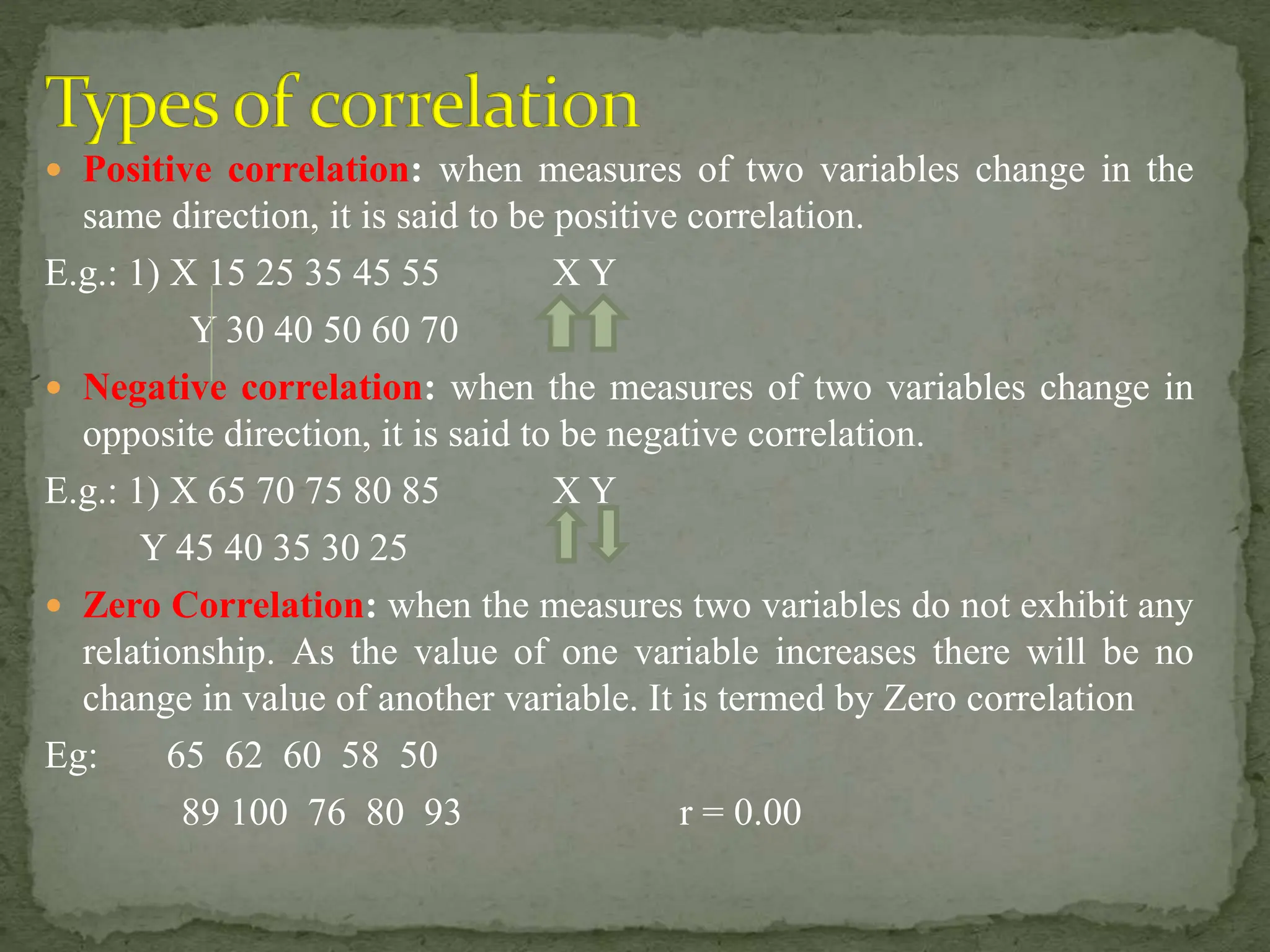
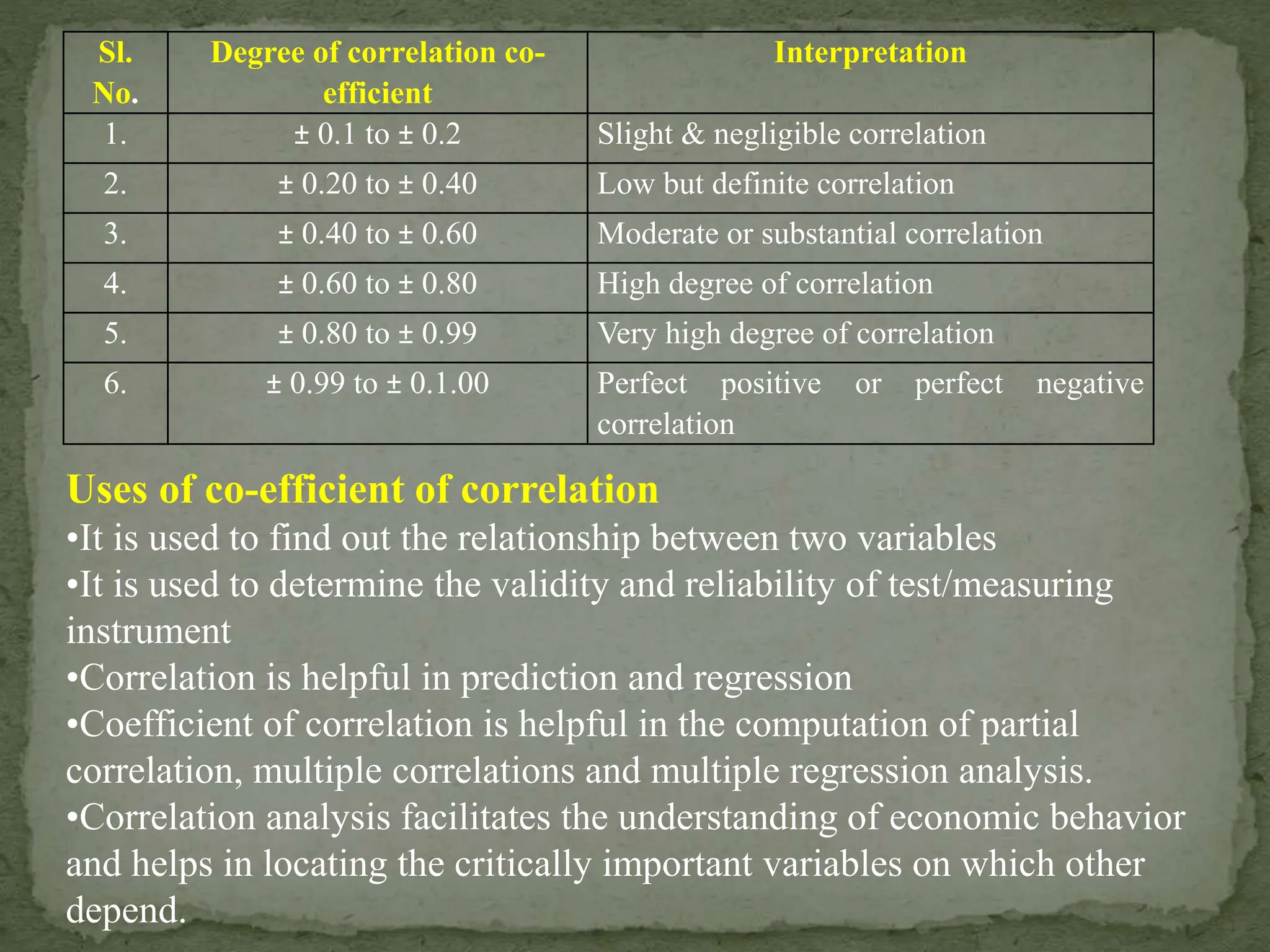
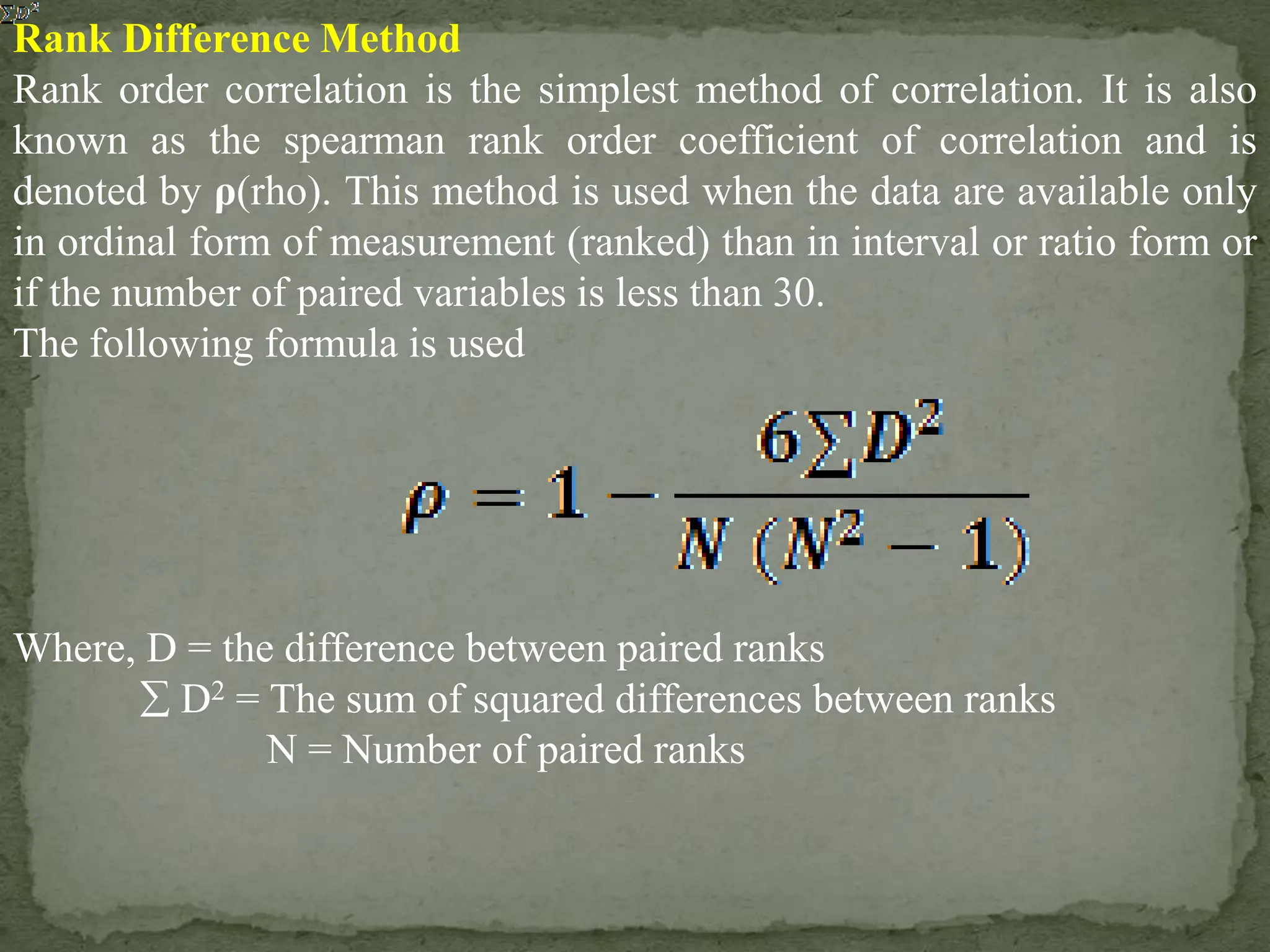
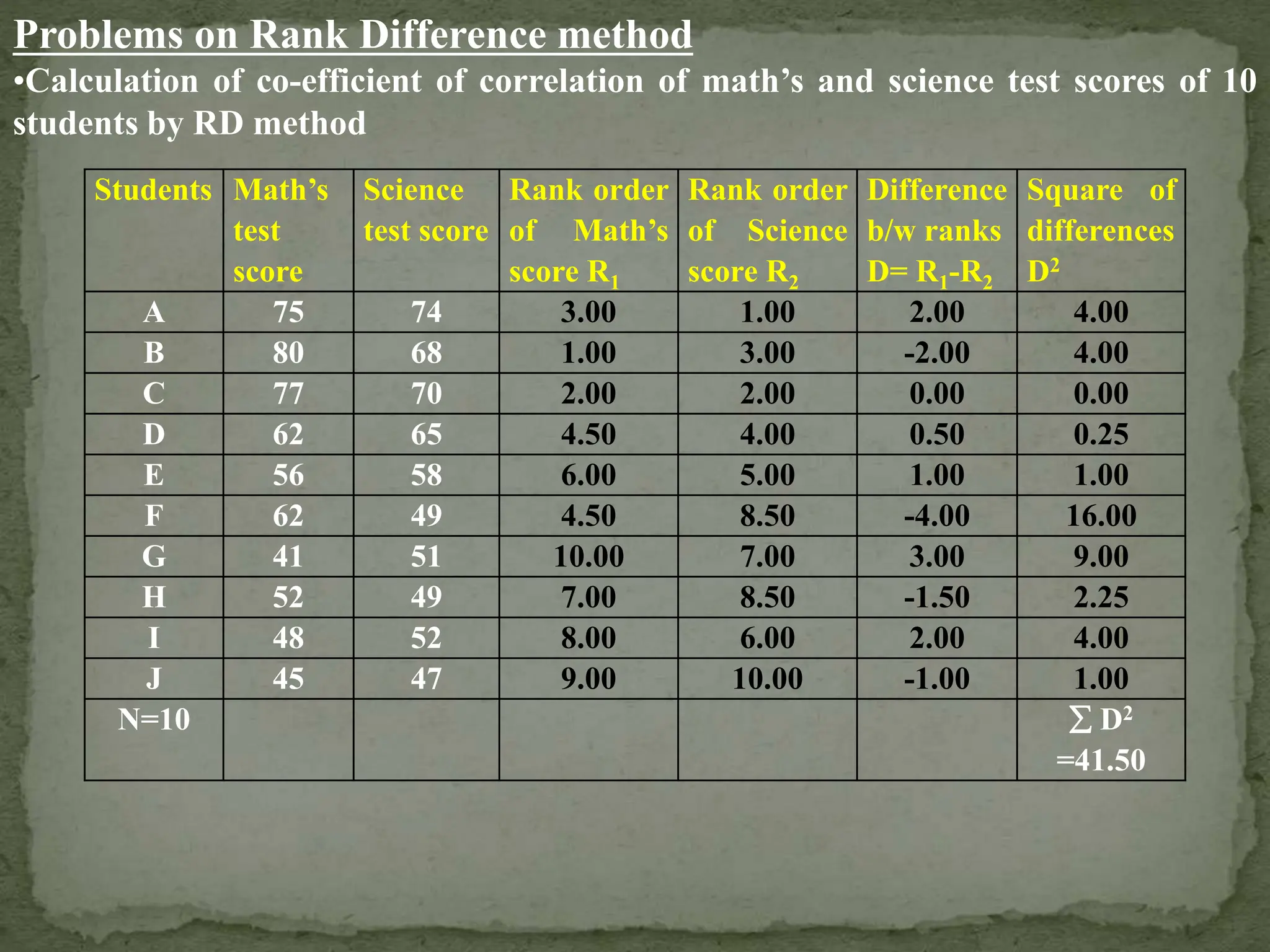
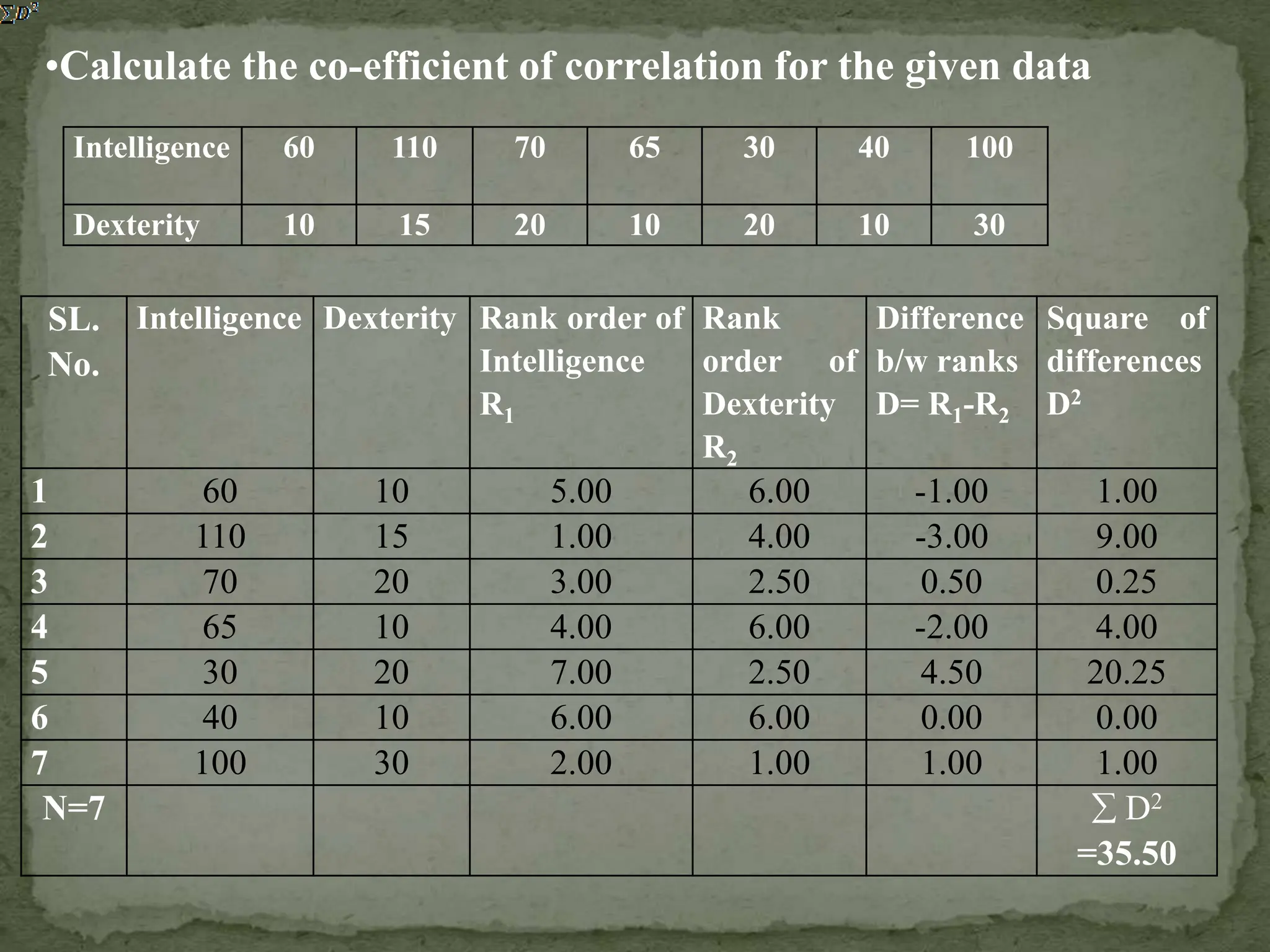
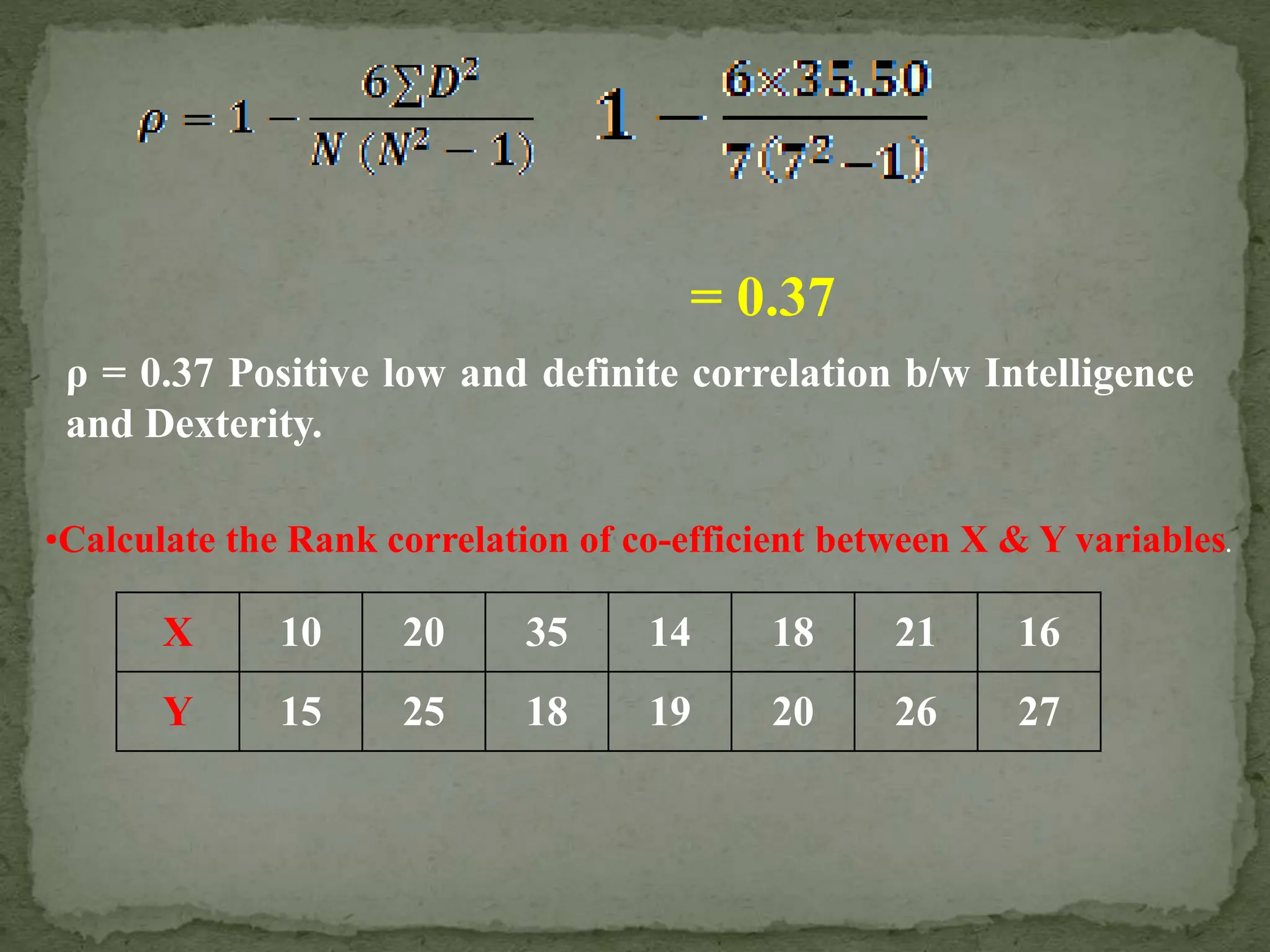
The document discusses the concept of correlation in educational research, detailing various types and methods to calculate the correlation coefficient using the rank difference method. It explains positive, negative, and zero correlation, as well as linear and non-linear relationships between variables, emphasizing the importance of these concepts in understanding relationships in educational data. The limitations of rank order correlation, particularly its application to datasets with less than 30 scores, are also highlighted.