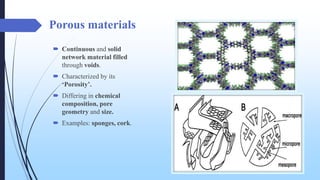
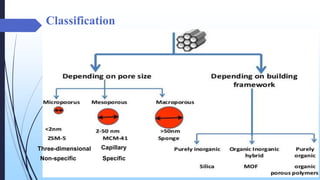
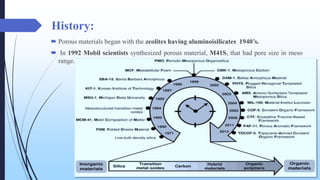
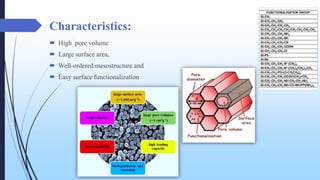
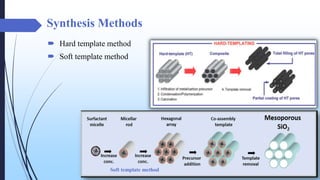
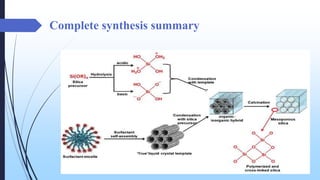
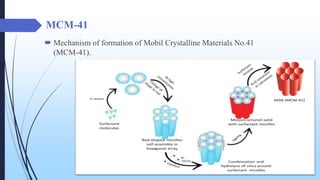
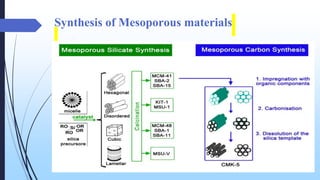
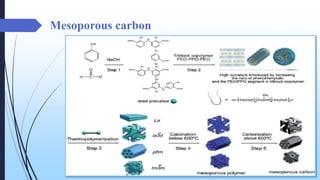
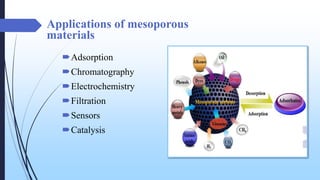
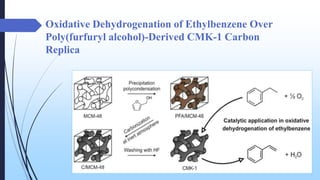
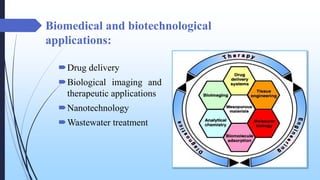
This document discusses mesoporous materials, including their classification, synthesis, and applications. Mesoporous materials have pore sizes between 2-50 nm and high surface areas between 400-1000 m2/g. They are commonly synthesized using a soft template method involving surfactants. Mesoporous materials have a wide range of applications including adsorption, chromatography, catalysis, sensors, and drug delivery due to their tunable pore sizes and large surface areas.