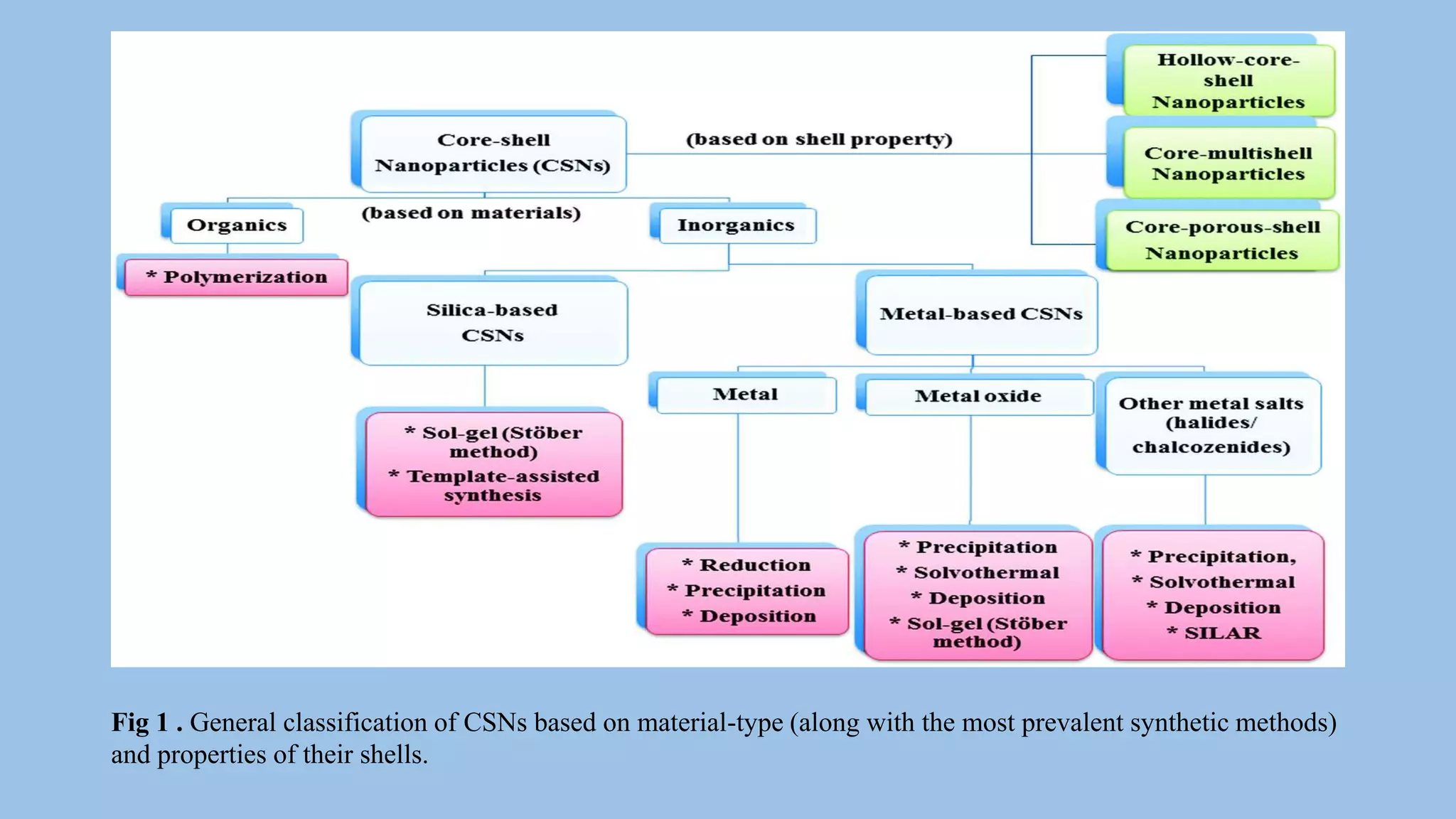
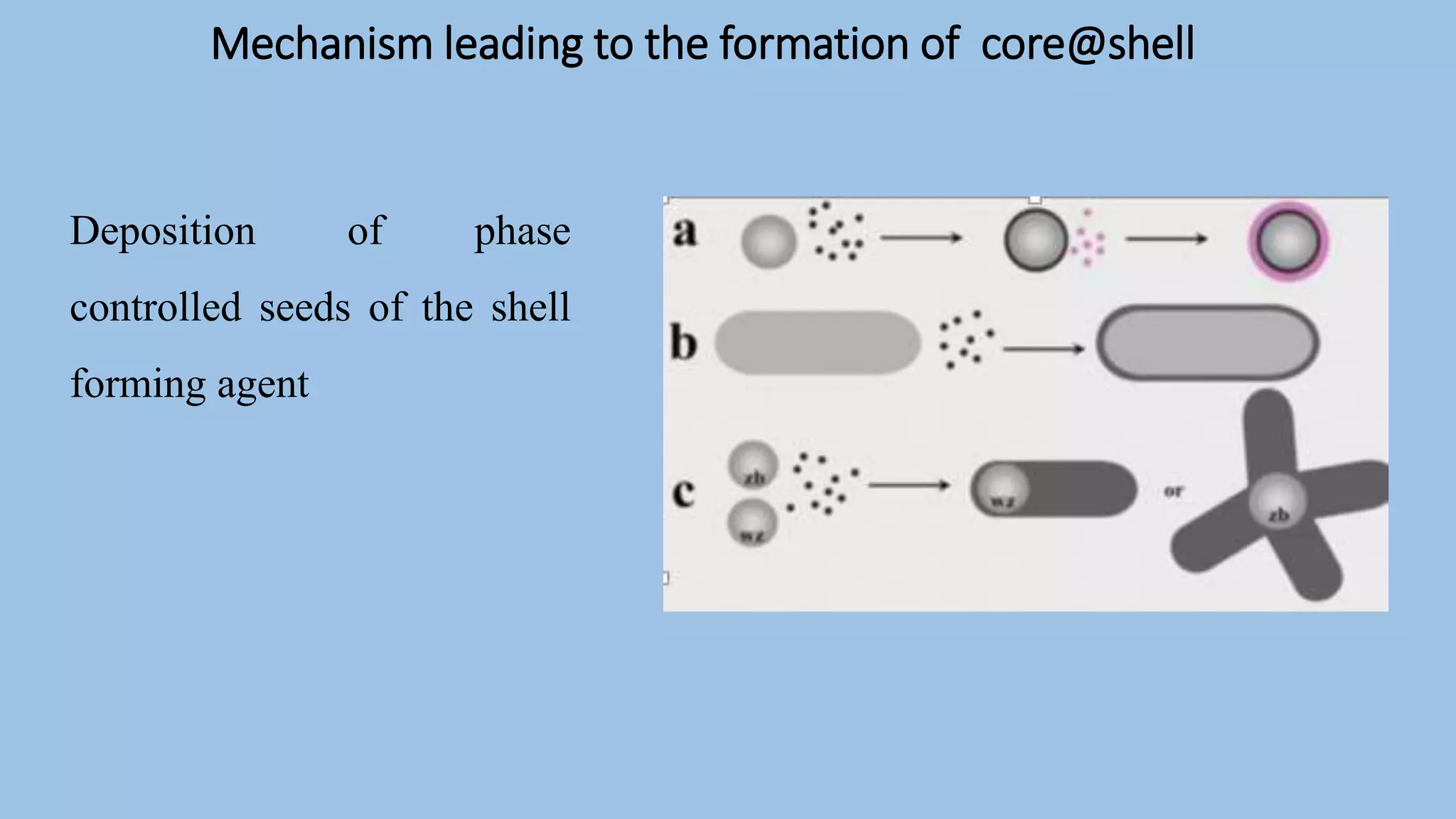
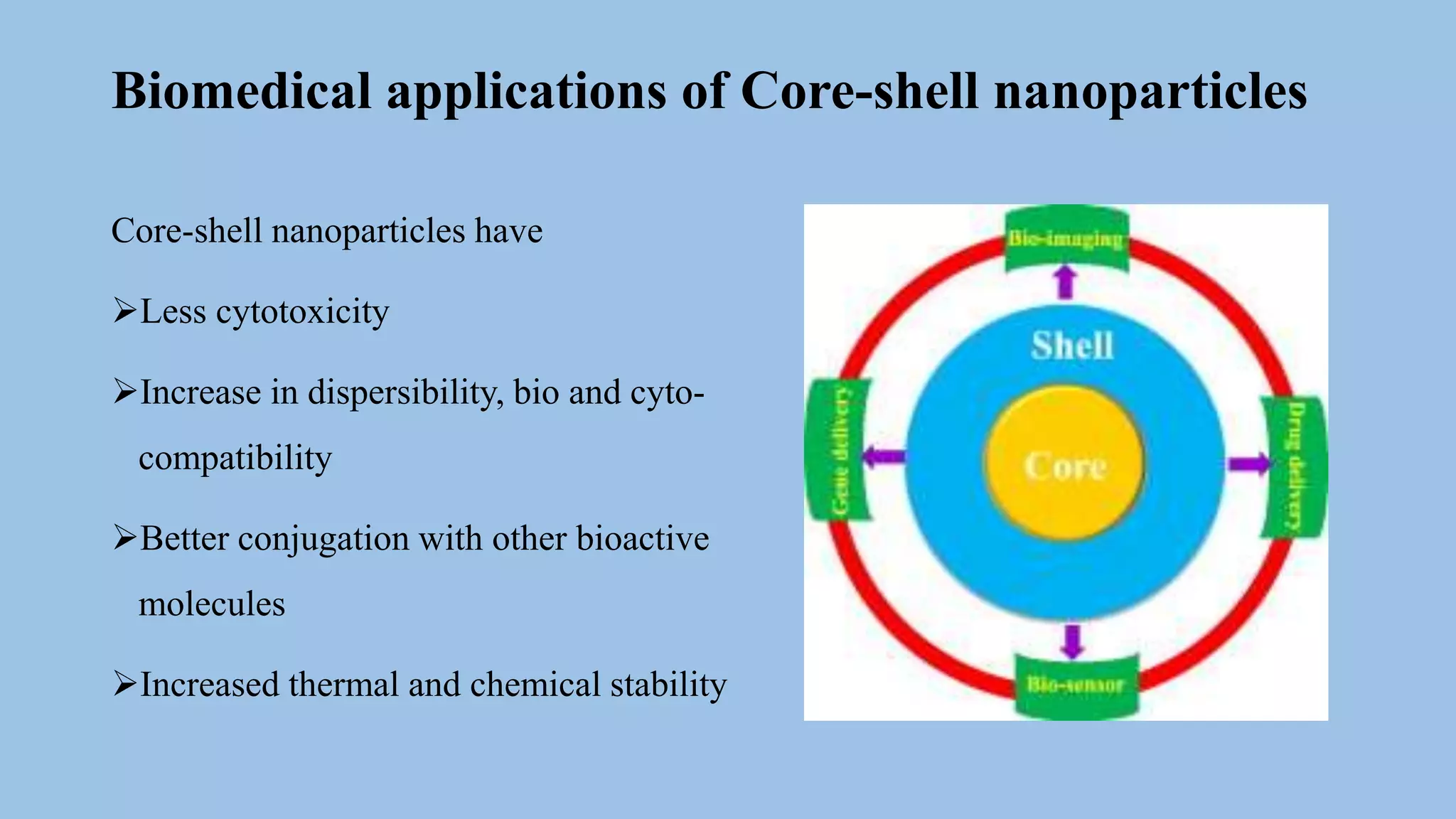
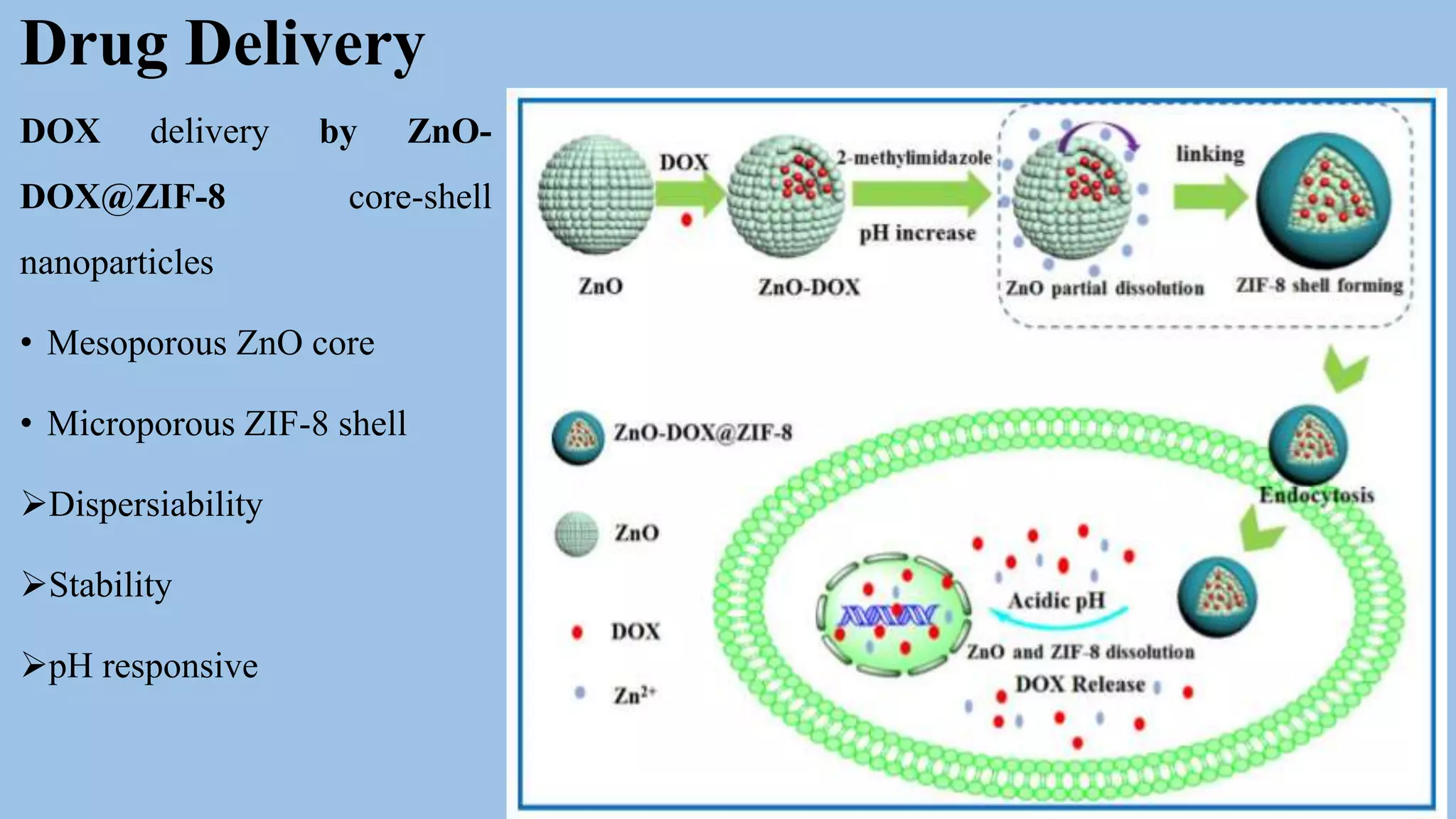
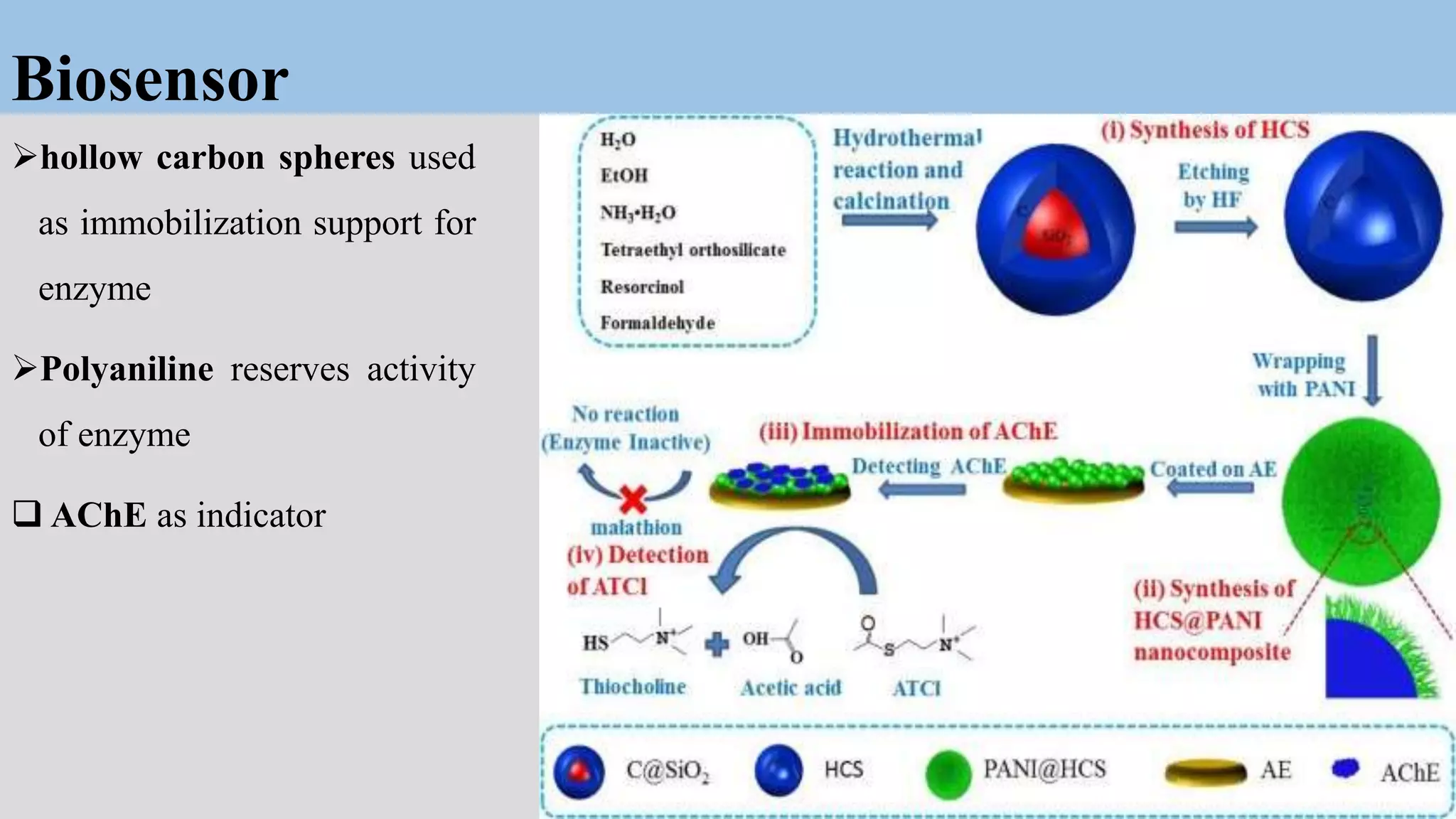
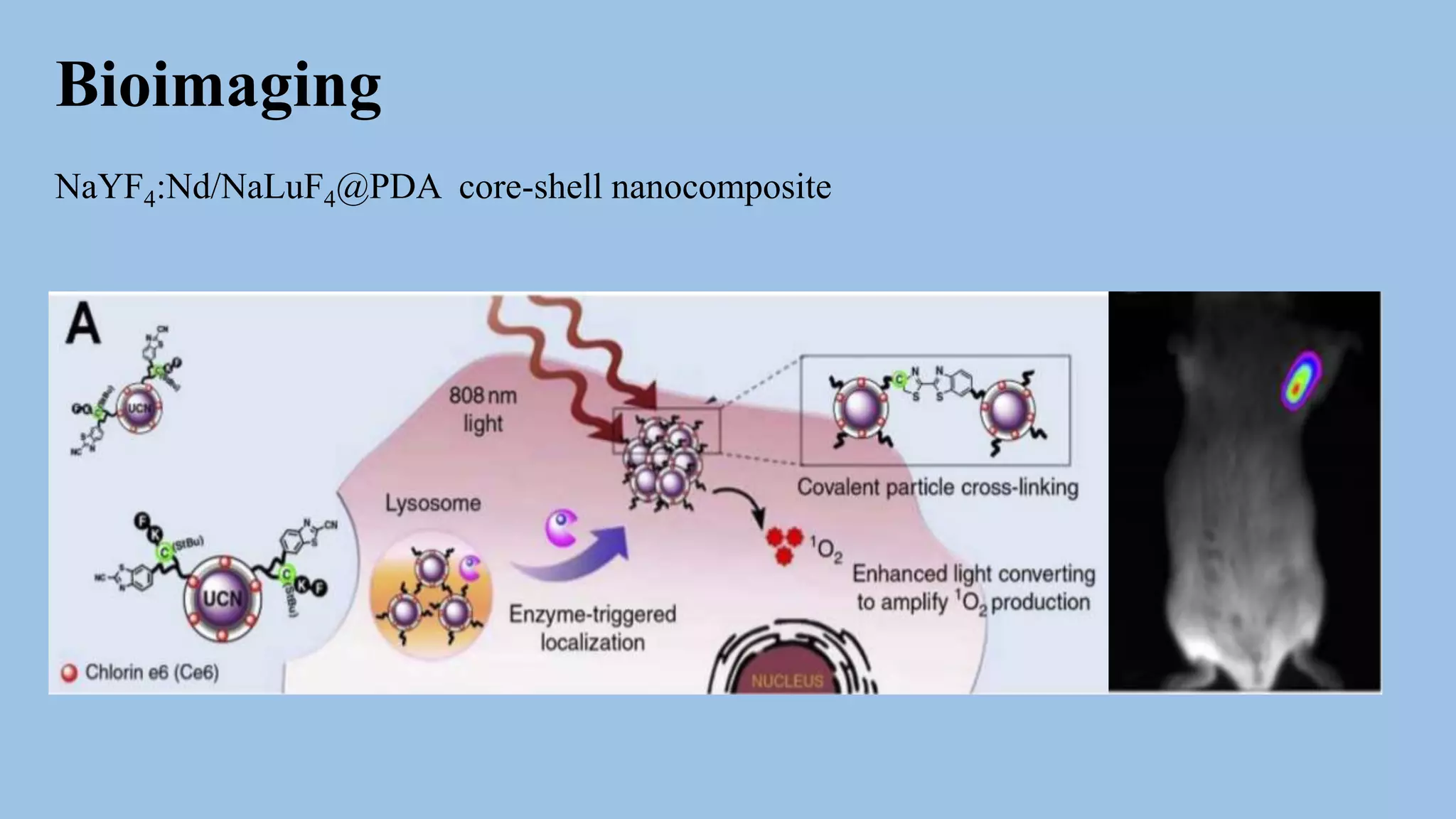
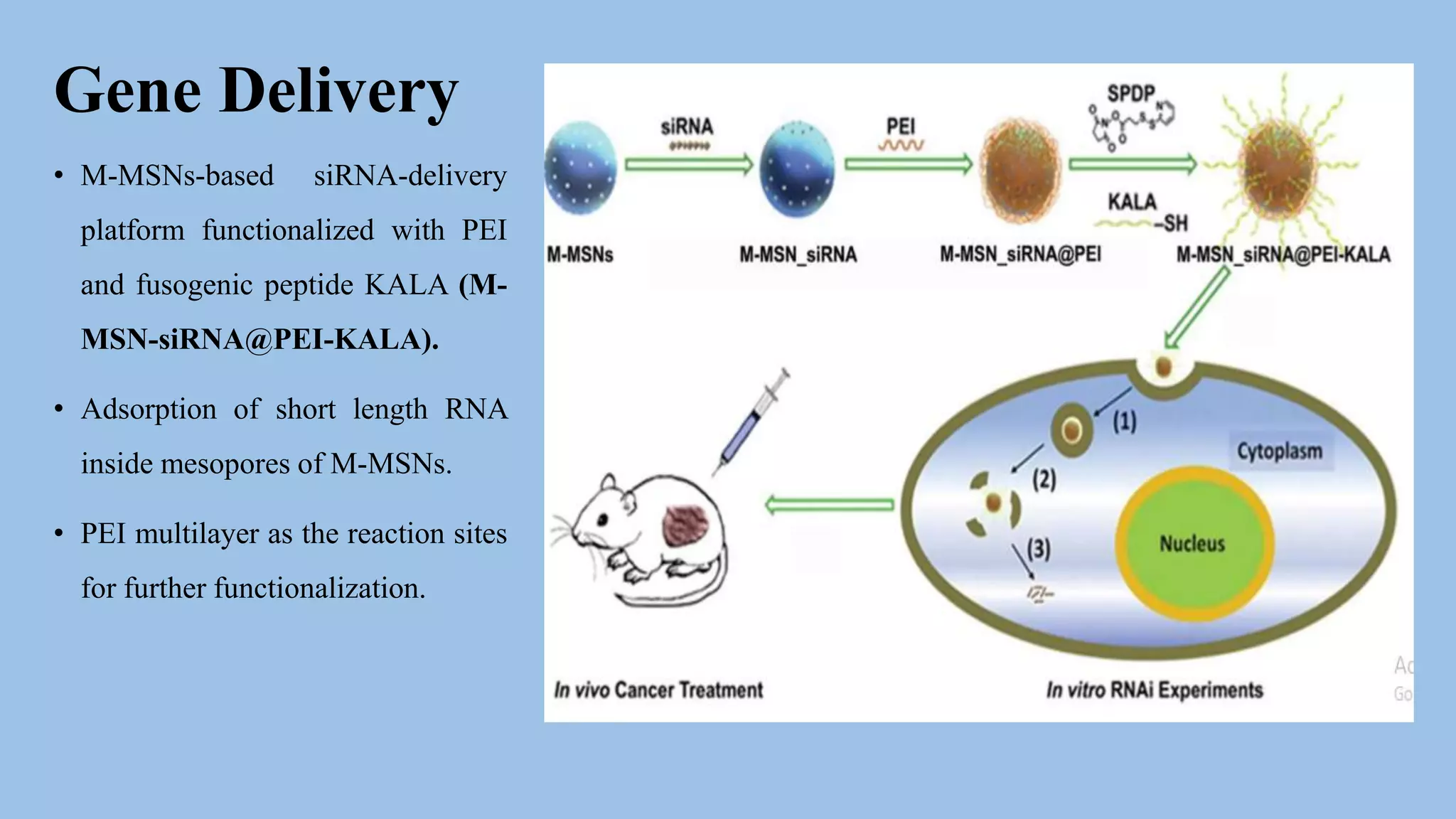
Core-shell nanoparticles consist of an inner core covered by an outer shell. They are classified based on their material properties as inorganic-inorganic, inorganic-organic, organic-inorganic, or organic-organic. Core-shell nanoparticles are widely used in biomedical applications due to their less cytotoxicity, increased dispersibility and biocompatibility, better conjugation with biomolecules, and greater thermal and chemical stability compared to single component nanoparticles. Examples of biomedical uses discussed in the document include using ZnO-DOX@ZIF-8 nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery, hollow carbon spheres for enzyme immobilization in biosensors, and NaYF4:Nd/NaLuF4@PDA nanoparticles