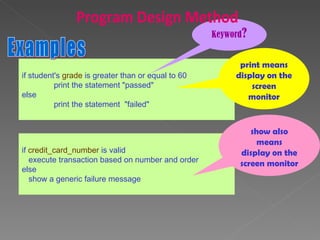
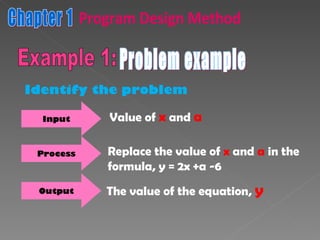
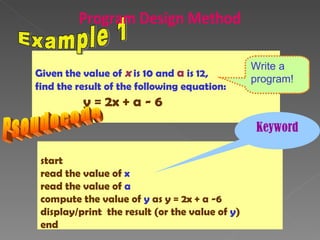
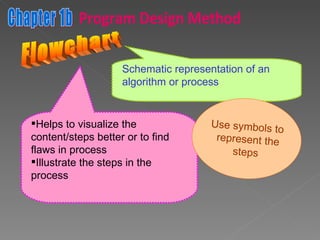
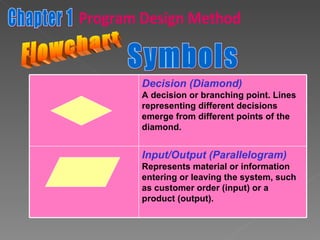
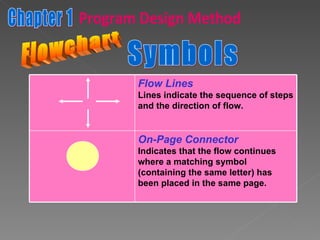
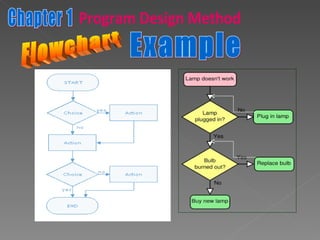
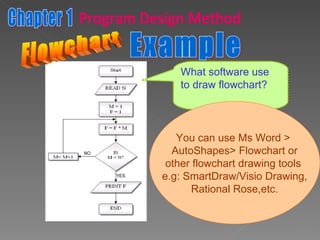
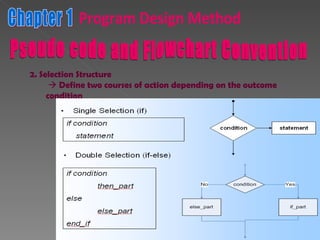
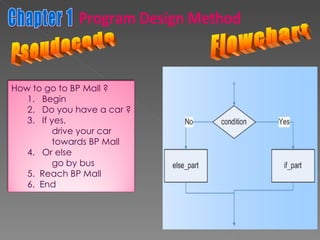
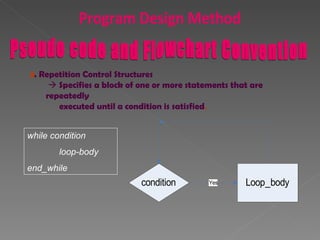
The document discusses program design methods including pseudocode, flowcharts, and their conventions. It provides examples of pseudocode for different problems and their corresponding flowcharts. Key points covered are the basic structure of pseudocode using keywords, and the common symbols used in flowcharts to represent different elements like processes, decisions, and flow of steps.