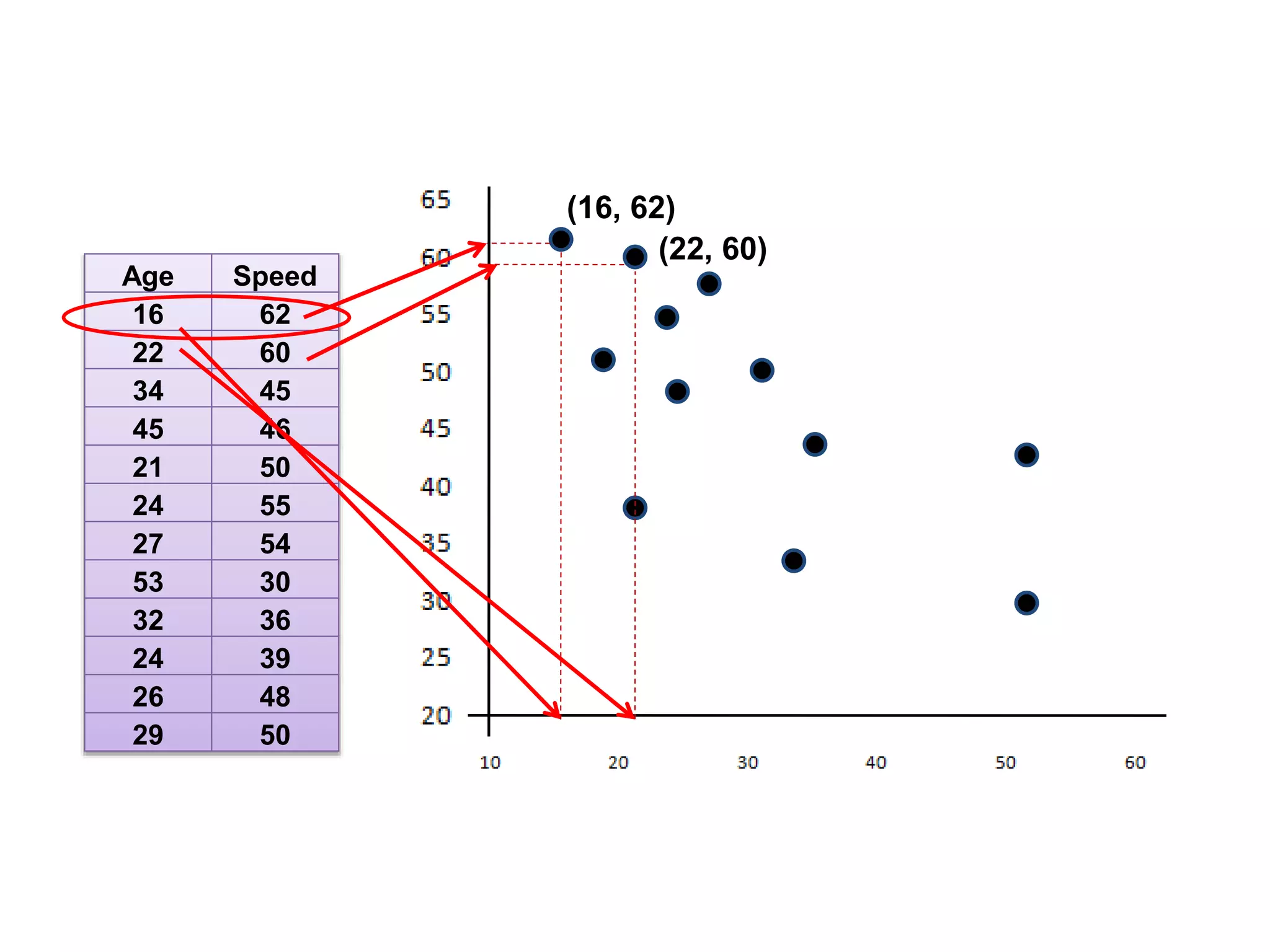
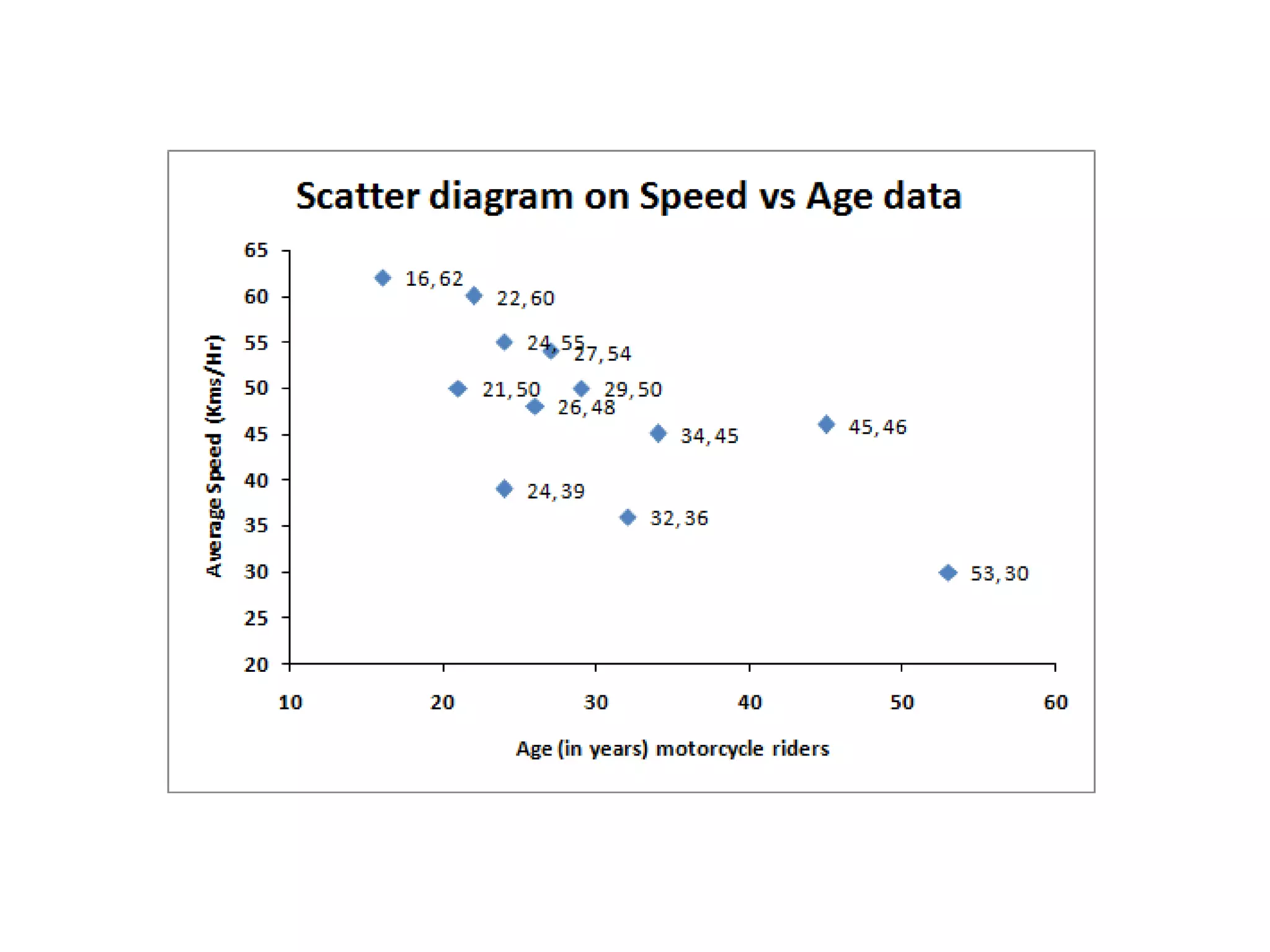
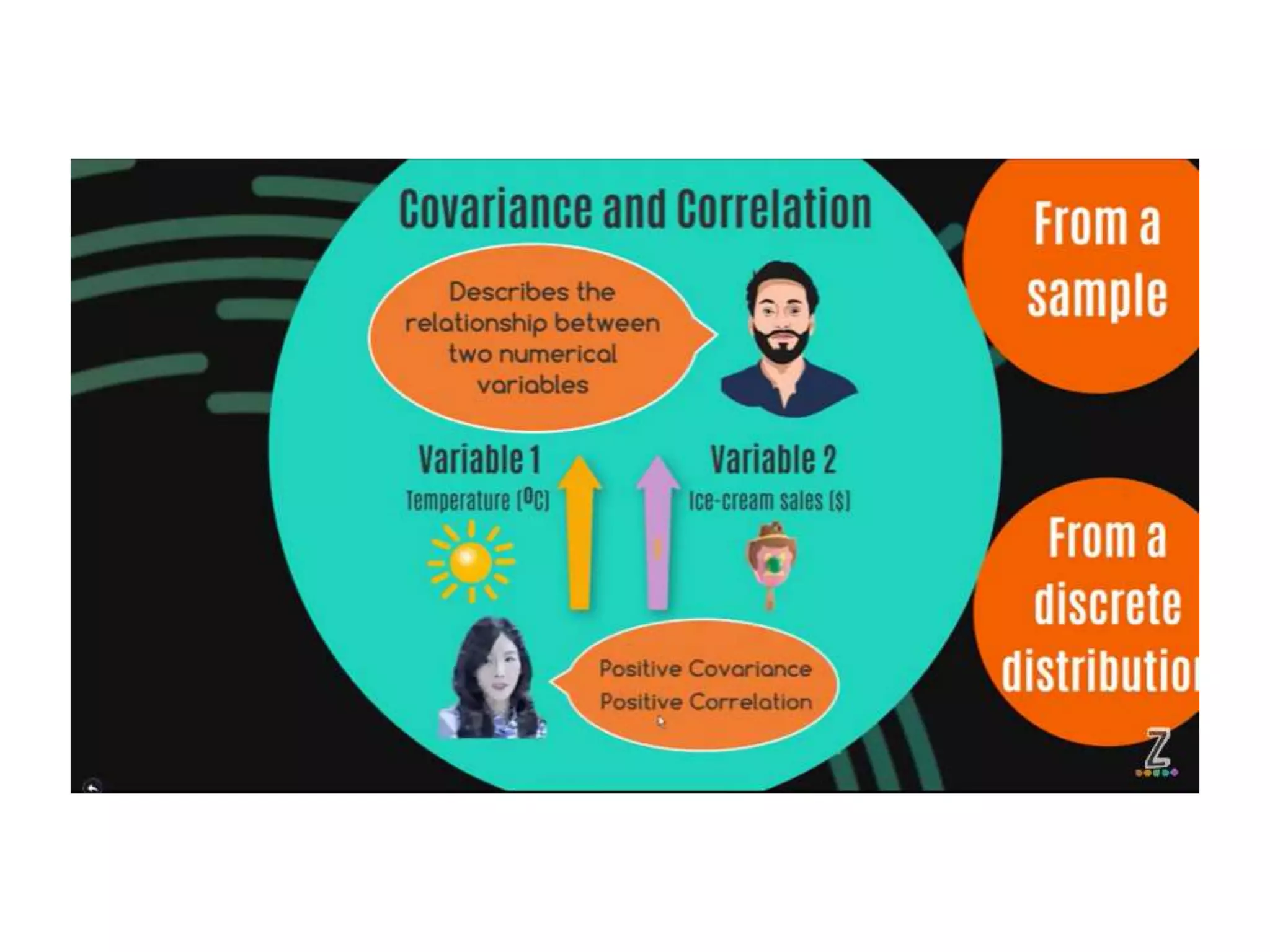
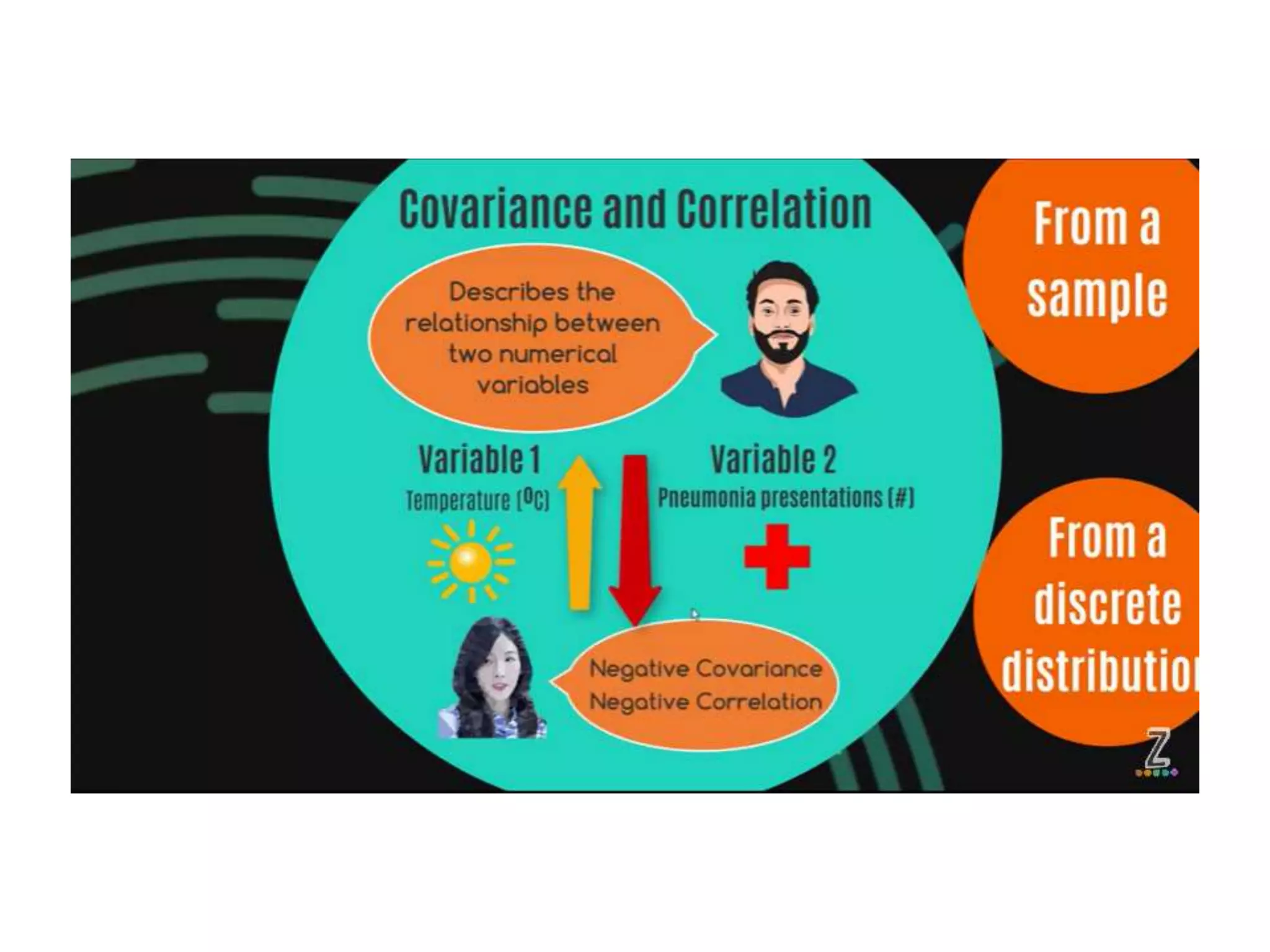
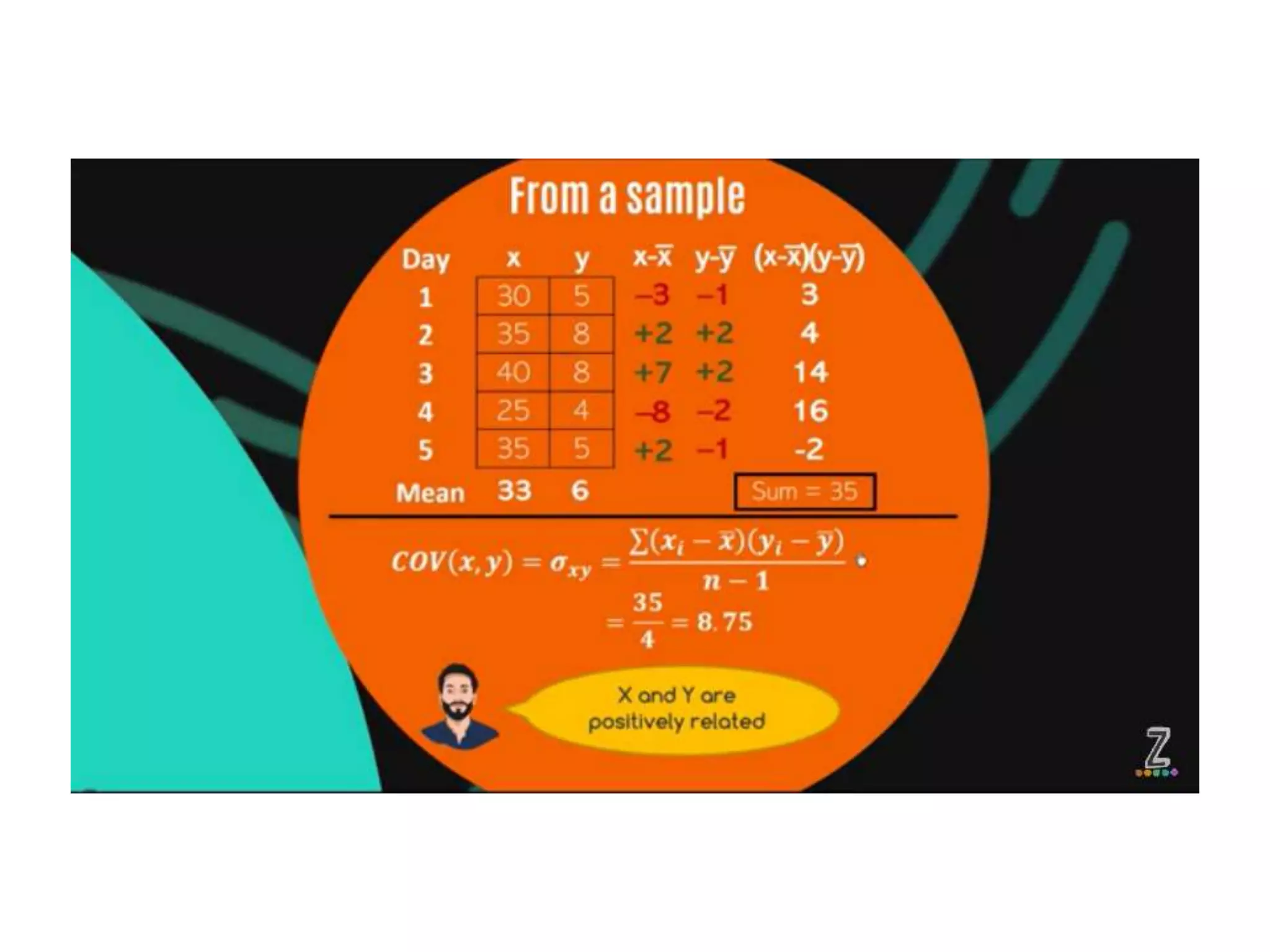
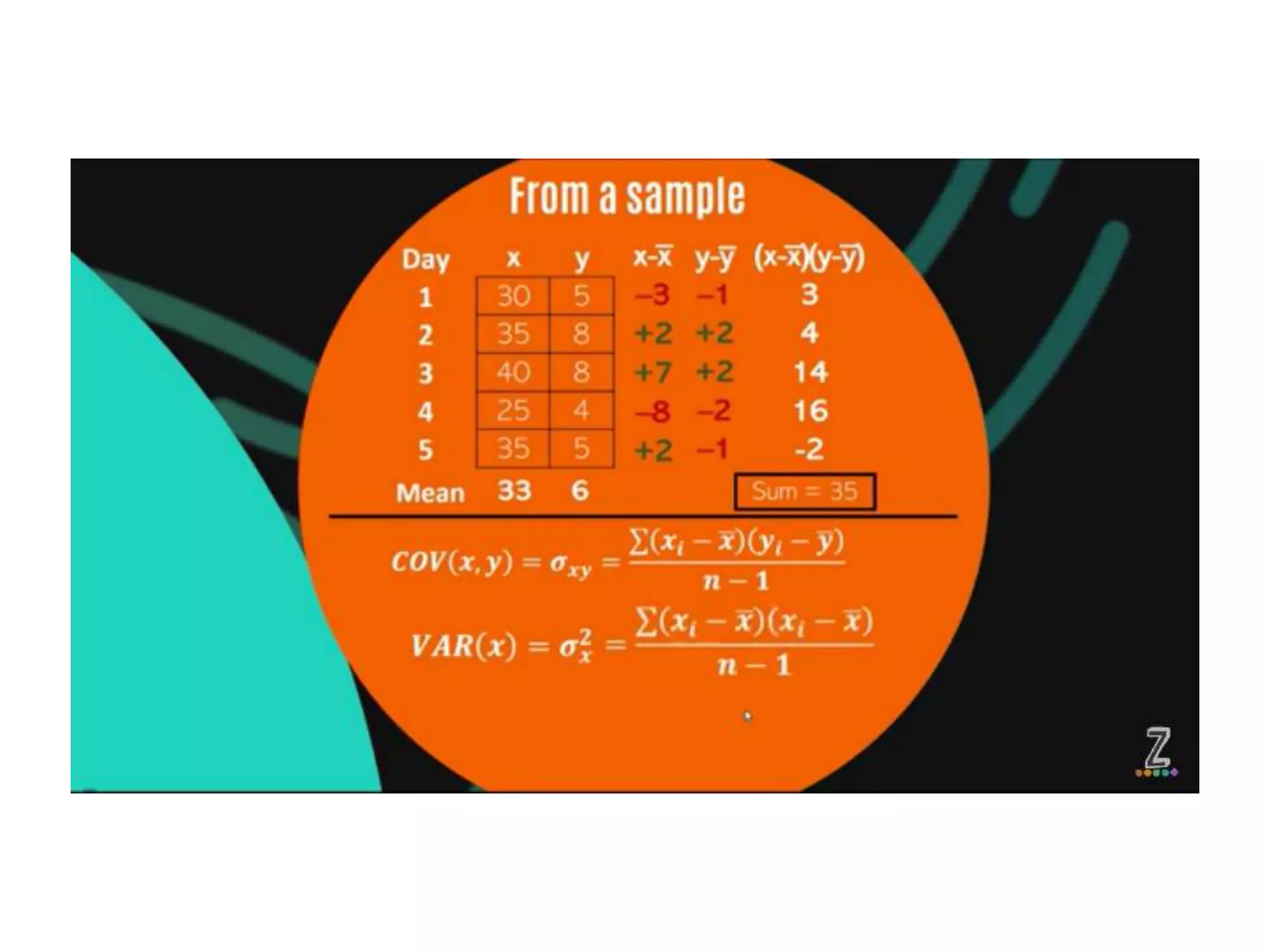
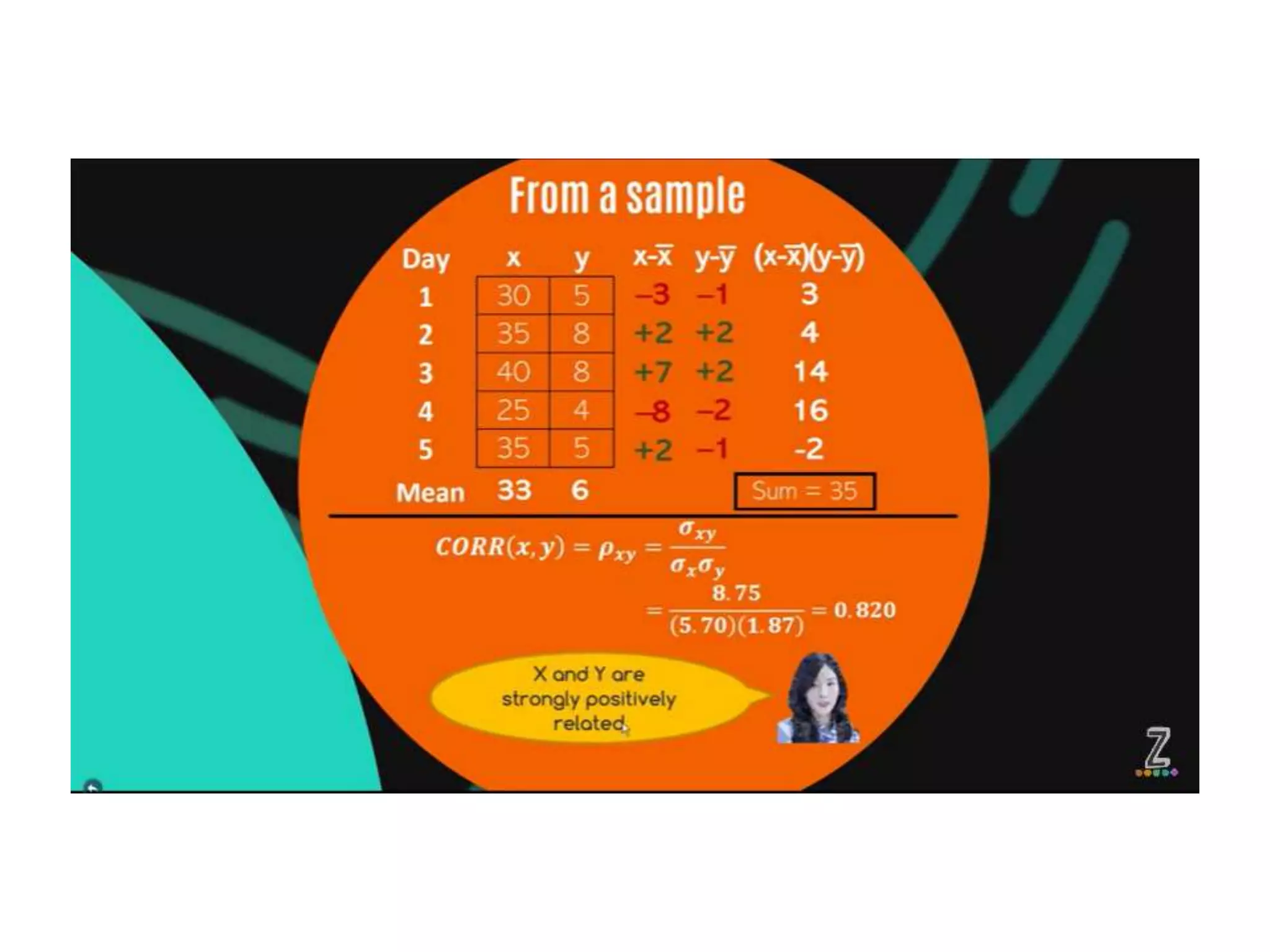
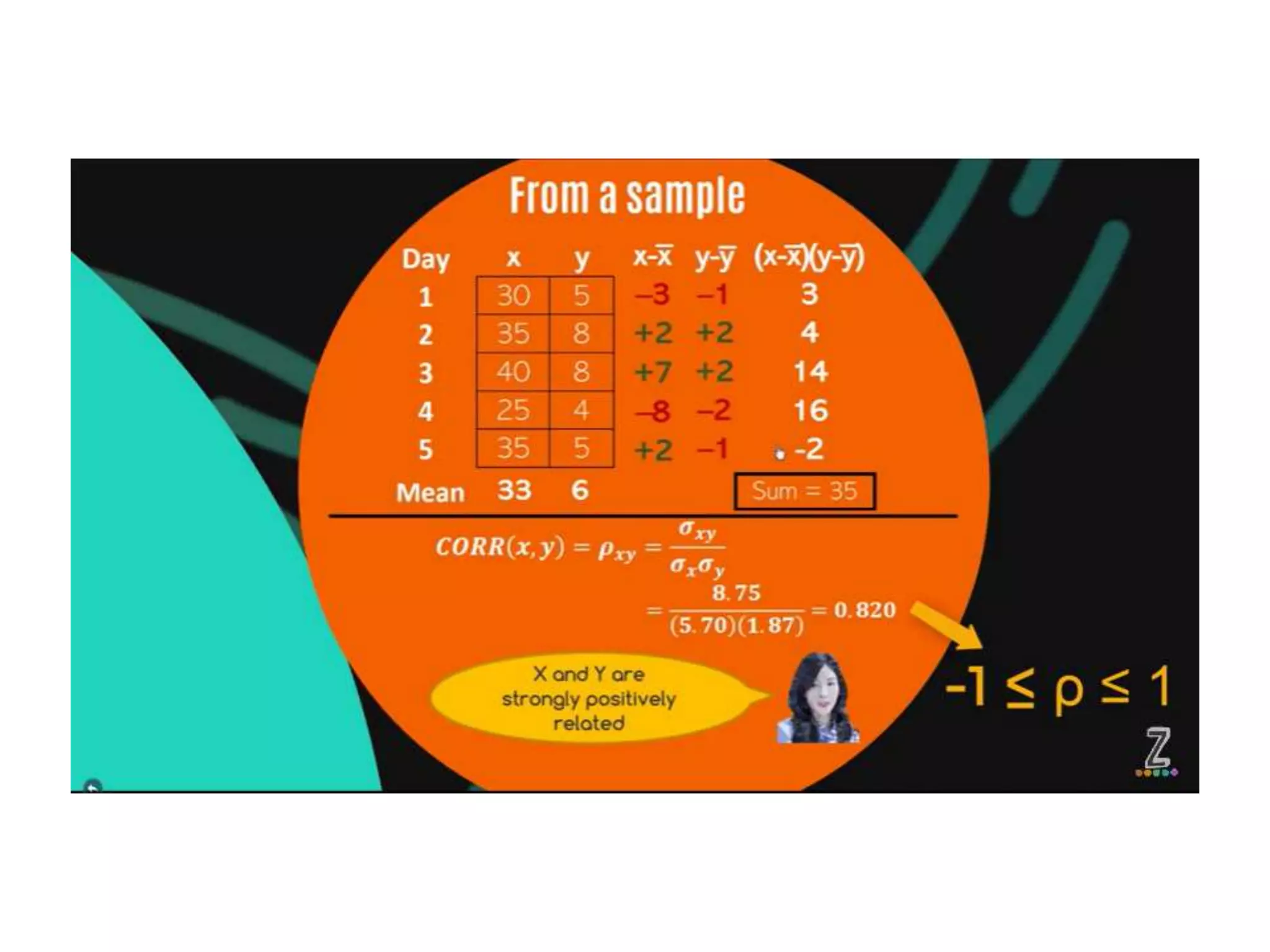
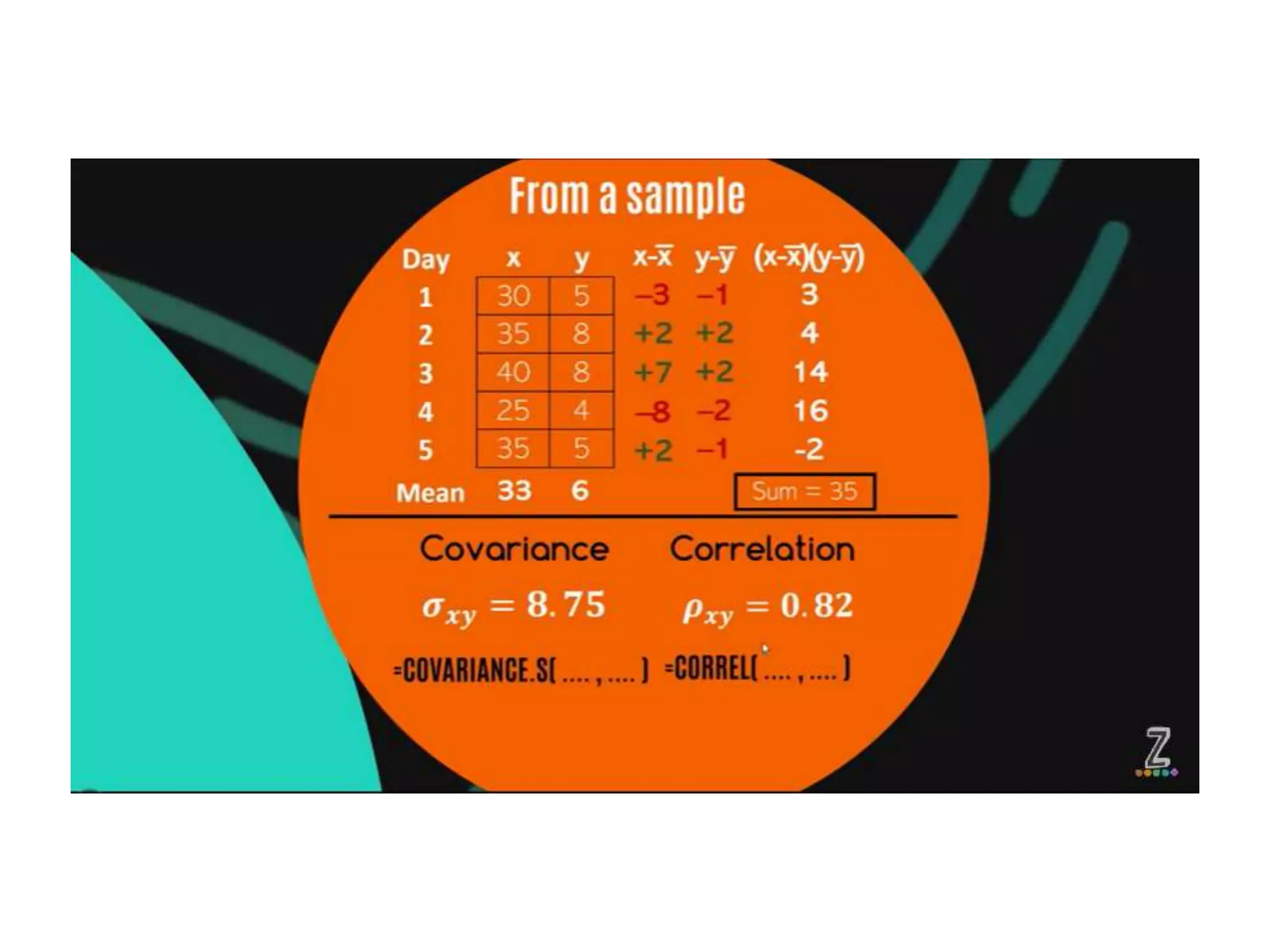
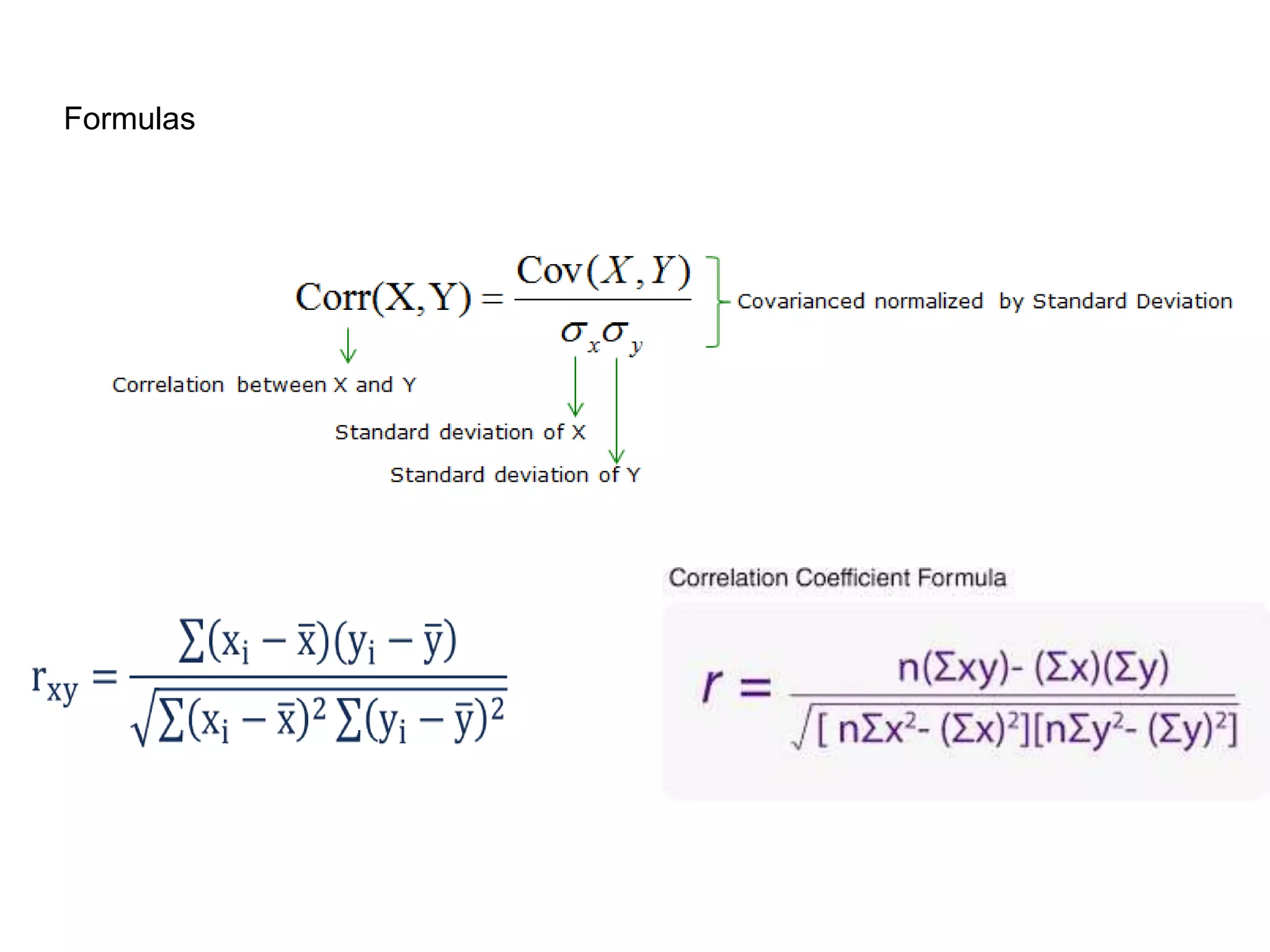
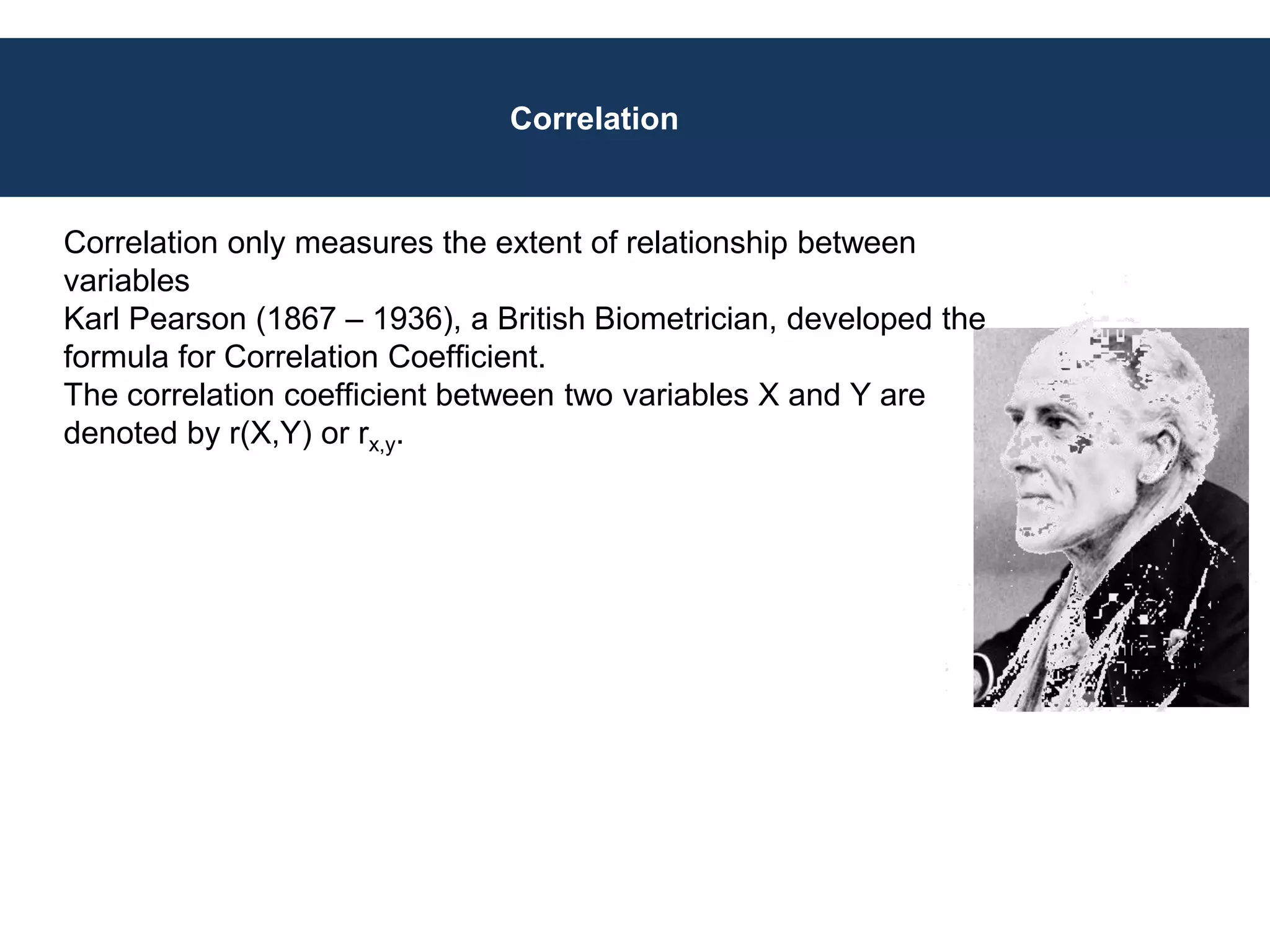
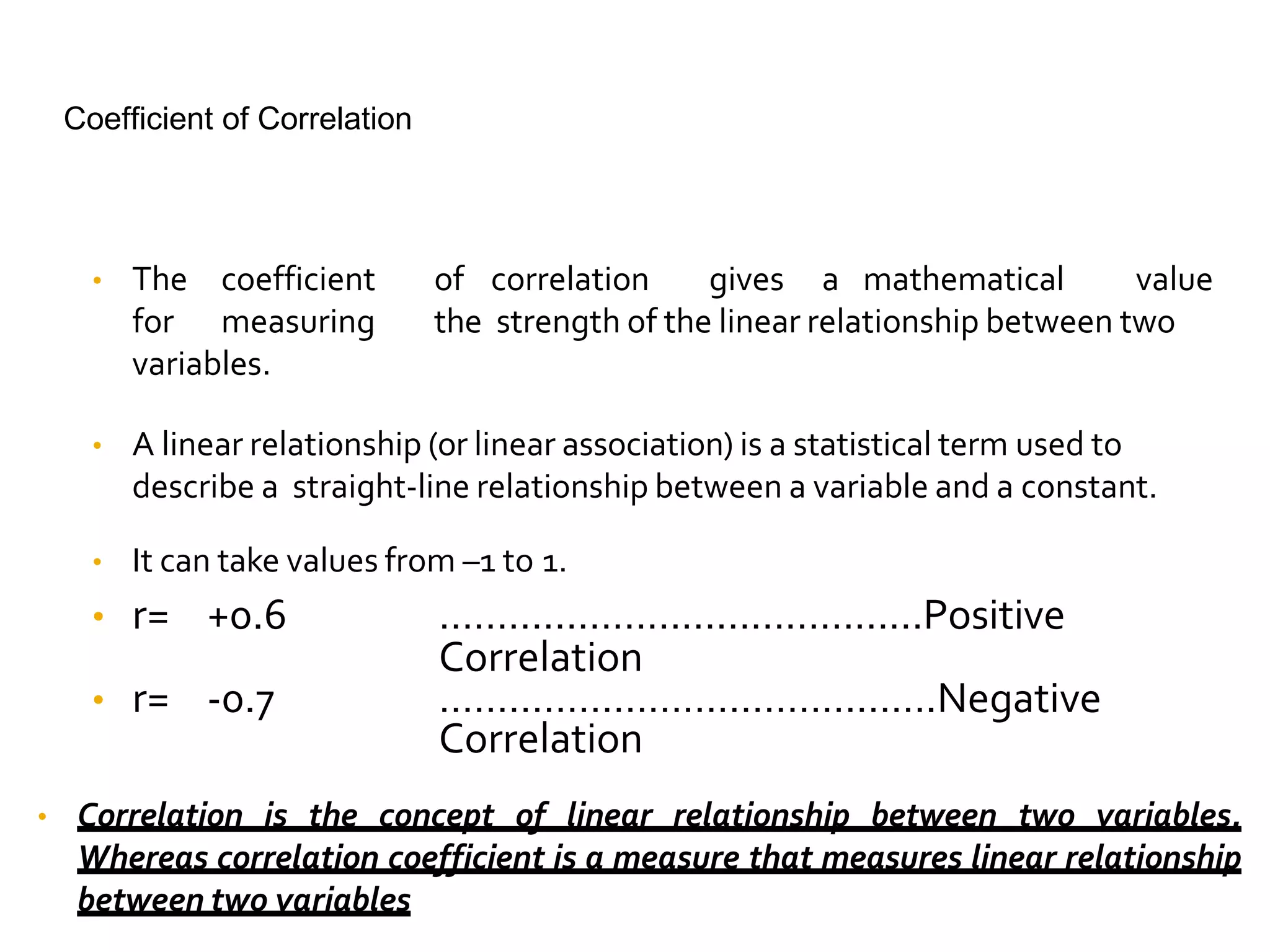
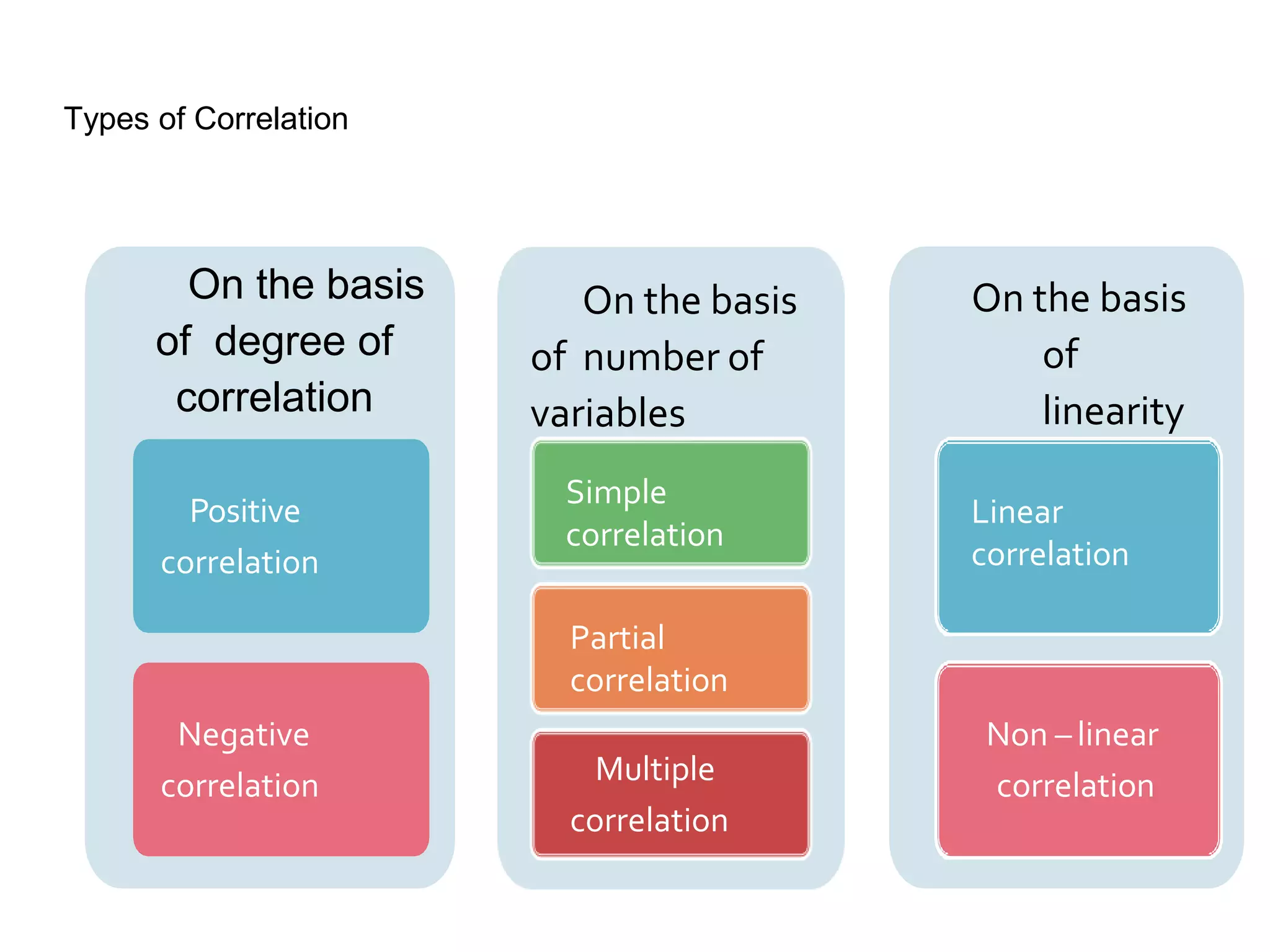
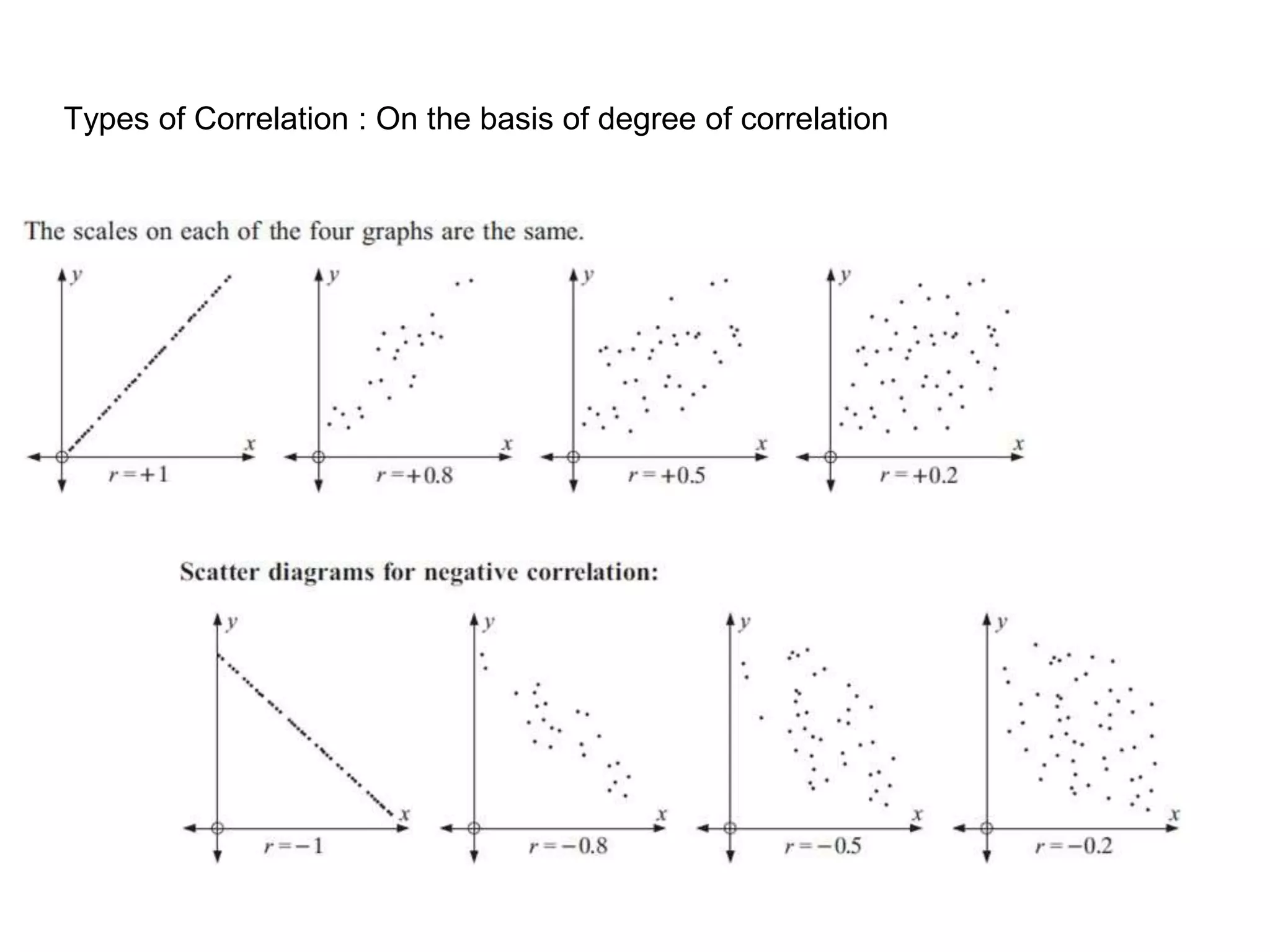
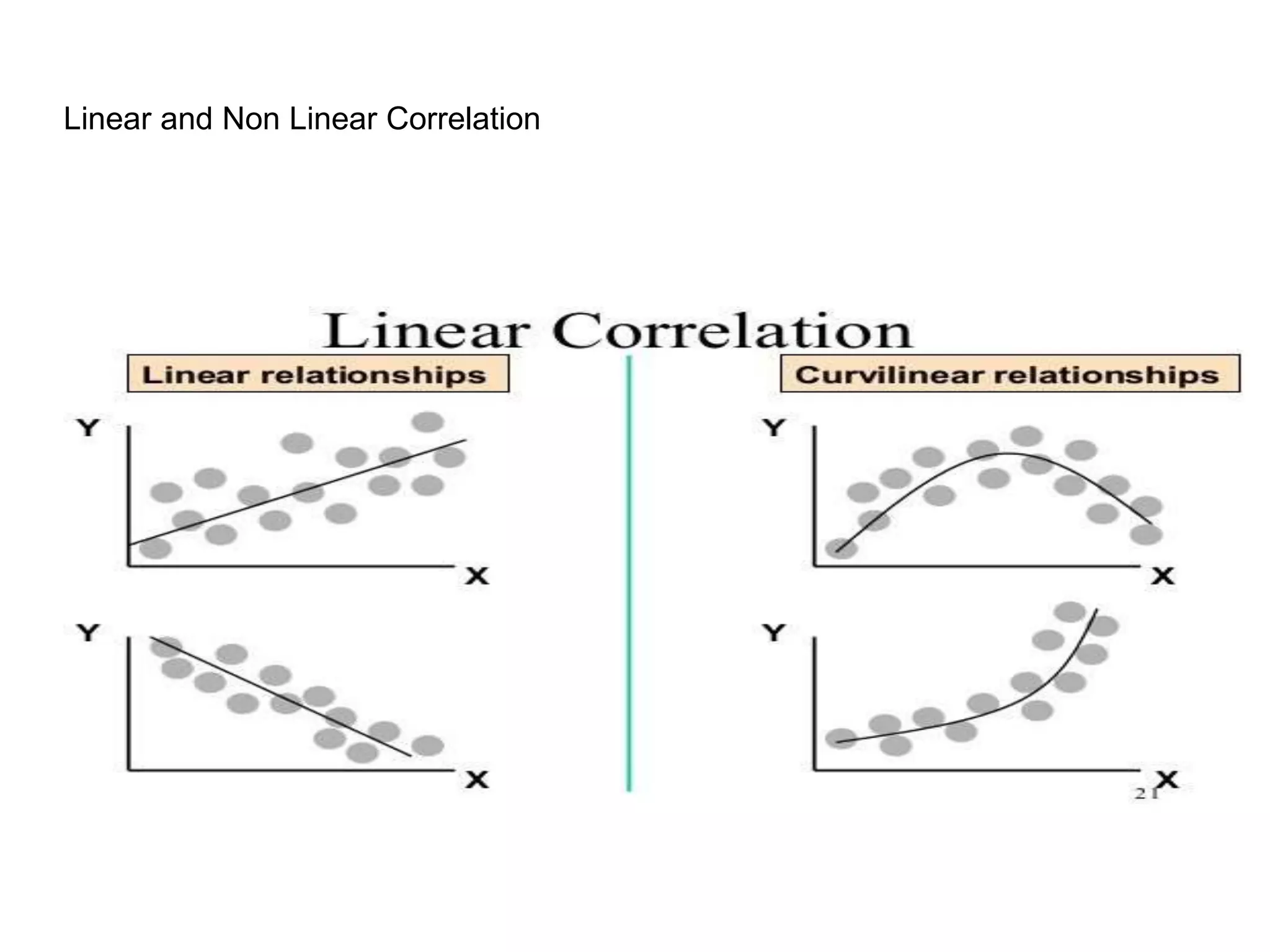
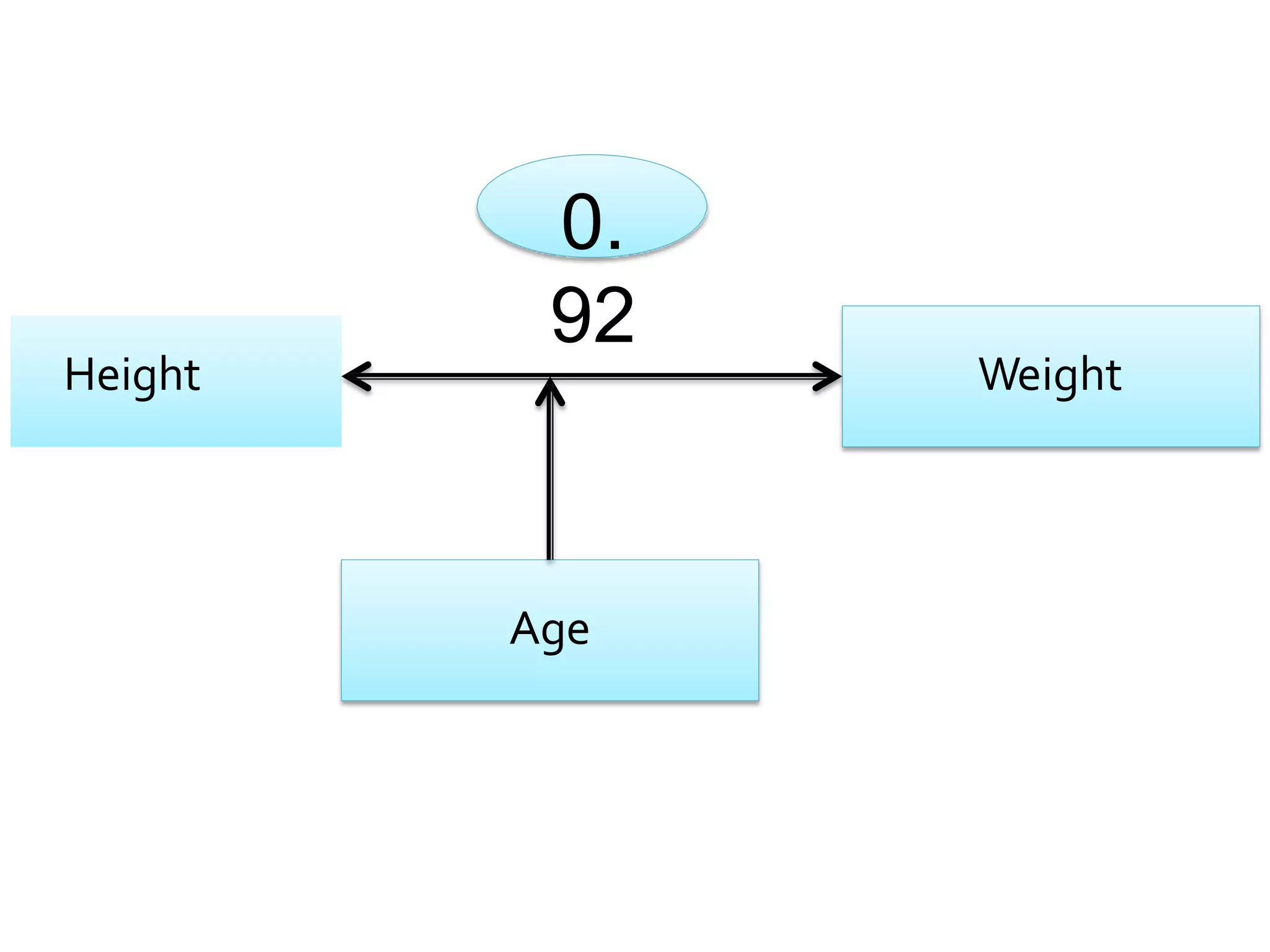
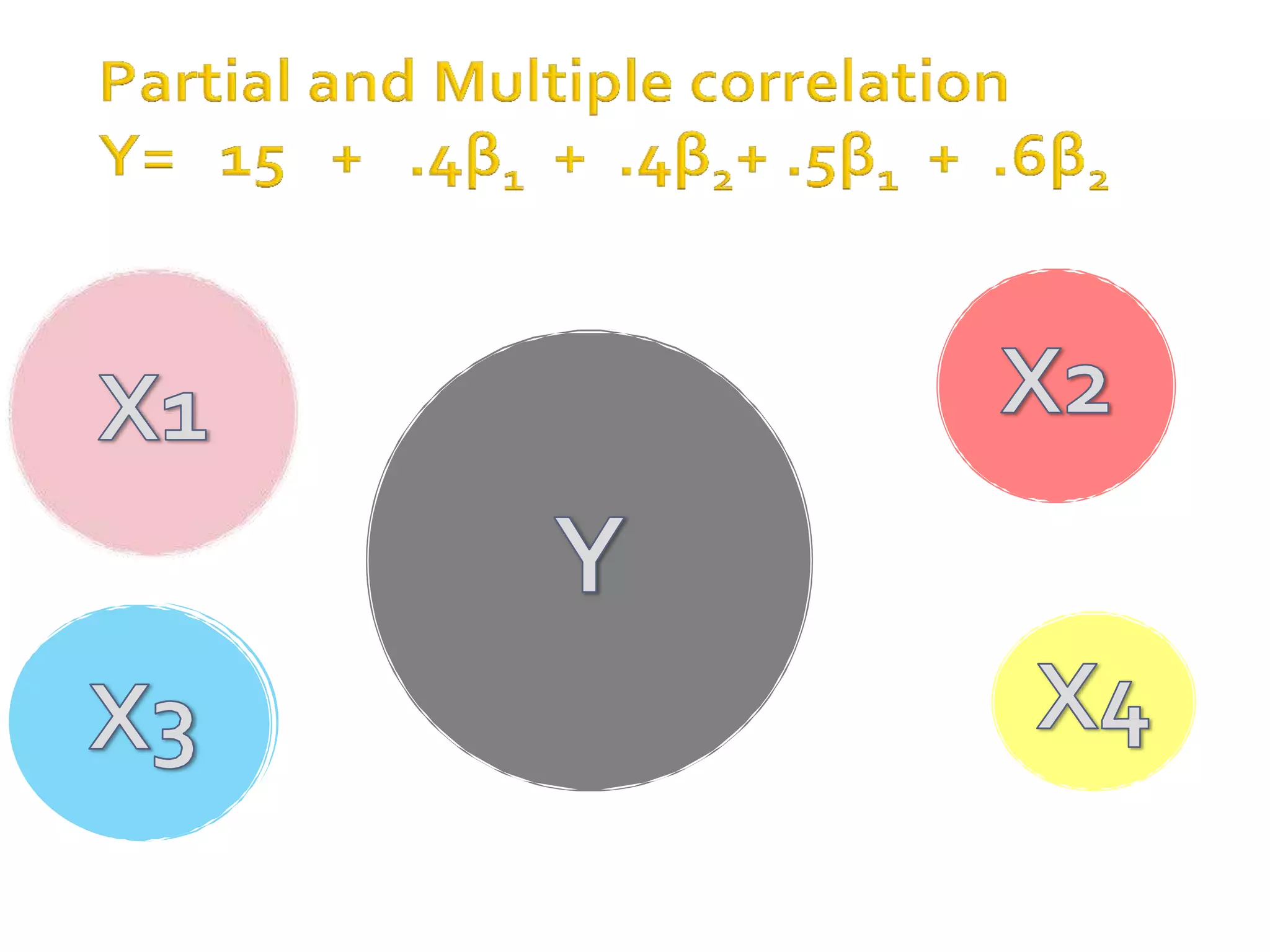
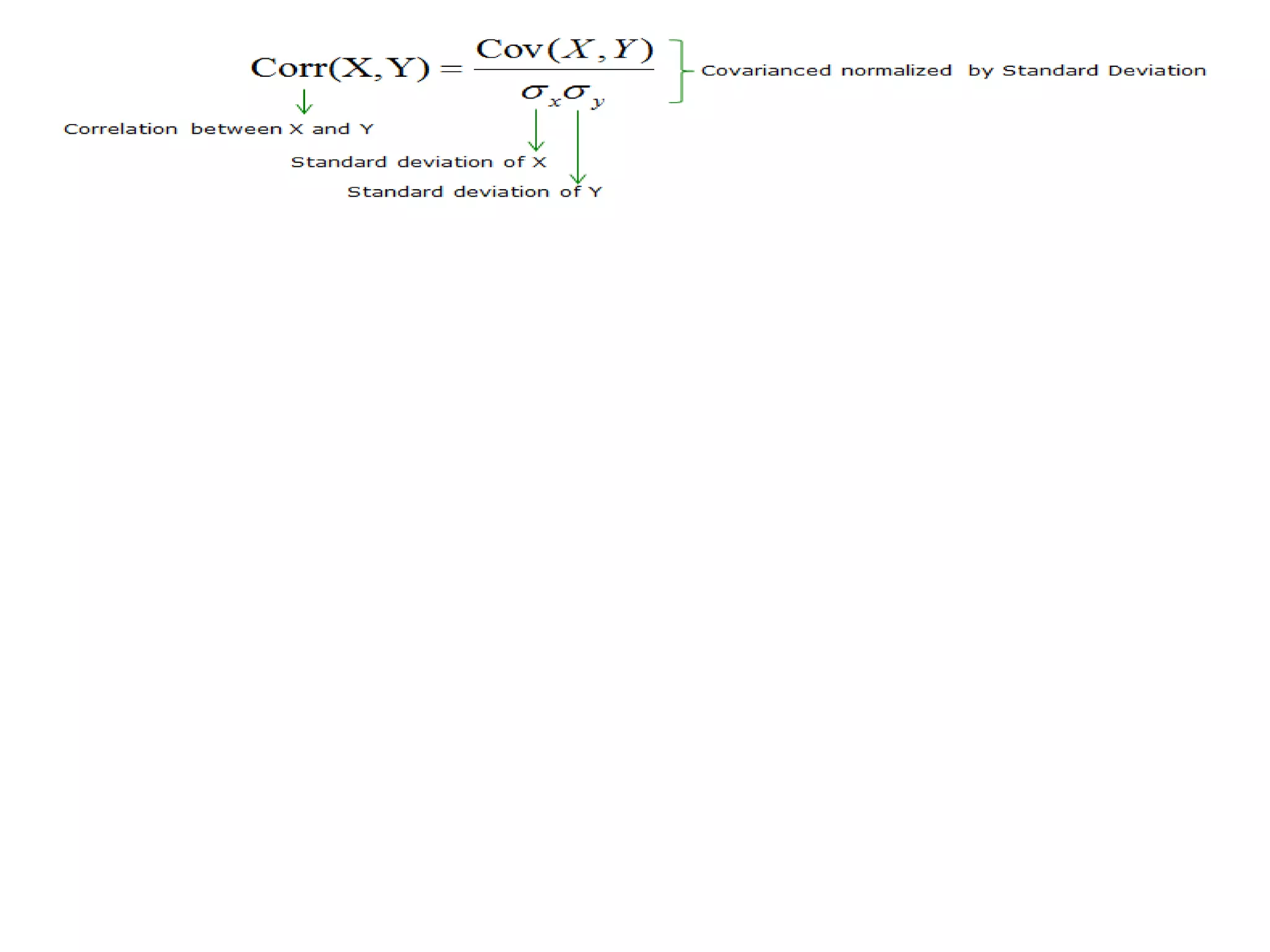
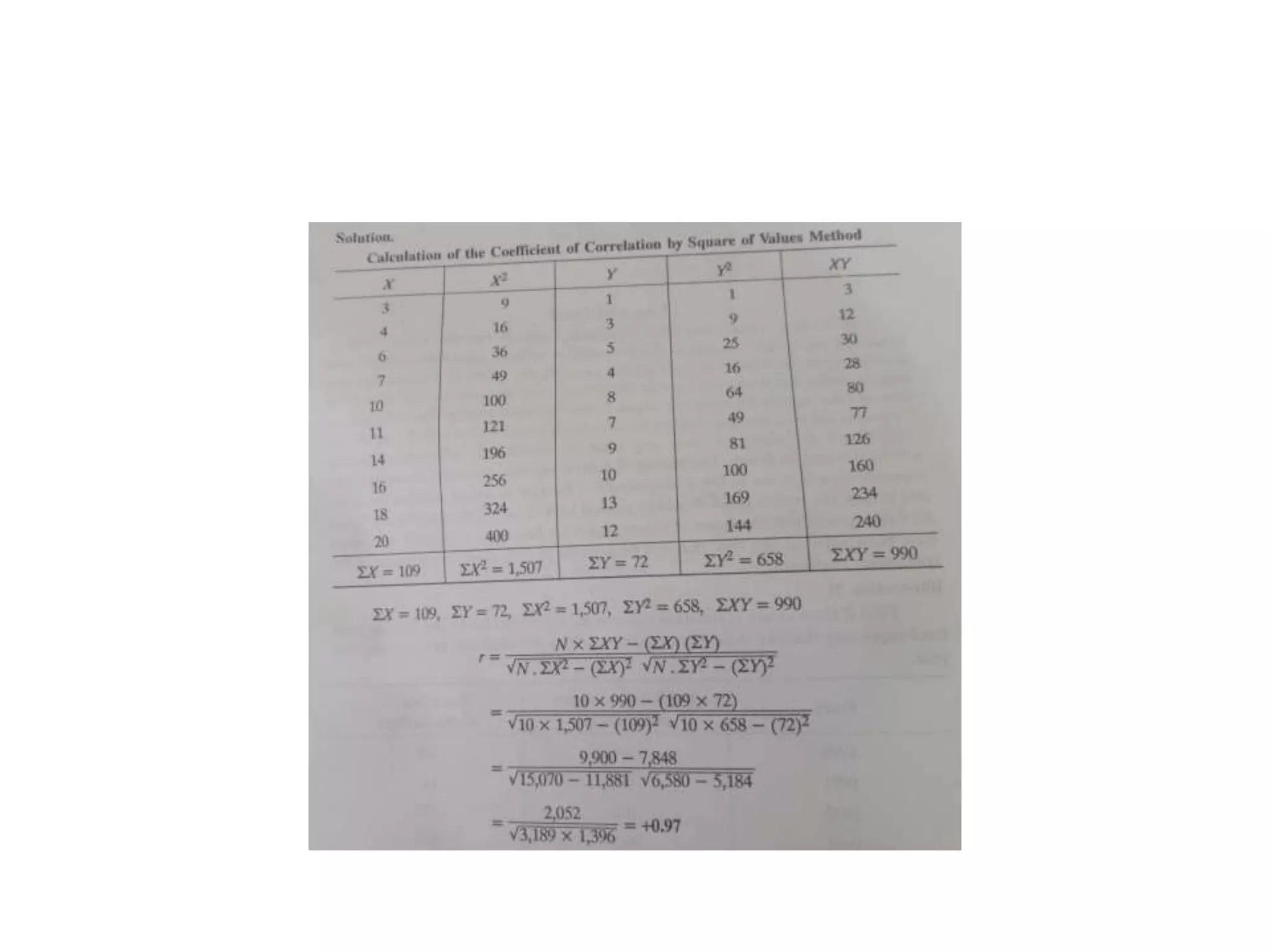
Covariance and correlation are measures of the relationship between two variables. Covariance measures how much two variables vary together, while correlation measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. Correlation values range from -1 to 1, with 0 indicating no relationship, positive values indicating a direct relationship, and negative values indicating an inverse relationship. Several methods can be used to calculate correlation, including Pearson's correlation coefficient, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient, and scatter plots. Correlation does not necessarily imply causation, as two variables can be correlated without one causing the other.















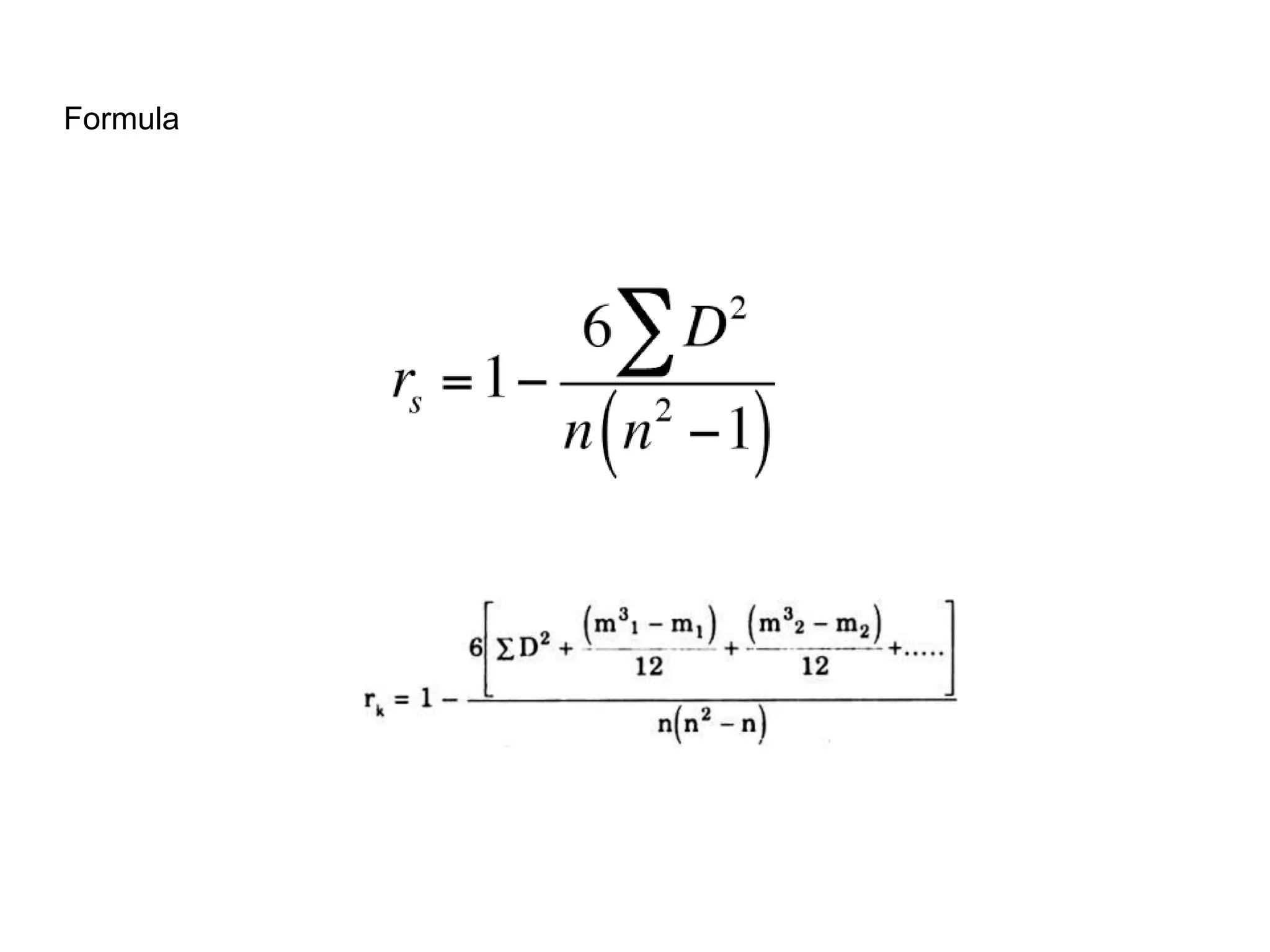
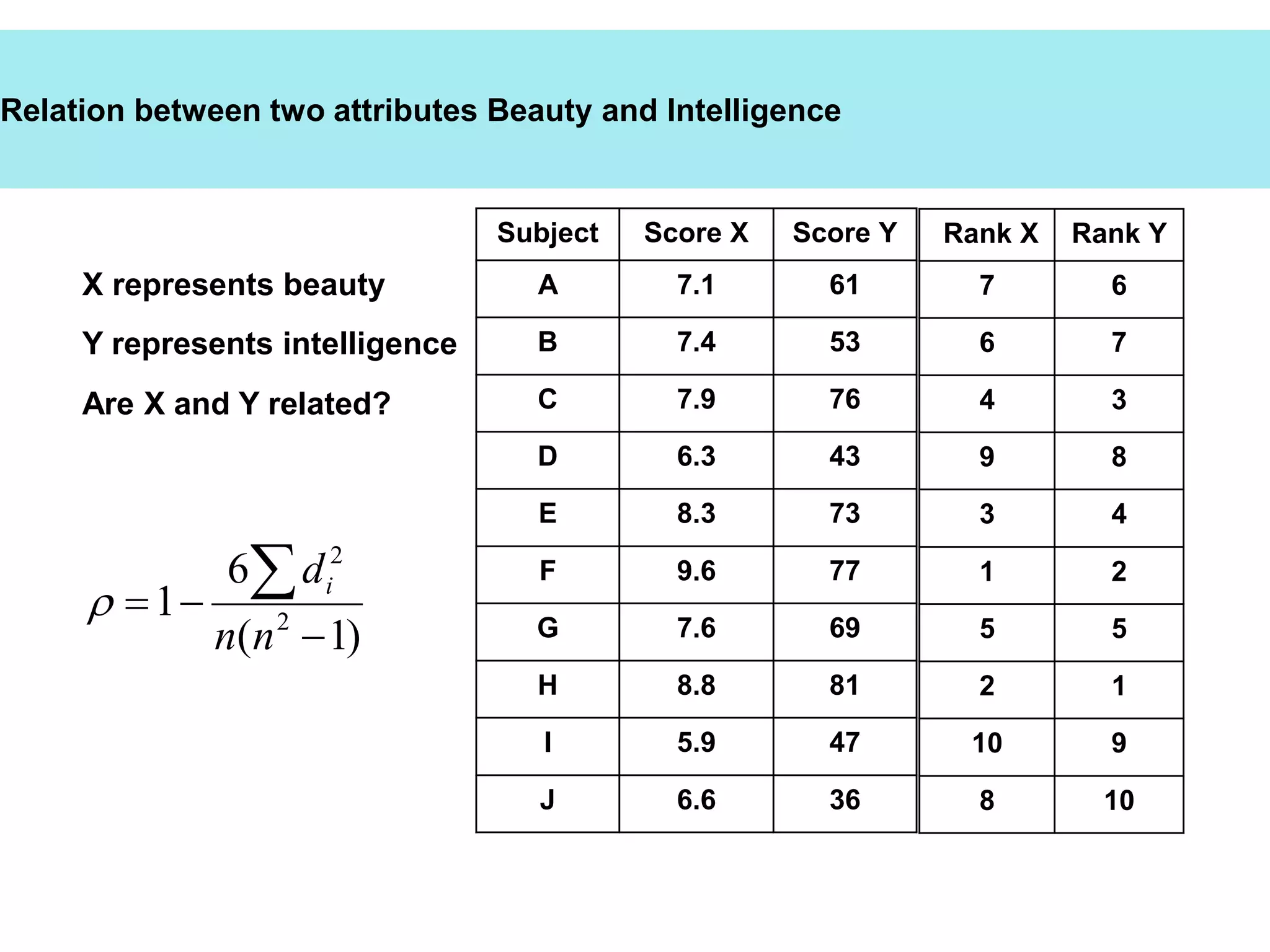
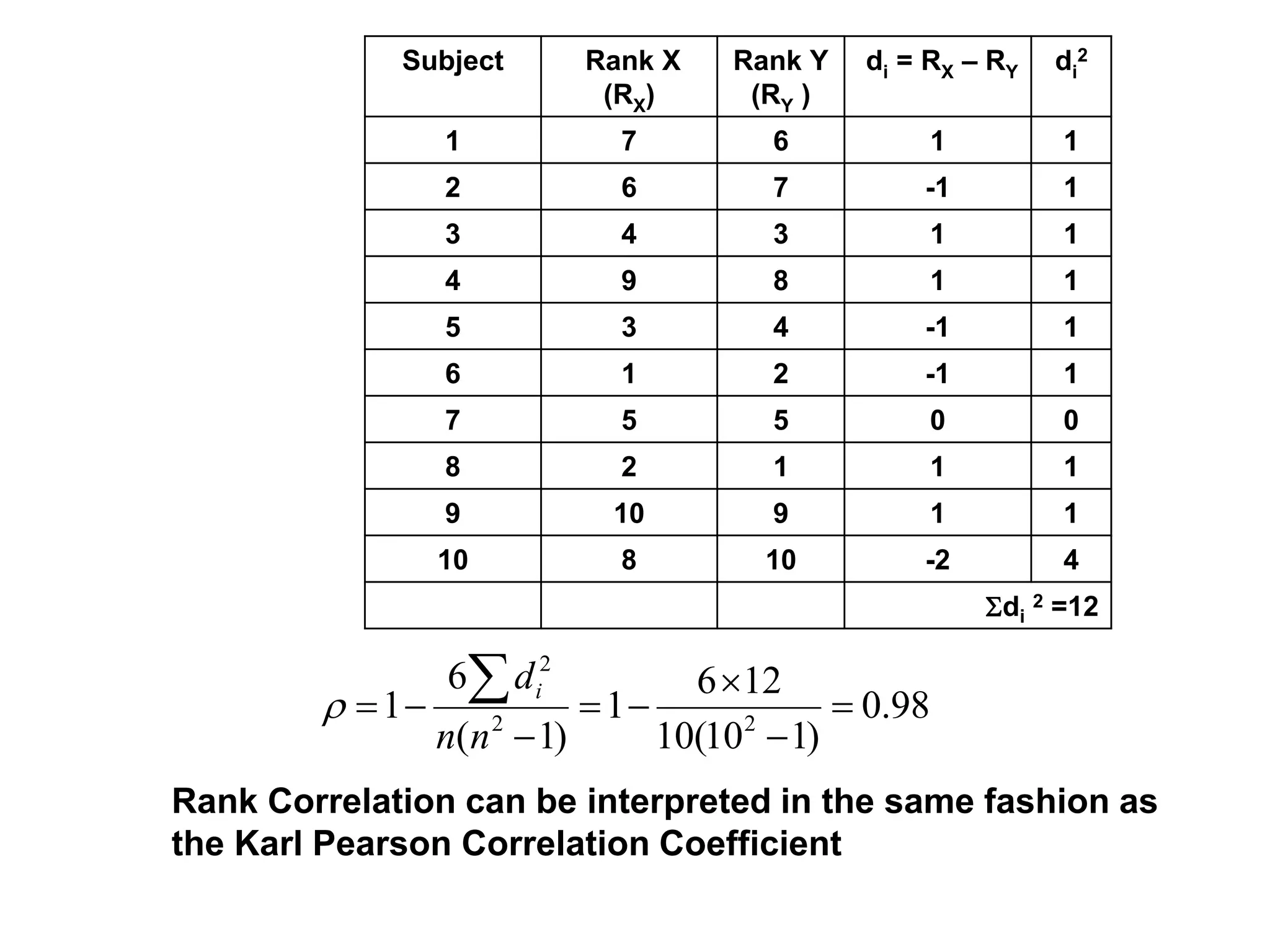
![Rank Correlation Coefficient
This correlation formula is used when relation between two variable are studied in
terms of the ranking of each case within each variable.
Mostly used when both the variables relate to some attribute.
Appropriate for data sets that are ordinal in nature.
The range is from [ -1, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/topic5covariancecorrelation-221127095330-7261abef/75/Topic-5-Covariance-Correlation-pptx-37-2048.jpg)