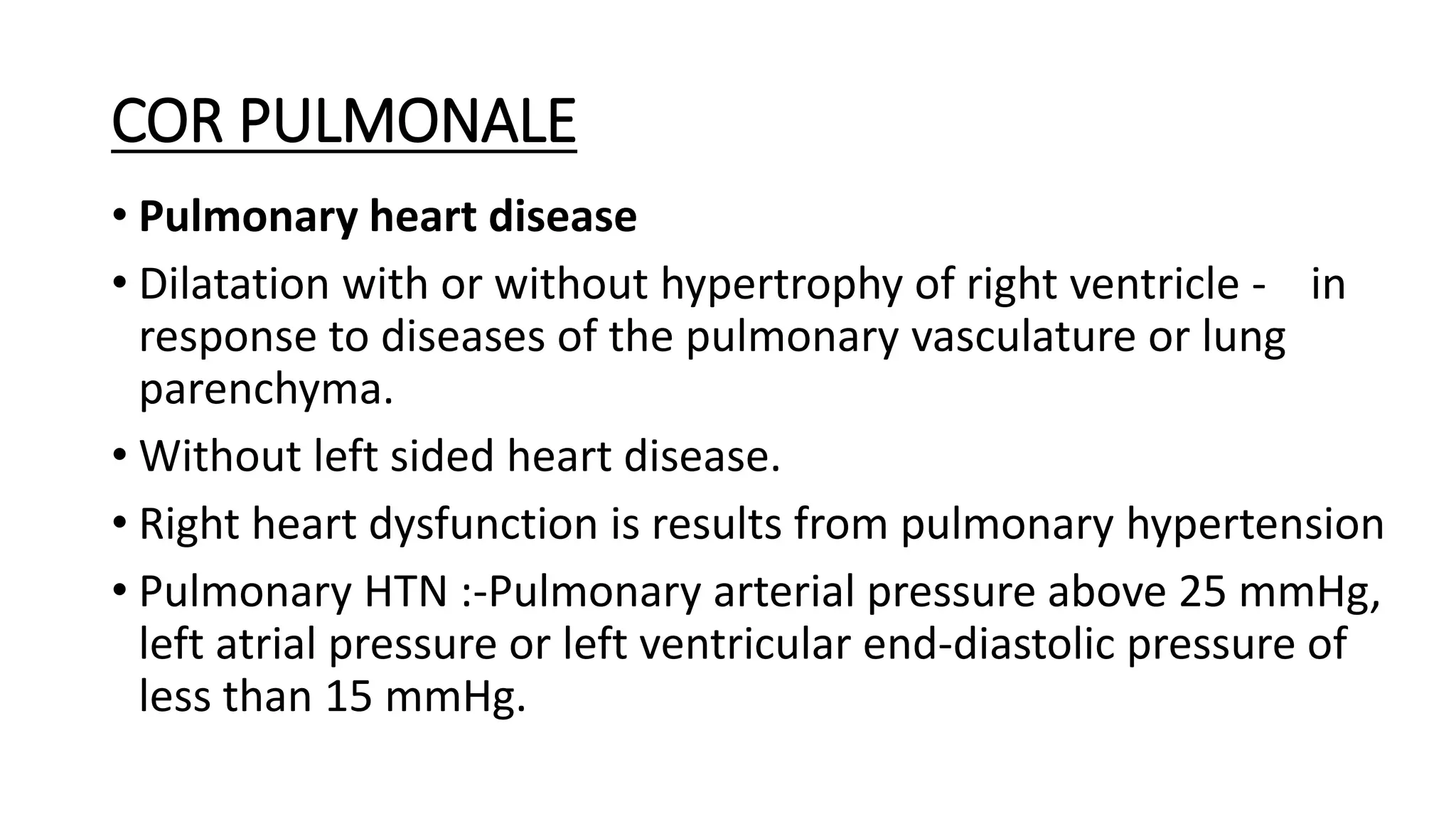
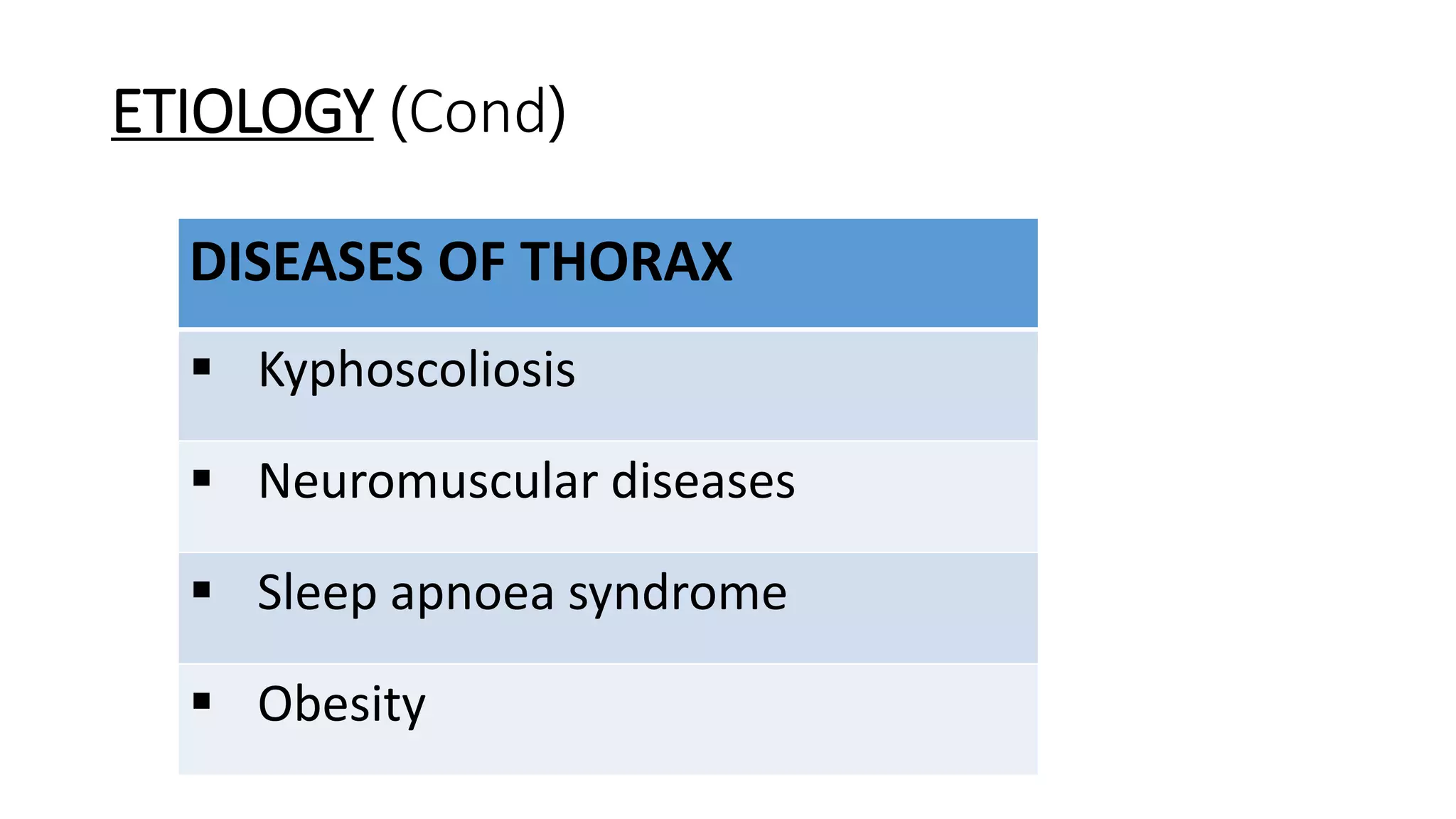
This document discusses cor pulmonale, which is right heart failure or pulmonary heart disease that occurs secondary to lung or pulmonary vascular diseases. It defines cor pulmonale and describes the types as acute or chronic. It covers the etiology, pathogenesis, clinical features, investigations and treatment of cor pulmonale. The main causes are chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary embolism. Signs and symptoms include dyspnea and right heart failure. Treatment involves managing the underlying lung or vascular condition, administering oxygen therapy, and treating right heart failure.