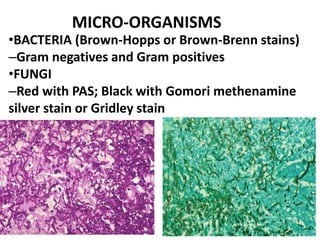
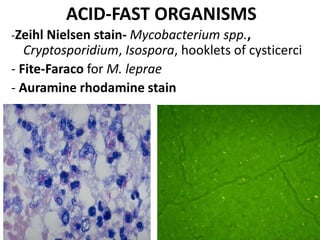
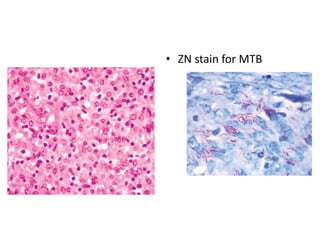
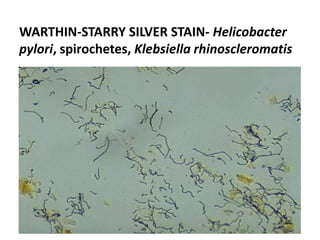
Ziehl-Neelsen stain uses carbol fuchsin to stain mycobacteria pink to red and a counterstain of methylene blue or malachite green. Fite acid fast stain combines peanut oil and xylene to retain acid fastness of mycobacteria stained red. Periodic acid Schiff stain oxidizes glycans magenta to demonstrate substances like glycogen, fungi, and mucins, using liver and intestine as controls.