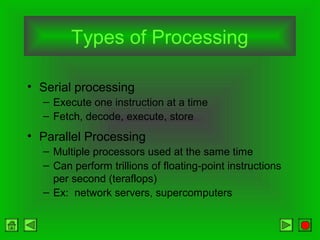
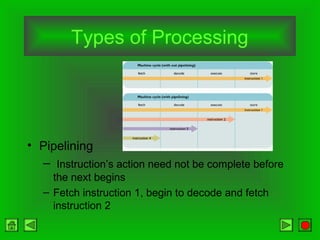
The CPU consists of a control unit and arithmetic logic unit that work together to execute instructions. The control unit fetches and decodes instructions while directing other hardware. The ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations on data from registers or memory. Memory holds both instructions and data for processing and comes in volatile RAM and non-volatile ROM forms. Faster microprocessors, larger bus widths, cache memory, and parallel processing all contribute to increased computer processing speed.