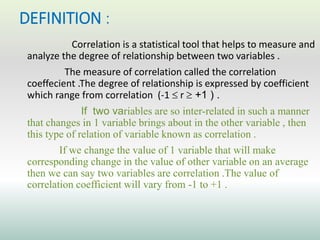
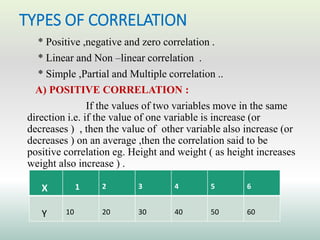
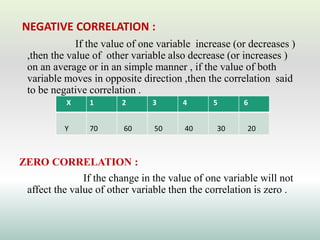
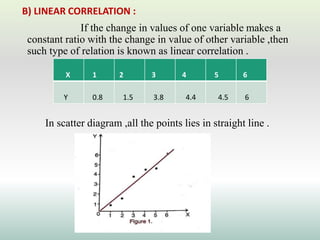
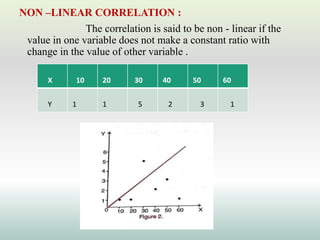
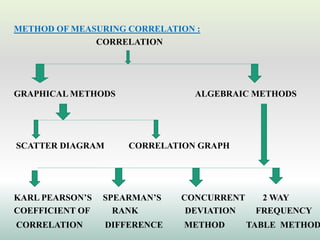
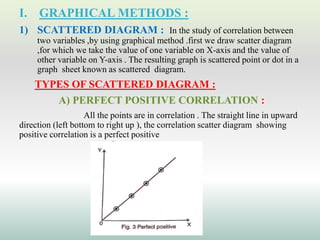
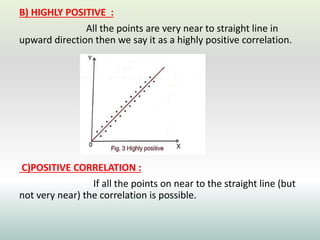
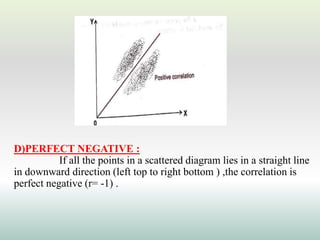
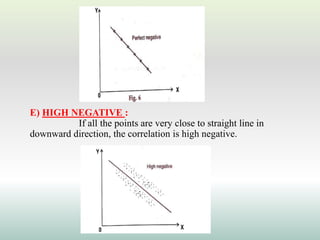
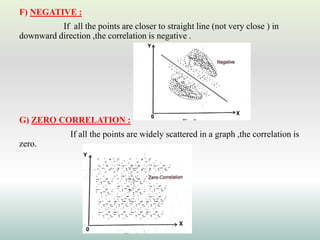
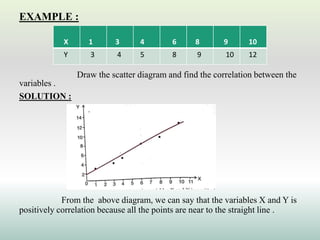
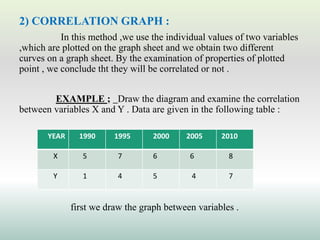
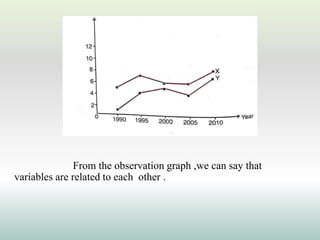
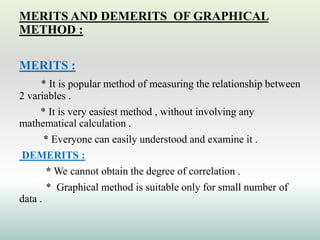
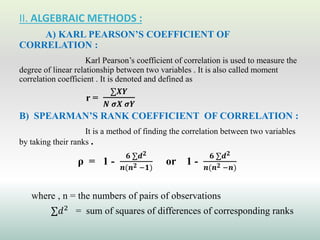
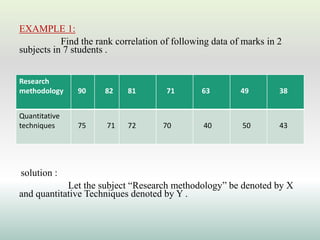
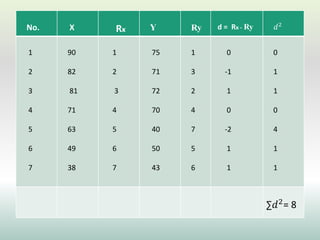
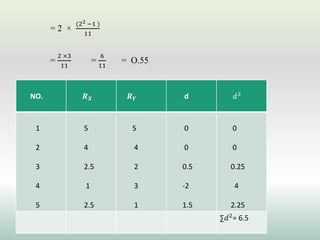
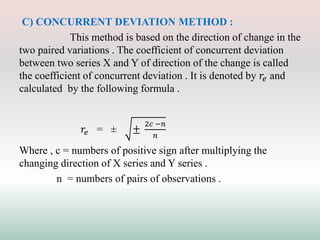
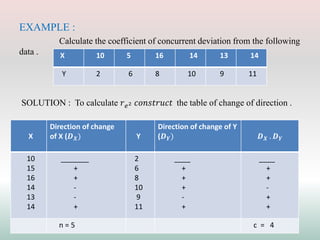
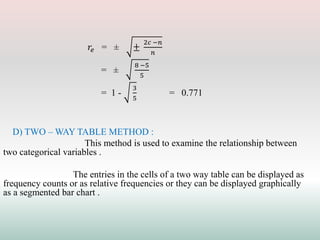
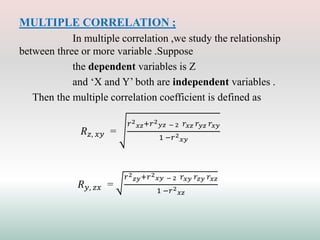
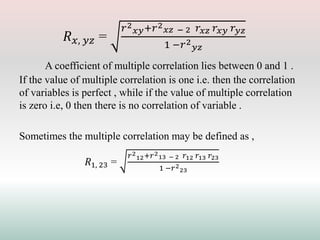
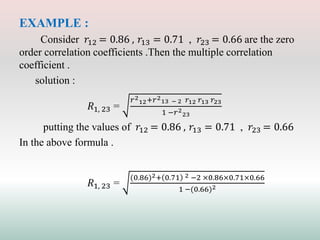
This document defines and explains different types of correlation. It begins by defining correlation as a statistical tool to measure the relationship between two variables. There are three main types of correlation discussed: positive correlation where both variables move in the same direction, negative correlation where the variables move in opposite directions, and zero correlation where a change in one variable does not affect the other. The document also discusses linear and non-linear correlation, as well as simple, partial, and multiple correlation. Different methods for measuring correlation are presented, including graphical methods like scatter diagrams and algebraic methods like Pearson's correlation coefficient.