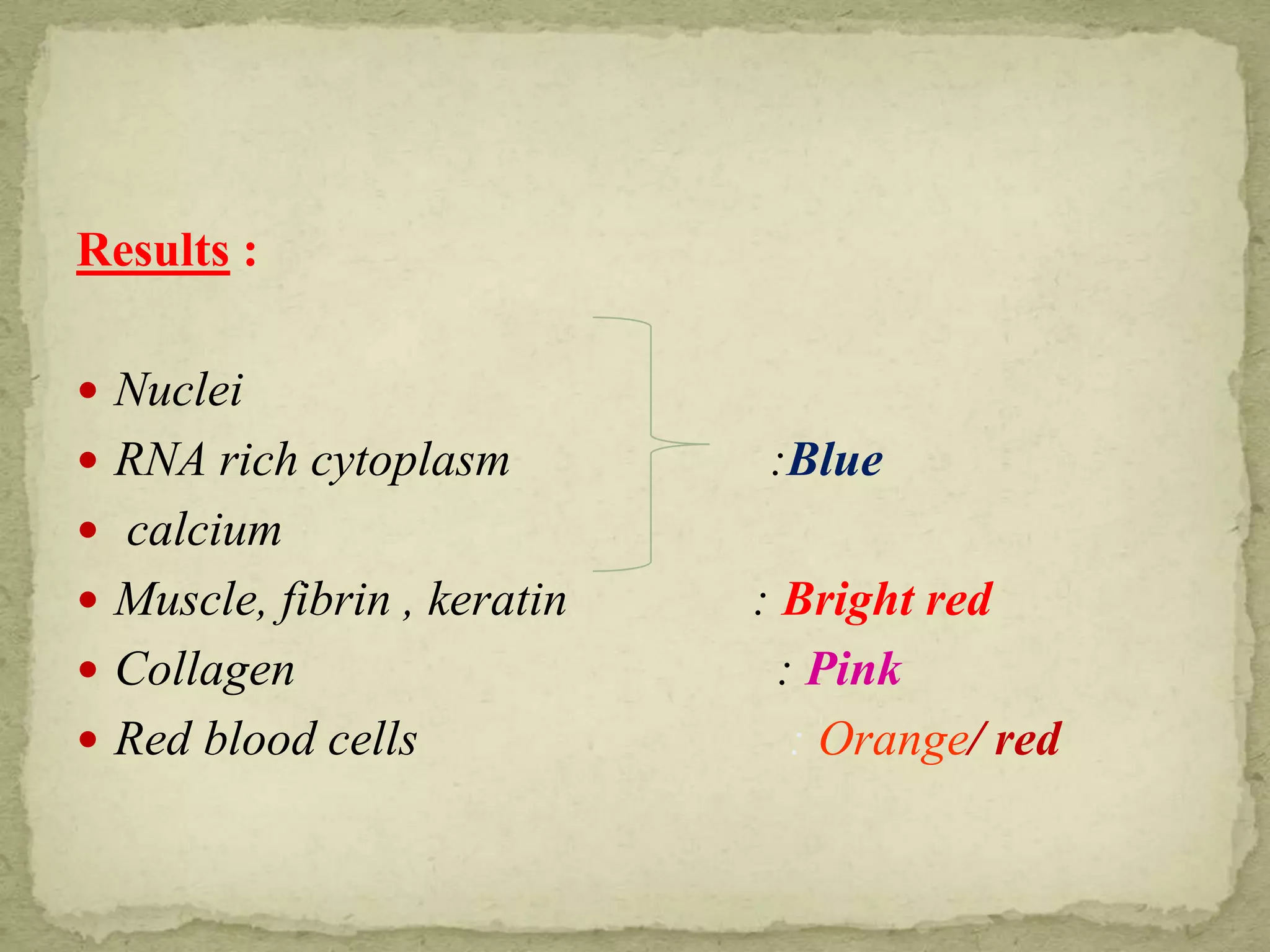
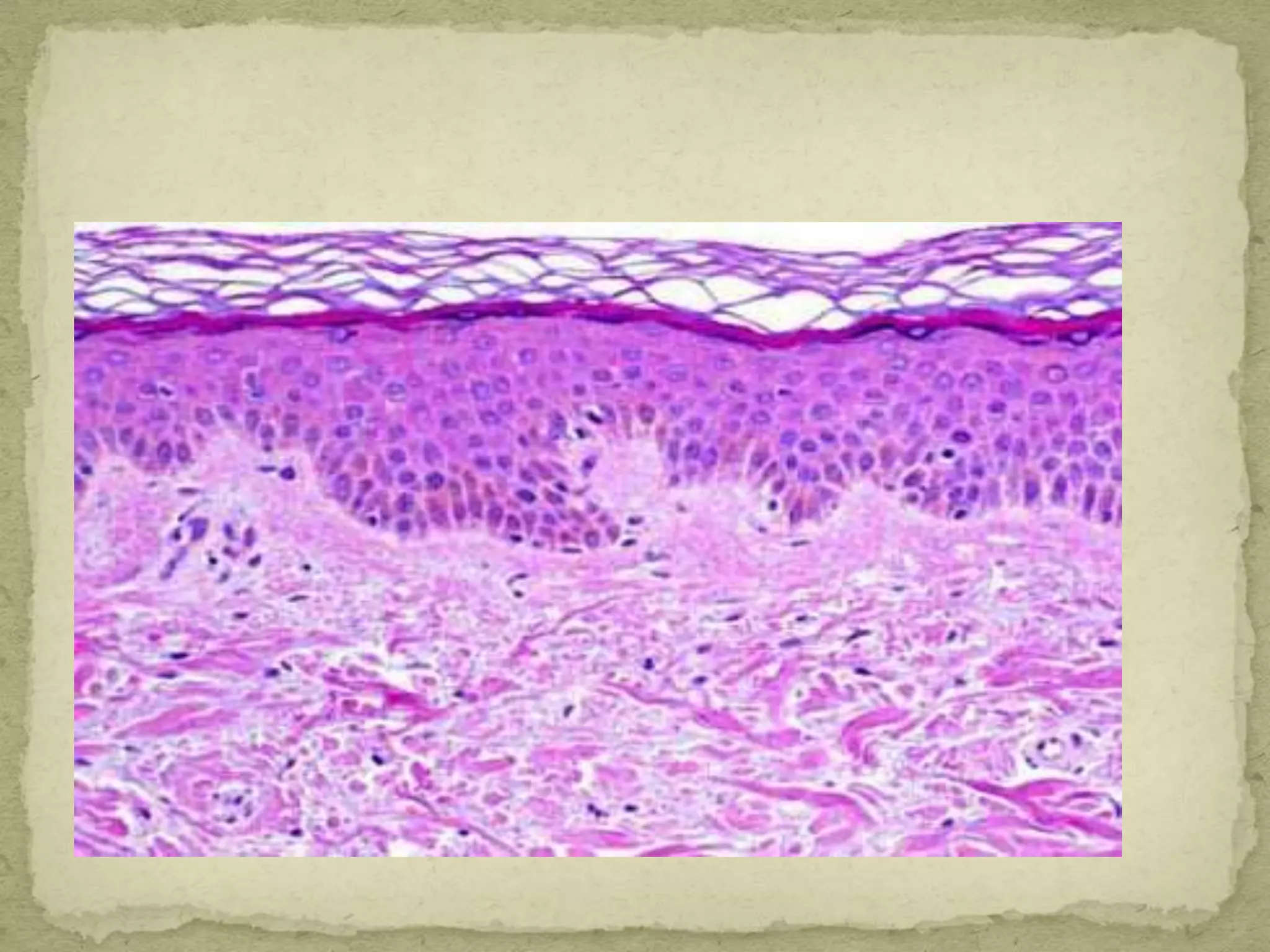
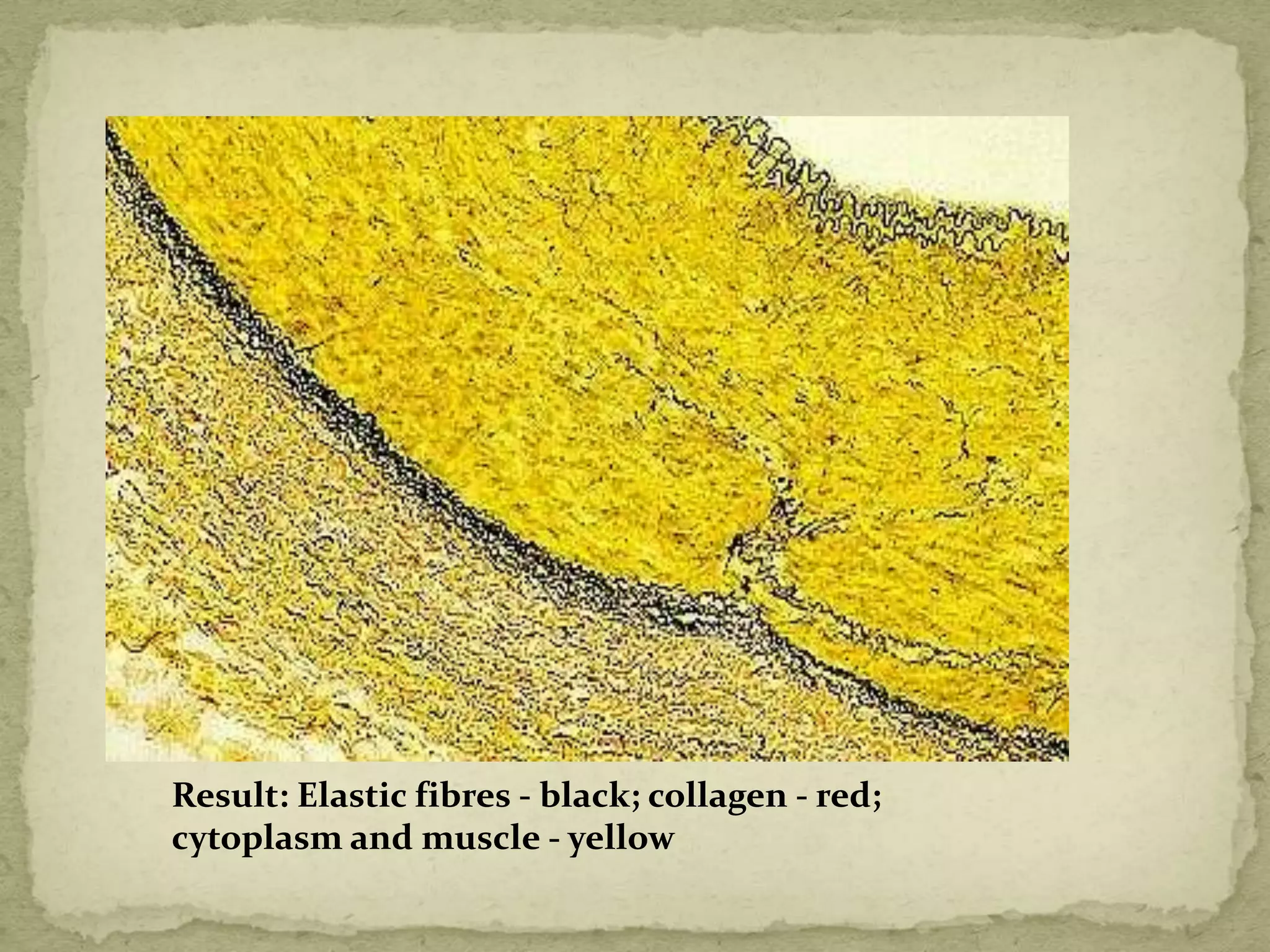
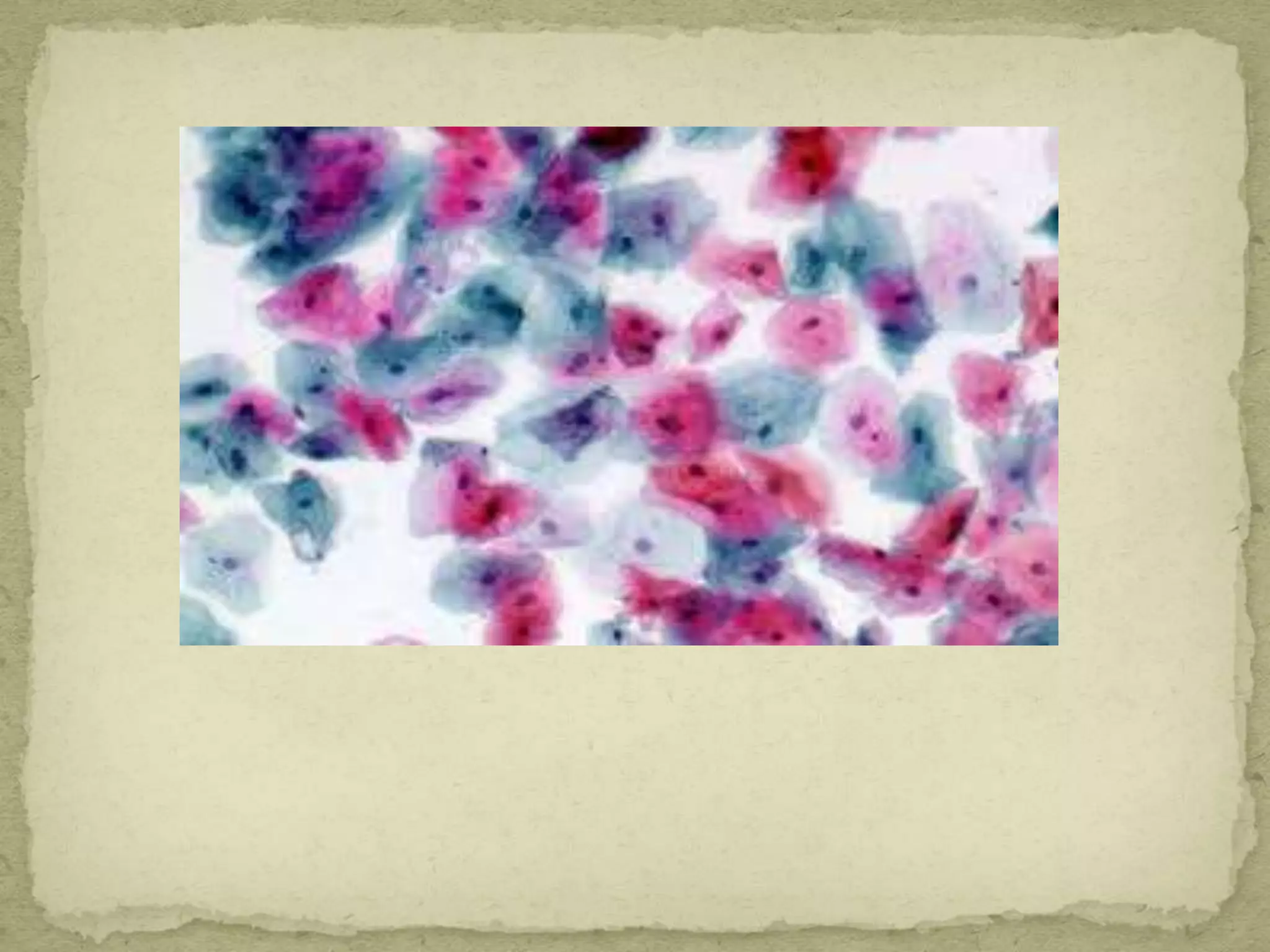
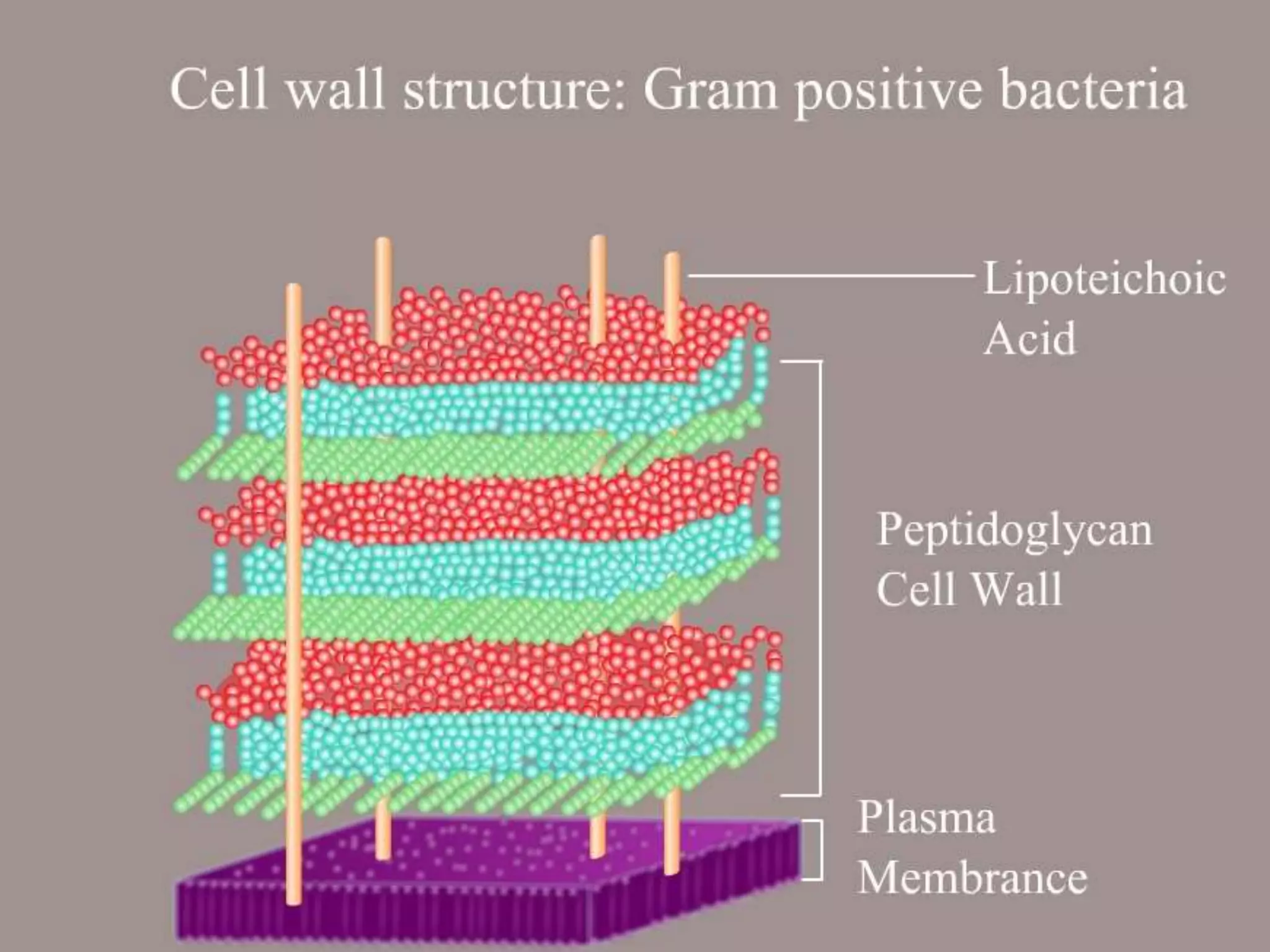
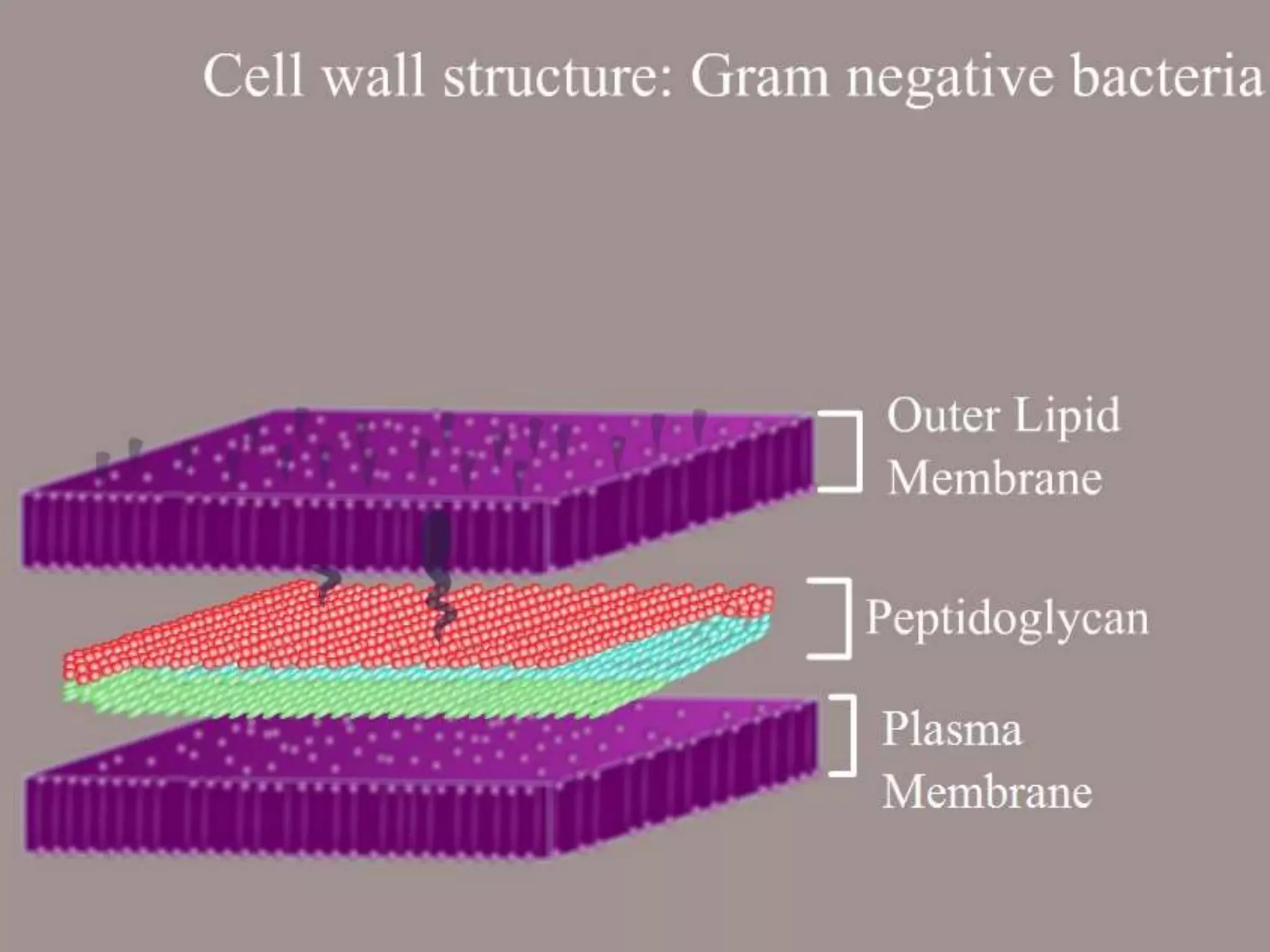
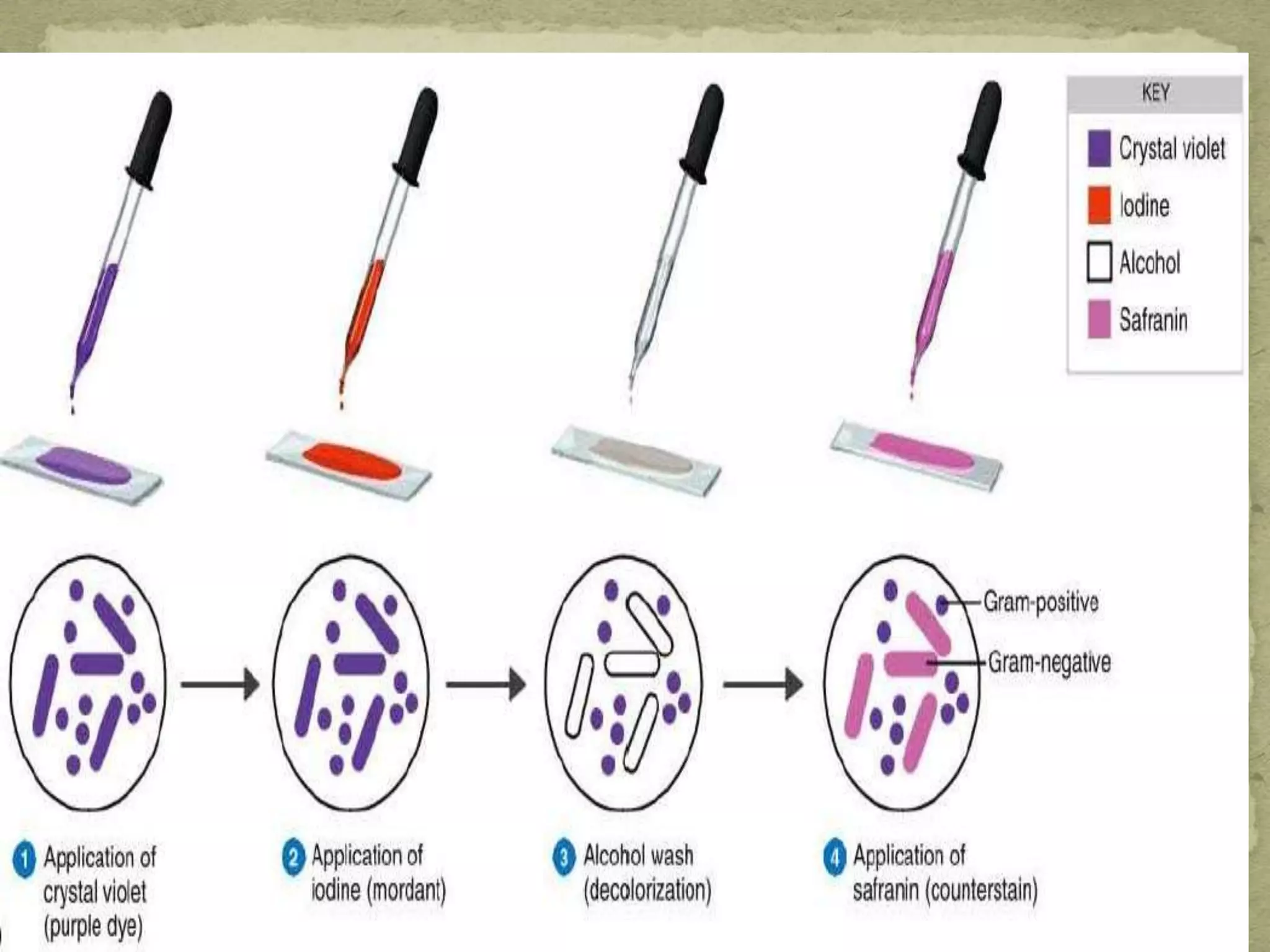
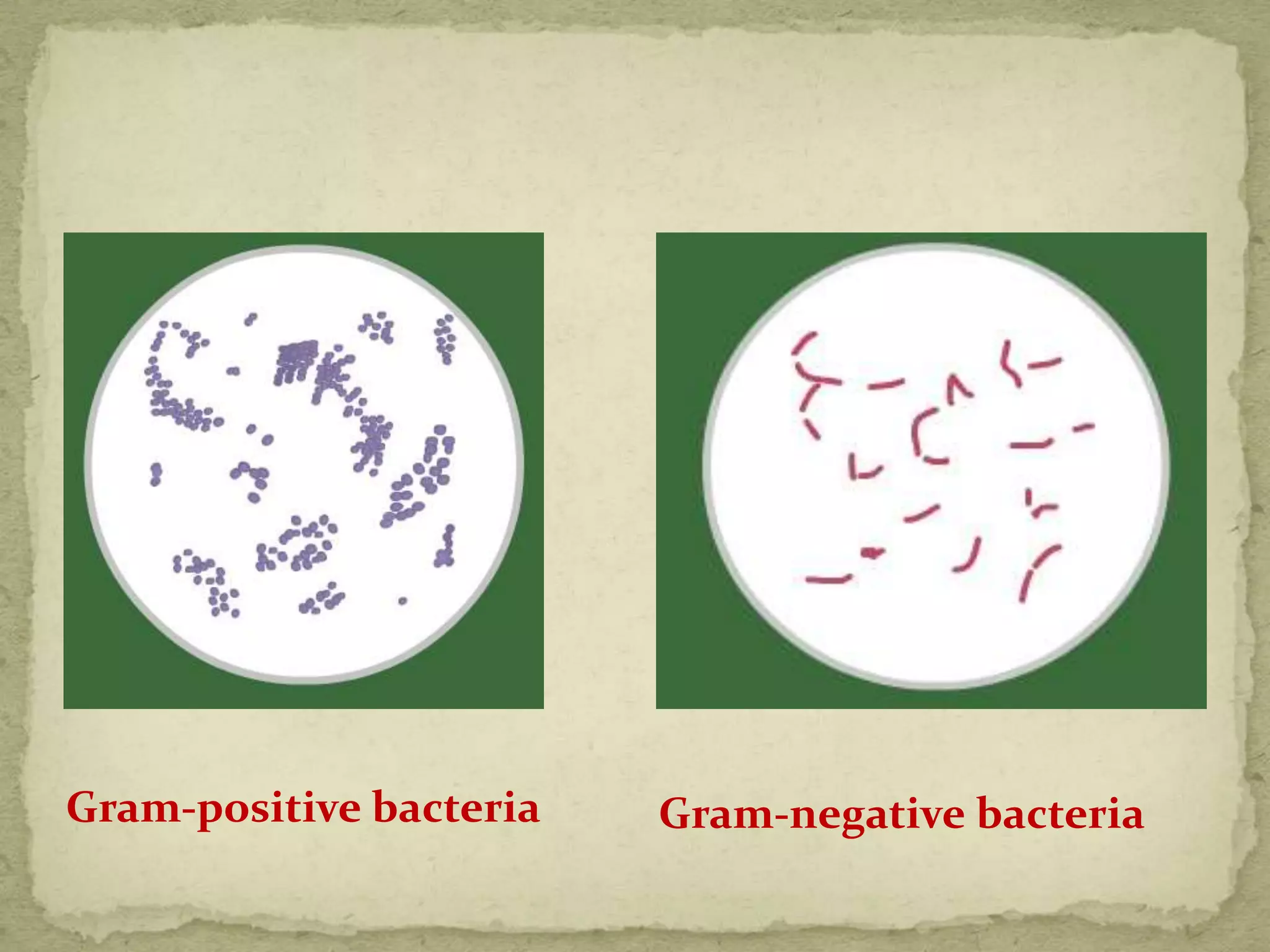
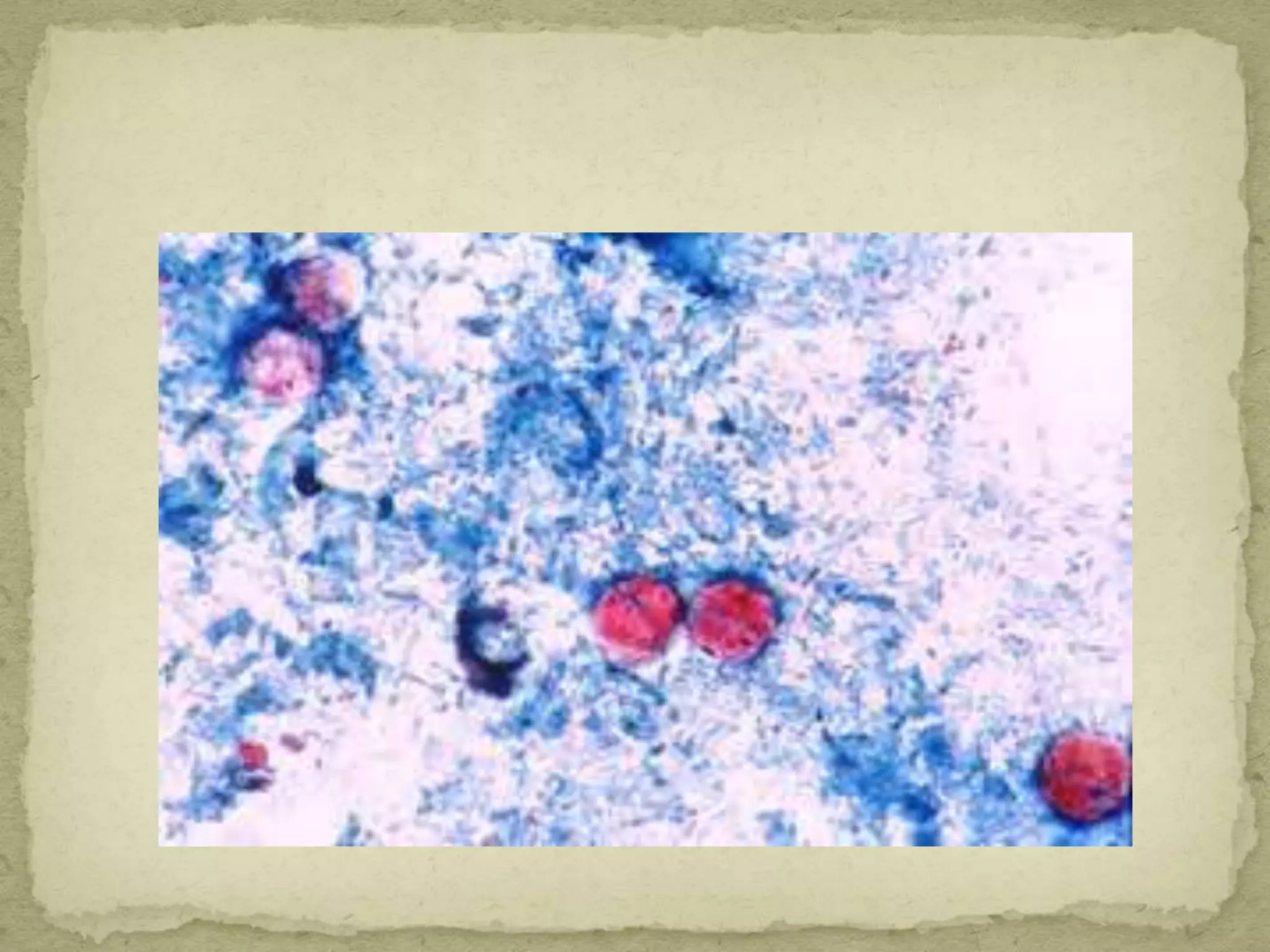
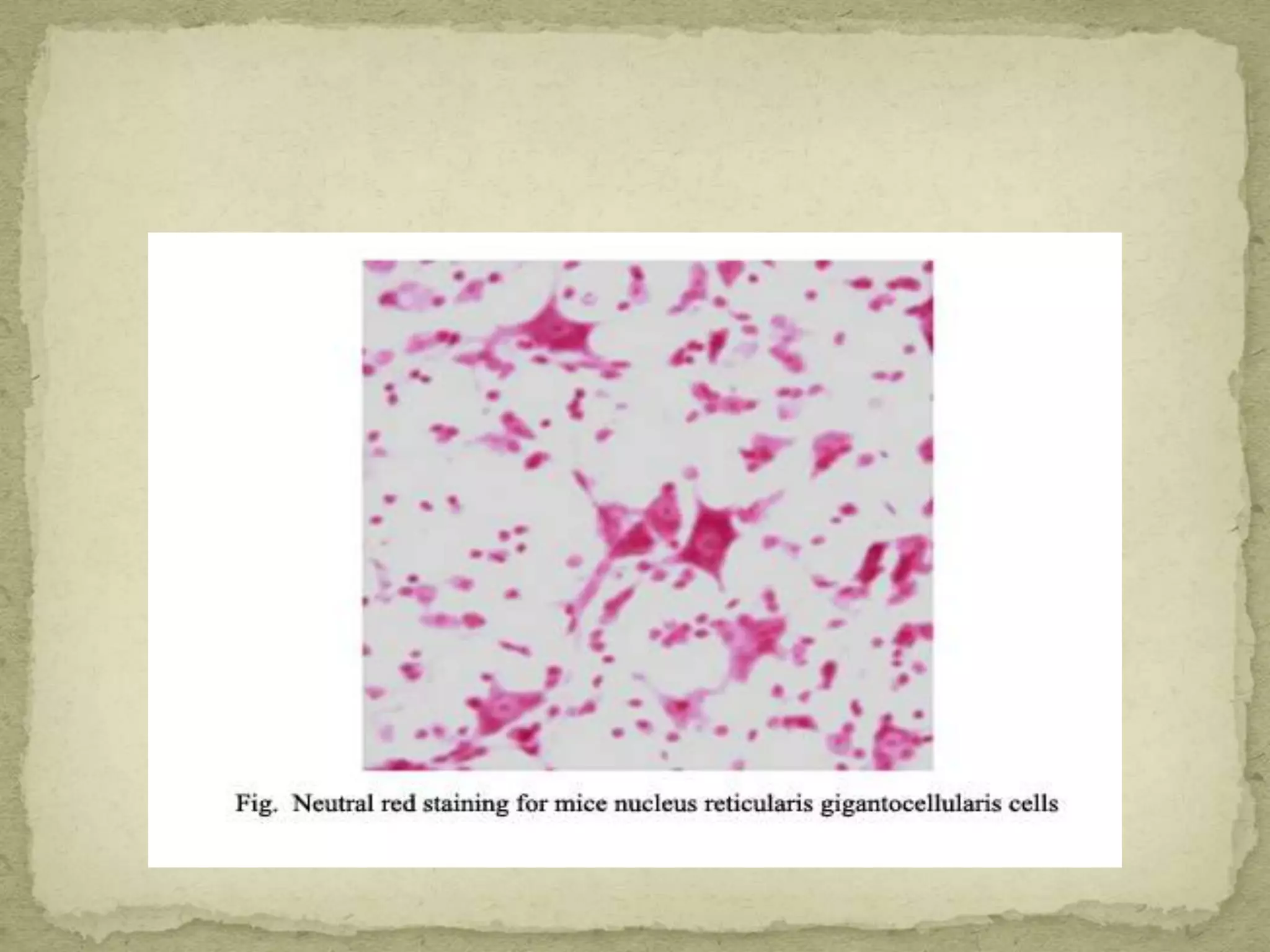
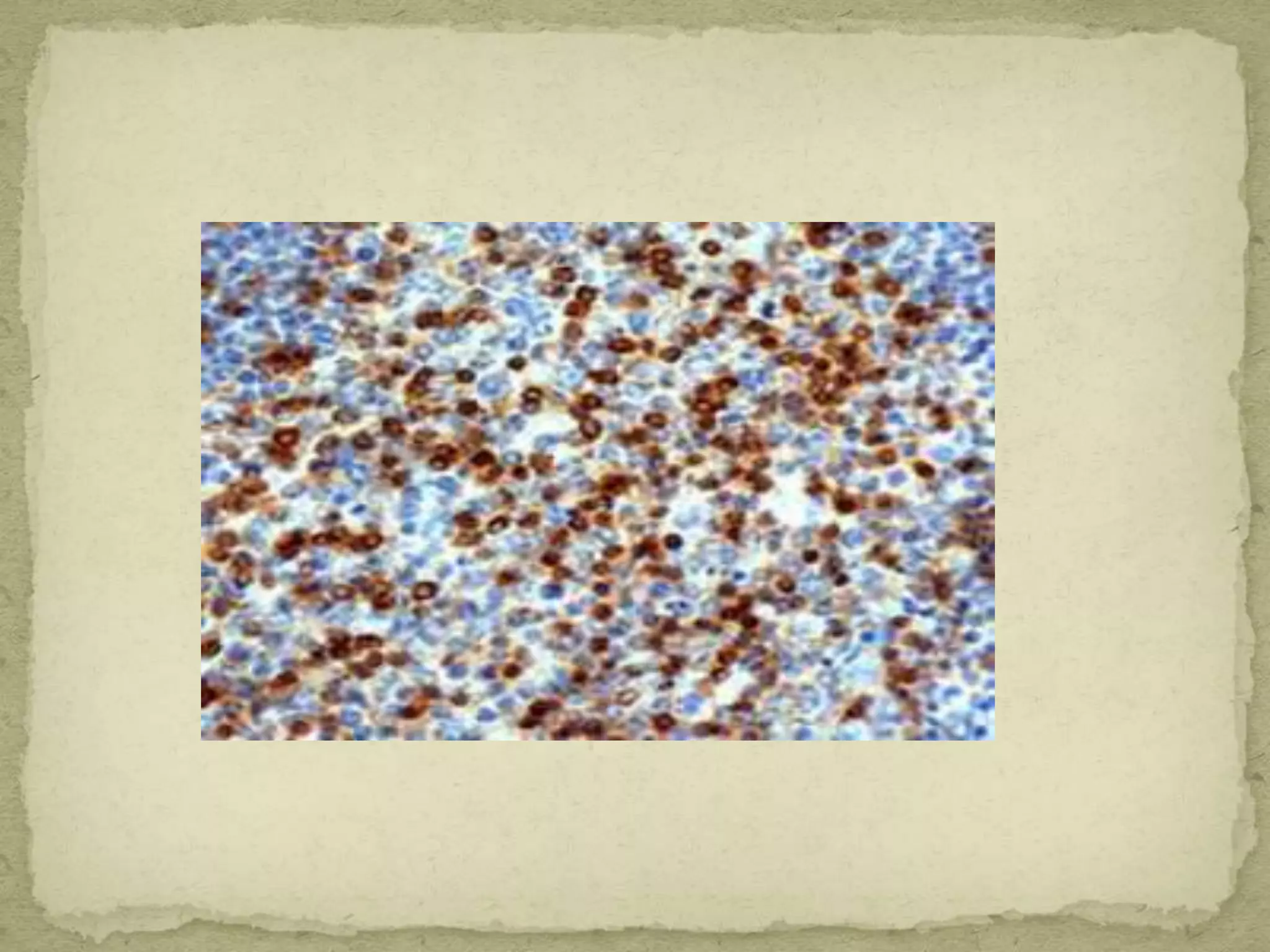
The Gram staining method differentiates bacteria into Gram-positive and Gram-negative groups based on differences in their cell wall structure. Gram-positive bacteria retain the primary purple stain due to their thick peptidoglycan layer, while Gram-negative bacteria are decolorized and take up the pink counterstain due to their thinner peptidoglycan layer and outer membrane. The procedure involves staining with crystal violet, iodine mordant, decolorization with alcohol, and counterstaining with safranin.