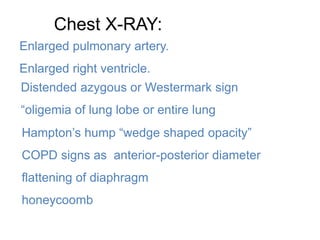
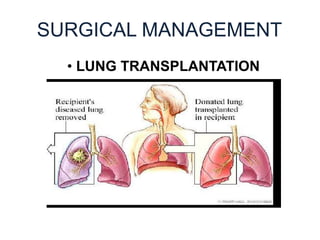
Cor pulmonale is defined as the enlargement of the right ventricle due to lung-related diseases, leading to hypertrophy and dilation. It can arise from various conditions such as COPD, pulmonary hypertension, and chronic hypoxia, manifesting symptoms like dyspnea, chronic cough, and fatigue. Diagnosis involves a combination of history, physical examination, and imaging techniques, with treatment options including oxygen therapy, medications, and surgical interventions.